Reduced platelet count in a child
Among the laboratory methods that help determine the state of health of children, blood tests are especially in demand. His results show the hemoglobin level, the number of different blood cells, their ratio and other parameters. The doctor primarily evaluates red blood cells and white blood cells in a blood test form, but platelets are equally important cells.
Seeing that their number is below normal, parents begin to worry. But, in order to understand whether a decrease in the number of platelets is dangerous for the health of a son or daughter, you first need to figure out what this means, why there is little blood platelets in a child, and what to do in such a situation.
What are platelets for?
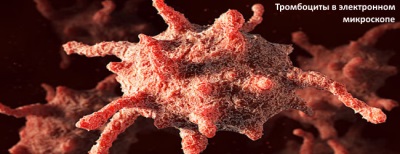
Such blood cells, also called blood platelets, play a large role in blood coagulation processes. In particular, if a blood vessel is damaged, platelets are involved in the formation of a clot that closes the damage, which causes the bleeding to stop.
What level of platelets is considered low
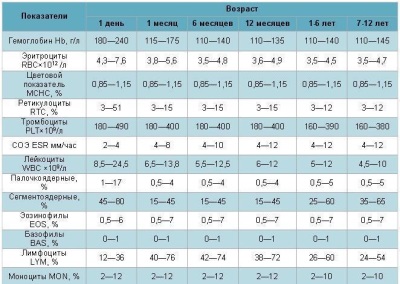
The rate of blood platelets at the age of one year is called the indicator above 180 x 109/ l, and for kids older than the year - 160 x 109/ l.
In newborns, the platelet count per liter of blood can be 100 x 109that is also considered a variant of the norm.
Gradually, the number of platelets increases, at a minimum of 150 x 10 at 10 days of age.9/ l.
If a blood test form of a child of any age indicates that platelets are less than 100 x 109/ l, this condition is called thrombocytopenia. As a result of a lower number of blood platelets, the blood liquefies and coagulates poorly, which leads to an increased risk of internal bleeding and external bleeding.
What causes a decrease in platelets
Low platelet count is caused by such factors:
- Violation of the formation of such cells in the bone marrow. Their production can be inhibited due to viral infections, tumors, drugs and other effects.
- Destruction of platelets under the action of various factors, for example, as a result of the production of antibodies to such blood cells during autoimmune disease or when infected with a certain strain of E. coli.
- Redistribution of blood cells, which results in a lower number of platelets in the bloodstream. The reason for this change is an increase in the spleen, which is often seen in hepatitis.
In adolescence in girls, the number of such blood cells may decrease due to the first heavy menstruation.
Leading the next video will tell for what reasons can be reduced platelet count in the blood.
Causes of Thrombocytopenia
Allocate primary thrombocytopenia, which is an independent disease. It is also called idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. The exact cause of this pathology has not yet been elucidated, but doctors associate it with the autoimmune process, which is often activated after a viral disease or vaccination.
More often, a decrease in the number of platelets is only one of the symptoms of such diseases:
- Bacterial infections.
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome.
- Anemia
- DIC syndrome.
- Allergic reactions, for example, to a drug.
- Hepatitis, measles, rubella and other viral infections.
- Parasitic invasions.
- Asphyxia in newborns.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
- Diseases of the blood.
- Autoimmune pathology.
- Heavy metal poisoning.
- Tuberculosis.
- Malignant tumors.
- Acute renal failure.
If a child is treated for a long time with the use of corticosteroids, diuretic drugs, antibiotics and some other drugs, this will also affect the blood count, including platelet count.
Severity
Depending on the indicator of the blood test and the condition of the child, there are:
- Mild or latent thrombocytopenia. With her blood platelets in a liter of blood, there are from 75 to 99 x 109. Any clinical manifestations with such a decrease may be absent and the problem is often detected only after a blood test.
- Moderate thrombocytopenia. It is diagnosed if the blood of a child is determined from 50 to 74 x 109/ l platelet. Symptoms with such a reduction are not pronounced. Often it is represented by the frequent appearance of bruises and longer bleeding, which can still end on its own.
- Medium thrombocytopenia. In this condition, platelets range from 20 to 49 x 109/ l, and stopping bleeding will require effort. A child with such a decrease in blood platelets must be treated.
- Severe thrombocytopenia. It is characterized by a decrease in the number of platelets less than 20 x 109/ l, which represents a danger to the life of the baby, therefore, requires urgent hospitalization.
Symptoms
Decreased platelets in childhood can occur:
- The frequent appearance of bruises (sometimes they can occur even from touch).
- Prolonged bleeding with a cut or abrasion.
- Point rash on the skin, as well as the appearance of spider veins or reticulums.
- Periodic appearance of nosebleeds.
- Headaches.
- Bleeding of the mucous membrane of the gums.
- Acquisition of urine pink or red.
- The appearance of vomiting with blood or blackened feces.
- Abundant and too long periods during adolescence.
In some children, the spleen is enlarged, and in severe cases hemorrhages occur with different localization, for example, in the retina or brain tissue.
When you need to see a doctor
Parents should take their daughter or son to a doctor as soon as possible if:
- Cutting bleeding does not finish longer than 10 minutes.
- Bruises are often formed on the body, and their appearance occurs effortlessly.
- The child often complains of a severe headache.
- The urine of the child reddened.
- Feces acquired a dark color (turned black).
Treatment
Tactics of the doctor will depend on the reason why the platelets in the child have dropped below normal. In most cases, after treating the underlying disease, for example, anemia, the platelet count is gradually restored.
With a severe decrease in platelets, the child should be in bed. If his mouth is bleeding, all food is given chilled. In the treatment of such a problem, immunoglobulins are used (they are administered intravenously), rutin, corticosteroid hormones, anti-rhesus serum and other drugs. If there is evidence, the platelet mass is transferred to the child from the donor or the spleen is removed.
What to do with a slight decrease
If the platelets are lowered slightly, the doctor will recommend:
- Change the child's diet, adding to the diet foods that are high in iron, vitamins C and A.Children with thrombocytopenia are advised to give buckwheat porridge, meat dishes, beets, carrots, cabbage, apples, fish, parsley, olive oil, bananas, nuts and other products. From drinking watermelon, seaweed, cowberry, cranberries, strawberries, strawberries, and also tomato juice are advised to give up.
- Monitor physical activity. The child should have enough rest, sleep at least 10-12 hours a day, play quiet games.
As for the recipes of traditional medicine, with a small decrease in the number of platelets, the child can be given to drink nettle juice, mixed 1: 1 with milk (only 100 ml per reception) or sesame oil (in a tablespoon per reception). Means are taken three times a day, half an hour before meals, but before they are started they should definitely discuss this issue with the pediatrician.