Hemoglobin norm in children
Determining the state of health of the child using laboratory methods, first of all conduct a blood test. At the same time one of the most important indicators of this study is hemoglobin level. And therefore, any mother should know what constitutes such an indicator, what it should be normal for, what it can change and what to do in case of deviations from the norm.
What is it
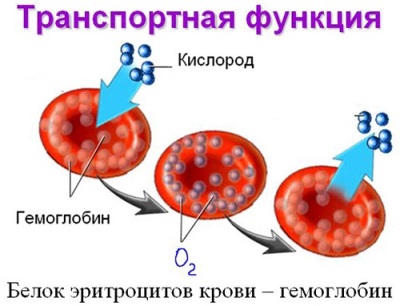
The main task of hemoglobin in the body of a child is the transfer of gases - both oxygen from the lungs to all tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
How is determined
What affects the level of hemoglobin in the blood?
The rate will vary depending on:
- Age of the child. The maximum level is observed in newborns, but after a few weeks the hemoglobin begins to gradually decrease. That is why it is impossible to estimate the indicator on a child’s blood test form without specifying age. For example, a hemoglobin level of 110 g / l in a 2-year-old child is within the normal range, but for a baby at the age of 3 months, this figure is a sign of anemia.
- Baby food. Breast-fed babies suffer from lower hemoglobin levels less than breast-fed babies. In children older than one year, eating disorders are the most common cause of changes in hemoglobin levels.
- Health conditions. Hemoglobin is reduced or increased in various diseases, which helps in their diagnosis.
- The course of pregnancy and childbirth. The hemoglobin level is influenced by the mother’s diseases during gestation, blood loss during childbirth, features of umbilical cord ligation, time of birth, multiple pregnancy and other factors.
- Genetic factor. If the mother's health is normal, but the hemoglobin level is always slightly below normal, this situation can also be observed in the child.
- Time of year The smaller frequency and duration of walks in the autumn-winter period leads to a slight decrease in hemoglobin in a child at this time.
Table by age
The following indicators are considered to be the hemoglobin rate at different ages:
|
Newborn baby |
180-240 g / l |
|
In 1 week |
160-200 g / l |
|
In 1 month |
120-160 g / l |
|
In 1 year |
110-130 g / l |
|
In 5 years |
110-140 g / l |
|
In 10 years and older |
120-140 g / l |
Hemoglobin in premature babies
The hemoglobin index in a child who was born ahead of time will be lower in the first month of life than in a full-term baby. For such an infant, the lower limit of normal is 160 g / l. By 1 month, the hemoglobin in the premature baby decreases, as in the time born toddler, while the lower limit of normal corresponds to 100 g / l.
Note that premature babies have anemia more often. This is due to the lack of maturity of the internal organs of the infant. In addition, in the first year of life, these children are often diagnosed with severe forms of anemia that require blood transfusions.
Hemoglobin is above normal
Why rises
The cause of a higher level of hemoglobin is:
- Dehydration, as a result of which the blood thickens. This condition is observed in intestinal infections with diarrhea and vomiting, diabetes mellitus, acute respiratory viral infections with fever, extensive burns and other pathologies.
- Chronic respiratory diseasein which respiratory failure develops, and the number of erythrocytes increases compensatory to provide the body with oxygen.
- Chronic heart failure, which in childhood is often caused by congenital heart disease.
- Erythrocytosis. This disease, also called polycythemia, is characterized by the activation of the formation of blood cells (mostly red) in the bone marrow.
- Kidney diseasein which an excess of erythropoietin is produced.
Non-dangerous causes of increased hemoglobin levels are exercise and living in the mountains. Also, a slight increase in this indicator is noted with a long stay in a warm and dry room. In adolescents, high hemoglobin can be caused by anabolic steroids (if a teenager is involved in sports) or smoking.
The opinion of Dr. Komarovsky regarding elevated hemoglobin can be found here:
What symptoms to suspect
Than dangerous
How to reduce
First of all, it should be understood that high hemoglobin is only one of the symptoms of the disease, and the task of parents and doctors should be to find out which particular disease. In most babies, an increase in hemoglobin is caused by non-dangerous causes, so dietary changes or air humidification can help reduce their rate.
The child should be given less iron-containing foods, replacing them with fish, seafood, white chicken meat and legumes. If hemoglobin has increased in an infectious disease or other pathology, the doctor will prescribe an appropriate treatment.
Sometimes it is necessary to resort to the use of medicines that thin the blood, but only a doctor should select such medicines, choosing the right dosage.
Hemoglobin is below normal
Why falls
The most common reason for reducing the amount of hemoglobin in the blood is iron deficiency, which provokes the development of anemia (and therefore it is called iron deficiency).
Newborns iron deficiency is often triggered by anemia in women during pregnancy, due to which the child received less iron and could not accumulate its reserves in his blood.
In children older than 6 months iron deficiency causes the late introduction of complementary foods. It is at this age that all the reserves of iron that the crumb has accumulated during fetal development are running out. And if the mother continues to breastfeed her baby with a breast or a mixture, the baby gradually develops a lack of iron, which leads to anemia.
School children and teenagers Iron deficiency is often caused by unbalanced nutrition, for example, if a child is on a vegetarian diet. Passion for adolescent girls diets for weight loss also threaten the development of iron deficiency anemia.
Among other causes of low hemoglobin note:
- Blood loss - acute (due to surgery or injury) or chronic (for example, frequent nosebleeds).
- Anemia caused by lack of folic acid and vitamin B12.
- Hemolytic anemia, in which red blood cells are destroyed.
- Other blood diseases.
