Low hemoglobin in a child
If a child’s blood test showed abnormalities, it always causes anxiety. Most often in childhood reveal changes in hemoglobin level, in particular, its decrease. What is affected by a decrease in hemoglobin, how dangerous a lowered index is and how to help a child - these questions are important for any parent.

What hemoglobin in children is considered low
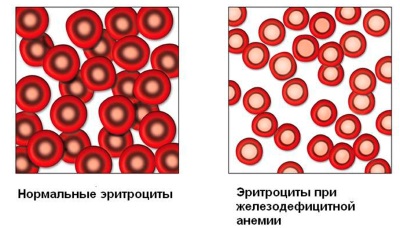
Hemoglobin is the blood protein that is present in red blood cells. It contains iron, therefore, due to lack of iron, the formation of such a protein is disturbed. The main function of this protein is the transport of oxygen through the body of a child. Hemoglobin gives oxygen to the tissues and takes carbon dioxide from them, which carries it to the lungs.
In order to assess whether a child’s normal hemoglobin is lowered or not, one should take into account the age of the baby, because such an indicator for a newly born child at 1 year, at 2 years, or at 10 years will be different. In newborns, the level of such protein is higher, and from the second week of life it gradually decreases. And because the indicator, for example, 110 g / l, for a 1 year old child will be within the normal range, and for an infant in the first months of life it will be dangerous anemia.
The lower limit of normal hemoglobin levels in children is considered:
Have a newborn | 145 g / l |
From 6 months to 5 years | 110 g / l |
5-11 years old | 115 g / l |
At 12-14 years | 120 g / l |
Why hemoglobin in children goes down
The most common cause of low hemoglobin in childhood is anemia, which is caused by iron deficiency. The famous pediatrician Komarovsky agrees with this. The lack of iron in infancy is caused by anemia in the mother, the late introduction of complementary foods and low physical activity of the baby. At an older age, iron deficiency is often associated with the nutrition of the child, for example, if he has a vegetarian diet.
The release of the program of Dr. Komarovsky devoted to the problem of low hemoglobin in children, see the following video:
In addition to iron deficiency anemia, a decrease in hemoglobin in children may be a sign:
- Hemolytic anemia, in which red blood cells are destroyed.
- Anemia, which provoked a deficiency of vitamins of group B (in particular, B12 and B9).
- Acute bleeding, for example, in case of injury or surgery.
- Chronic bleeding, for example, with frequent bleeding from the nose or heavy periods in a teenage girl.
- Crohn's Diseases and other intestinal diseases.
- Hemophilia and other blood disorders.
- Infectious disease.
- Worm invasion.
- Taking some medication.
- Allergies.
- Tumors.
Signs of hemoglobin decline
Anemia in childhood is manifested:
- Pale skin.
- Lethargy
- The rapid appearance of fatigue.
- Weakness
- Dizziness.
- Drowsiness.
- Changes of nails (white dashes and spots appear on them).
- Decreased appetite.
- Worse sleep
- Increased body temperature.
- Bad mood.
- Circles under the eyes.
- Frequent viral infections.
- Peeling and dry skin.
If you do not pay attention to such symptoms immediately, the child develop shortness of breath and tachycardia, apathy appears, attention and memory deteriorates, and developmental delay occurs.
What to do
Effects of anemia
If the reduced hemoglobin does not reveal on time or leave the situation to drift, it threatens the child with serious health problems. Lack of hemoglobin causes insufficient oxygen to all tissues of the child’s body, including brain tissue.
The consequences of prolonged hypoxia will be a lag in the development and deterioration of the brain activity of the child, as well as disruption of the work of the internal organs.
Treatment
The approach to treating a child with low hemoglobin should be comprehensive and based on the reason for lowering this blood index:
- If the child is identified Iron-deficiency anemia, he is shown iron preparations. Prescribe them to a pediatrician, choosing the appropriate age dosage. It is impossible to give a child any iron preparation on their own. Iron-deficient babies are usually prescribed by ingestion. They are represented by drops or syrup, for example, drugs Actiferrin, Ferrum Lek, Maltofer and Ferronal 35.
- If the cause of low hemoglobin is acute blood loss, a child may be assigned a blood transfusion. Also, this procedure is recommended for children with severe iron deficiency anemia.
- At the same time, the doctor will advise you to correct the nutrition of the child.by adding foods high in iron, which contributes to the formation of hemoglobin in the body. These products include meat (from which iron is absorbed much better than from any vegetable food), legumes, eggs, by-products, cereals, pomegranates, berries, nuts and other products.
- Children with anemia are also advised to take a long walk in the fresh air.because the access of oxygen stimulates the formation of red blood cells.
Parents should understand that it is impossible to treat anemia only with a change in the nutrition of the child; correction of the diet will only help to supplement the treatment.
The opinion of the famous pediatrician Yevgeny Komarovsky regarding the diet during the treatment of anemia can be found here:
Prevention
In order to prevent a decrease in hemoglobin in childhood, the following measures should be taken:
- In the period of gestation, the expectant mother should regularly undergo blood tests and take complex vitamins. If anemia is detected in a pregnant woman, treatment should be started in time so that the fetus can accumulate iron before birth in the right amount.
- It is important to breastfeed the newborn for iron is better absorbed from human milk than from any other food, even from an iron-rich quality mixture. This is due to the presence in breast milk of a special enzyme called lactoferrin. By the way, this enzyme helps the child to absorb iron from food products, so breastfeeding during the period of acquaintance with a new food is not advised to complete.
- Complementary feeding infants should be introduced in a timely manner. The pediatricians' advice to introduce new products to infants from 6 months of age is also due to the fact that the reserves of iron in the body of an infant run low by this age. With the introduction of complementary foods, it is important to take into account modern recommendations, since the early introduction of cow milk into the diet of crumbs is considered a risk factor for the development of both anemia and rickets.
- In the diet of children of preschool and school age there should be enough foods rich in proteins, iron and vitamins of group B. Such products are chicken, beef, liver, apples, persimmon, blueberry, buckwheat, nuts, turkey, dried apricots and others. It is also important to ensure the child sufficient physical activity and daily stay in the fresh air.
- For timely detection of the risk of anemia, the child should regularly undergo a blood test. It is best to do such a survey once a year.