The use of dioxidine in the treatment of children, whether to bury it in the nose?
"Dioxidine" has long established itself as an effective antimicrobial agent, which is often prescribed for purulent-infectious processes in adults. However, in pediatrics due to toxicity, this medicine is used with caution. When a doctor prescribes Dioxidine to a child, the mother is interested in how such a drug acts on the children's body and when its use is justified. Since the instructions for the medication do not contain information about the treatment of otitis, rhinitis, bronchitis and many other diseases with this remedy, many parents begin to worry if Dioxidin will harm the little patient. Not everyone knows how to properly bury it in the nose.
Release form
"Dioxidin" in the present time is available in several forms:
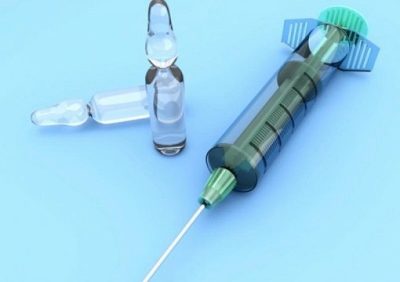
- Solution that can be used externally or injected. It is produced in two concentrations. A drug with a lower concentration (0.5%) can also be injected into a vein. "Dioxidin" in this form is an ampoule with an odorless greenish-yellow transparent solution. In one ampoule is 5 or 10 ml of the drug, and one package includes 5-10 ampoules.
- 5% ointment, which is used only locally. Such a drug is produced in tubes and jars, which contain from 30 to 100 g of greenish-yellow substance.
Composition
The main component of the drug is called hydroxymethylquinoxalinedioxide. Its 0.5% solution contains 5 mg per 1 ml, and the content in 1% drug is 10 mg / ml. The only excipient of this form is sterile water. In 100 g of ointment, the active substance is contained in an amount of 5 g and is supplemented with monoglycerides, nipagin, macrogol and nipazol.
Operating principle
The drug is an antimicrobial bactericidal drug effective against pseudomonads, Proteus, Klebsiella, Shigella, Staphylococcus, Clostridium and other microbes. The drug prevents the synthesis of DNA in the cells of such bacteria, which interferes with the formation of nucleotides and the structure of membranes, which leads to the death of microorganisms. The drug is especially effective in anaerobic conditions, because it stimulates the formation of reactive oxygen species.
Indications
In hospitals, "Dioxidin" is especially in demand for infectious purulent diseases. Intravenous injections (0.5% solution) are usually prescribed for purulent meningitis, sepsis and other life-threatening pathologies. but In childhood, injections are not used because there is a high risk of overdose and the harmful effects of such drugs on the adrenal glands. There are a lot of effective antibacterial agents approved for children, even for infants and premature babies.
Local use of the drug is prescribed by dentists, urologists and surgeons. The drug is administered with purulent pleurisy, pneumonia with abscesses, peritonitis, purulent cystitis, or suppuration of the gallbladder. “Dioxidin” washes deep wounds, as well as neglected trophic skin lesions and burns complicated by infection. External treatment with the drug (lotions, compresses) is also prescribed for pustular infections of the skin.
ENT doctors often prescribe "Dioxidin" in the nose, and ophthalmologists can prescribe such a drug in the eye if bacteria have infected the conjunctiva. In case of sore throat with this medicine, gargling is performed in the throat, and in case of purulent otitis it is dripped into the ears.
The reason for the drug to drip into the nasal passages is a long runny nose that is not treatable by other means, including antibiotics of other groups. At the same time, medication in the nose can be used with a greenish color of discharge and their unpleasant odor, which indicates the bacterial nature of the disease.
Some mommies still use Dioxidine in their babies for instillation into their nose. Why and why they do it can be found in the next view.
Quite often, complex drops are prescribed, which include "Dioxidin", as well as vasoconstrictor, hormonal and other means - for example, "Dexamethasone», «Xylen"," Nazivin ","Hydrocortisone". The recipe of such drops is selected individually for each patient. They are used not only for rhinitis, but also for adenoiditis, sinusitis, prolonged sinusitis or frontal sinusitis.