- Diseases of the digestive tract.
- Infectious diseases.
- Take some medication.
- Autoimmune pathology.
- Malignant tumors.
We recommend to watch the webinar recording for parents in the framework of the seminar of the social project "MD Class". It discusses in detail the problems of anemia in children, its causes and consequences.
How low hemoglobin appears
You can assume anemia in a child by the appearance of:
- Fatigue.
- Reduced appetite.
- Weaknesses and fatigue.
- Dizziness.
- Pale skin tone.
- Sleep disturbance
- Dry skin and peeling.
- White spots and dashes on the nails.
- Circles under the eyes.
- Irritability and capriciousness.
- Increased heart rate.
- Increased body temperature.
Than dangerous

At what rate is anemia diagnosed
According to WHO recommendations, the boundary indicators of hemoglobin, for which anemia is not diagnosed in a child, are:
|
Aged 5 months to 5 years |
Above 110 g / l |
|
At the age of 5-11 years |
Above 115 g / l |
|
Aged 12 and over |
Above 120 g / l |
Mild anemia is diagnosed with such indicators:
|
Aged 5 months to 5 years |
From 100 to 109 g / l |
|
At the age of 5-11 years |
From 110 to 114 g / l |
|
Aged 12 and over |
From 110 to 119 g / l |
If a child under 5 years old has hemoglobin in the range of 70 to 99 g / l, and a child over 5 years old has between 80 and 109 g / l, this indicates moderate anemia. Acute anemia is characterized by a drop in hemoglobin level below 70 g / l in children under five years old and below 80 g / l in children over 5 years old.
Komarovsky about low hemoglobin
Famous doctor notes that the most common cause of declining hemoglobin in the blood of a child is iron deficiency. Komarovsky stresses that he has encountered many times in his practice situations where anemia caused by iron deficiency is diagnosed in an infant at 5-6 months of age.
And therefore, a popular doctor advises that it is mandatory to check each baby at this age, especially if hemoglobin was reduced in the future mother’s pregnancy. In addition to the general blood test, Komarovsky recommends that ferritin be determined in order to know whether the child has iron reserves or they are already running out.
Regarding treatment, a popular pediatrician assures that feeding a child with iron-rich foods, if anemia has already developed, cannot be remedied.Komarovsky emphasizes that such children should take iron supplements, choosing the right product with their doctor. Enrichment of the diet with iron from food can only be as an addition to the treatment of such drugs.
Record of the program of Evgeny Komarovsky about low hemoglobin in a child, see below:
What to do when lowering
Making sure that the child really has anemia, it is important to find out its cause, as this will determine the medical tactics. If confirmed Iron-deficiency anemia, the child will be given iron supplements in the form of syrup or drops, for example, Maltofer or Actiferrin. Such drugs are prescribed for a long period - not less than 1-2 months.
If a child under one year old has a hemoglobin level of less than 85 g / l, this condition is considered critical by doctors and requires a blood transfusion. For children older than a year, transfusions are performed when hemoglobin is lowered to 70 g / l and below.
Low Hemoglobin Prevention
- During the period of gestation regularly donate blood, in time to detect a decrease in hemoglobin and eliminate it. Also, a pregnant woman should take a multivitamin as prescribed by a doctor.
- Do not refuse breastfeeding, because iron is better absorbed from mother's milk than from the highest quality mixtures.
- During breastfeeding, mom should control her diet, enriching it with products from which it will receive proteins, iron and all the vitamins necessary for blood formation.
- Introduce baby food in a timely manner.After all, by the age of 6 months the child no longer has enough iron accumulated in his body, as well as the mineral that comes in with breast milk.
- Do not wean a child from the breast, as soon as he began to enter lure. Lactoferrin from human milk will help the baby absorb iron from the new food.
- Do not put in the feed cow's milk children who are not 1 year old, and some pediatricians advise to postpone with such a product to 1.5-3 years of age. Its infant consumption is a risk factor for anemia, as well as rickets.
- Black tea should not be given to children under two years of age., because it contains substances that bind iron.
- Daily walk with your child in the fresh air, as walks stimulate the formation of new blood cells.
- Regularly go with the child for checkups to the pediatrician and pass all routine tests in time to identify any violations in the general condition and blood of the baby.
Products that help keep hemoglobin normal
- Veal, beef, lean pork, chicken, turkey and other meats, as well as offal.
- Beans, peas, lentils and other legumes.
- Buckwheat, barley, oatmeal and other cereals, as well as wheat dishes.
- Apples, persimmon, figs, pears and other fruits.
- Greens and various vegetables.
- Almonds, pistachios and other nuts.
- Dried apricots, prunes and other dried fruits.
How often to check hemoglobin
Survey of a healthy child is recommended to be carried out 1 time per year. If the baby has a chronic disease, then after registration, such a child will be regularly examined, including donating blood.
If parents are overly worried about the child, they are always alerted by any changes in his condition, for example, very pale skin. However, tests without a doctor's referral are not worth it. If you suspect anemia in a baby, you should first go to a pediatrician. There are situations when a pale child with normal hemoglobin, so the doctor will take into account other symptoms, and then determine whether an unscheduled blood test is needed.
In the analysis should consider such nuances:
- If you take blood from a child while lying down, the concentration of hemoglobin will be lower.
- After eating, the amount of hemoglobin may decrease.Also a slight decrease (by 5-10%) is observed in the evening.
- If excessive pressure is put on it during finger blood sampling, intercellular fluid will get into the blood sample, so the result will be lower due to dilution.
- If blood is taken from a vein, and the tourniquet was applied for too long a time, the result will be increased due to vascular stasis.