Thick blood in a child
The blood of the child is always in liquid form due to the constant interaction of the system, which ensures its coagulation, as well as the system that resists coagulation. The ratio of plasma (liquid blood) to cells is normally constant and, with minor fluctuations, quickly returns to its normal values. However, there are situations when the blood thickens.
Let's analyze why a child can have thick blood, is it dangerous for him and what should parents do when blood is thickened in a daughter or son.
The reasons
The most common cause of a more dense blood state in childhood is dehydration. It can be caused by insufficient drinking, vomiting, kidney failure, diarrhea, burns (if they are extensive), high temperature, heavy sweating during exercise, too dry room air, and other factors.
Other causes of blood clots in children include:
- Hypovitaminosis, especially B vitamins and ascorbic acid.
- Congenital heart defects.
- Taking certain medications, including glucocorticoids and diuretic drugs.
- Obesity.
- Erythremia.
- Fermentopathy.
- Obstructive diseases of the respiratory system.
- Tumors of the kidneys.
- Endocrine pathology.
- Injuries.
- Parasitic infections.
- Leukemia
- Diseases that increase coagulation.
- Splenectomy.
- Acute inflammatory process.
Symptoms
If the child’s blood thickens, it can manifest itself:
- Vertigo.
- Cyanosis of the skin.
- Swollen limbs.
- Feeling of heaviness in the arms and legs.
- Weakness
- Pain in fingertips.
- Drowsiness.
- Dry mouth.
- Increased fatigue.
- Deterioration of attention.
- Headaches.
- Thirst.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Cold limbs.
- Shortness of breath.
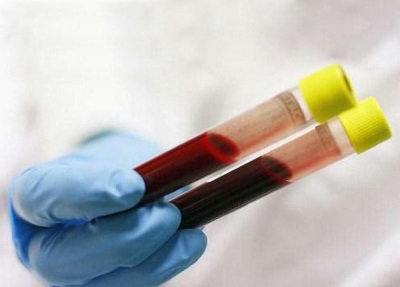
In the blood test, the increased blood density will be visible in the number of red blood cells (it rises) and the change in hematocrit (this indicator will also be increased). The number of other blood cells may also increase.
What is dangerous
If the blood in the child's body becomes thicker than normal, it will hardly move through the vessels. Since, with an excessively thick blood, it will not be sufficiently saturated with oxygen, the transport of nutrients and oxygen to the tissues is disturbed. This threatens the deterioration of the internal organs, as well as gluing blood cells together with the formation of blood clots. As a result, the child increases the risk of strokes, heart attacks, intestinal necrosis and other pathologies.
Treatment
If the blood test showed its thickening, the child should be shown to the doctor. The pediatrician will evaluate the clinical symptoms and find out the cause of the increased blood density, after which he will prescribe the treatment. It will be determined by the diagnosis, including drugs to eliminate the underlying disease, as well as medications for blood thinning.
At the same time, the doctor will advise parents to review the nutrition of the baby. Foods that can thin the blood, such as garlic, citrus fruits, beets, sunflower seeds, ginger, sour berries, olive oil, cocoa and others should be included in the child's diet. With thick blood, you should not eat bananas, smoked products, fatty foods, carbonated drinks, buckwheat, lentils, walnuts, rosehips.
In addition, parents should pay particular attention to the child's drinking regime. Children are given more pure water, herbal or green tea, vegetable or fruit juices. As for the use of any infusions, decoctions and other recipes of traditional medicine, before giving any means to a child, you should definitely discuss this with your pediatrician.