The rate of reticulocytes in the blood of children
The blood test of the child is an important method of examination that helps to identify various disorders in the body of children. This analysis determines a variety of indicators, among which there is the level of reticulocytes. What are these cells, what should their normal number in children be and how can it change with diseases?
The role of reticulocytes
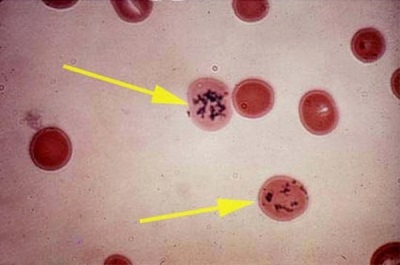
The name “reticulocytes” was given to young erythrocytes for the presence of reticular structures inside such cells.
Reticulocytes are an intermediate form between normoblasts formed in the bone marrow and mature erythrocytes, which are abundant in the peripheral blood of a child.
Erythrocytes are formed from reticulocytes, therefore the content of these progenitor cells in the blood is insignificant. Their transformation is regulated by a hormone secreted by the kidneys called "erythropoietin" and occurs on average for 1-3 days.
Norm in children
In the child's blood, reticulocytes (RTC) are determined in ppm. Newborn babies normally have more of these cells than babies older than a month. From the fifth day after birth, the level of reticulocytes decreases.
The norm of such cells at different ages is considered:
|
On the first day of life |
10 to 40 ‰ |
|
From the 5th day of life |
From 0 ‰ to 15-20 ‰ |
|
From 1 month to a year |
5 to 13 ‰ |
|
From year to five years |
5 to 12 ‰ |
|
From 5 to 15 years |
From 3 ‰ to 10 ‰ |
|
In children over 15 years |
4 to 9 ‰ |
Based on the number of reticulocytes in the blood of children, one can judge the work of the bone marrow (activity of the production of red blood cells). Such an indicator is especially important when anemia is suspected, after bleeding, bone marrow transplantation, when taking toxic drugs or treating with iron, folic acid and vitamin B12.
Elevated reticulocytes
Increased blood levels of reticulocytes is called reticulocytosis. Its detection, depending on the reason for the high percentage of such cells, can be both a positive fact and a symptom of the disease.
For example, the doctor will be happy to see elevated reticulocytes, if the child began to treat deficient anemia, because it means that therapy helps. Also, reticulocytosis will be a good sign after three to four days after bleeding, since it will mean adequate work of the bone marrow to restore the lost red blood cells.
If a child has undergone chemotherapy or radiation therapy, reticulocytosis is also considered to be a positive symptom of recovery in the bone marrow. Elevated reticulocytes in the blood of a child in a mountainous area indicate that the body is well able to cope with the increased oxygen demand.
However, reticulocytosis may be a symptom of some pathologies:
- Hemolytic or deficient anemia.
- Internal bleeding.
- Malaria.
- Poisoning, in which the poison affects the bone marrow.
- Inflammation of the bone marrow.
- Metastasis to the bone marrow.
Reduced reticulocytes
Reducing the level of reticulocytes in the blood of a child is called reticulocytopenia. Such a picture in a children's blood test may indicate a violation of the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow, resulting in erythropenia and tissue hypoxia.
This occurs when:
- Anemia caused by iron deficiency.
- B12 or folic deficiency anemia.
- Aplastic anemia.
- Kidney disease.
- Tumors of the bone marrow or its defeat by metastases.
- Radiation Disease.
- Toxic effects on bone marrow.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning.
What to do when changing the level of reticulocytes
By itself, the fact of elevated or decreased reticulocytes is not a diagnosis and does not indicate a disease. To find out if a child has a disease, it is important to conduct a series of additional examinations.
Only after identifying the pathological cause of reticulocytosis or lowering the level of such cells, the child is prescribed the required treatment, after which the level of reticulocytes becomes normal.