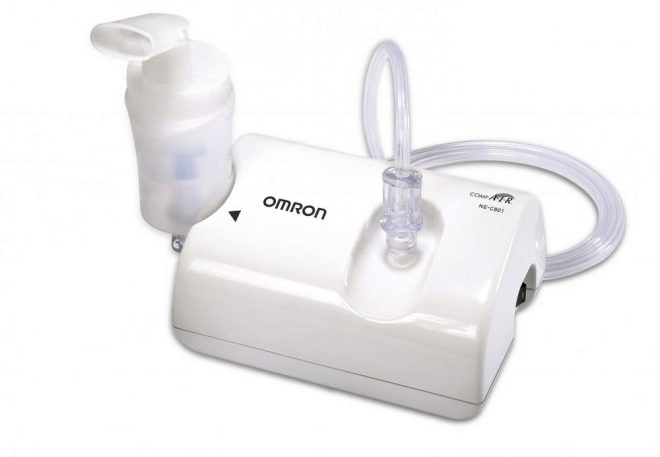
In case of purulent bronchitis, pneumonia or lung abscess, inhalations with “Dioxidin” can be administered, which make it a nebulizer. Since the drug goes directly into infected tissue and acts on pathogens. For such procedures, the medication must be diluted with saline.
At what age is it allowed to take
One of the contraindications noted in the annotation to "Dioxidin" is up to 18 years old. In this case, the drug can be used for children, but only when prescribed by a doctor who will ascertain the availability of indications for such treatment and determine the desired dosage. Drip "Dioxidine" child in the nose without consulting a pediatrician is prohibited.
Contraindications
The drug should not be used in such cases:
- If the child has individual intolerance.
- If the adrenal function of the small patient is impaired.
With impaired renal function, the use of the medication requires medical supervision.
Side effects
Since the drug affects not only the DKN of bacterial cells, but also human cells, it is considered toxic, but such a harmful effect is not observed when using the drug locally, if the dosage prescribed by the doctor is not exceeded. In this case, treatment with “Dioxidin” of the skin or mucous membrane may cause an allergic reaction in the form of itch or dermatitis.
To avoid this side effect, treatment should begin with a sensitivity test. The drug is treated with a small area of skin. If the medication is prescribed in the nose, then injected into each nostril with 1 drop. If after 3-6 hours there are no negative symptoms, then the medication is used in the dose prescribed by the doctor.
Instructions for use and dosage
Injections into the vein of 0.5% "Dioxidin" are made only when serious indications and under the supervision of a specialist. Typically, this drug is used in case of intolerance or ineffectiveness of cephalosporins, carbapenems and other effective antibiotics. Intravenous administration of the drug is prescribed only drip, and in the cavity or bronchi the medication is injected with a syringe, drainage or a catheter. The dose and mode of such use "Dioxidin" is determined individually.
For purulent wounds or burns, treatment with Dioxidin involves the use of tampons soaked in a solution. They are applied to cleaned wound surfaces and regularly changed. For this treatment, both 0.5% and 1% solutions can be used, but in some cases a more diluted liquid preparation is used. It is diluted with water for injection or saline to a concentration of 0.1-0.2%.
Going to drip 0.5% "dioxidine" in an ear or in the nose, you should clean the nasal cavity or ear canal from pathological secretions. You can also do the washing with saline or a preparation based on seawater. Next, the drug is administered in the dose prescribed by the doctor.
Usually, 2-3 drops of a 0.5% solution are instilled into the nose (1-3 times a day). If there are any warning signs (such as dizziness or itching), treatment should be stopped immediately. The duration of the drug is often 3-5 days. Longer than 7 days to drip such a tool is not recommended.
Inhalations when coughing with Dioxidin require dilution of 0.5% of the drug with saline in a ratio of 1 to 2, and 1% solution in a ratio of 1 to 4. For one procedure, take 3-4 ml of the diluted medication. The child should calmly inhale such medicine through a nebulizer (within 5-10 minutes).
Overdose
A high dose of Dioxidine can damage the adrenal glands, causing dystrophic changes in the organ's bark. For this reason, it is very important to control the concentration of the solution and the dosage prescribed to children.
Interaction with other drugs
"Dioxidine" is compatible with many other drugs, including antihistamines, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory hormones and others. At the same time to decide whether it is possible to use drugs at the same time, the doctor must, given the diagnosis and other factors.
Terms of sale
Since the use of the drug has its own characteristics and limitations, you can buy Dioxidine at the pharmacy only after presenting a prescription from the doctor. For 10 ampoules of the drug you need to pay about 340-400 rubles, and the price of a tube with 30 g of ointment is about 320-350 rubles.
Storage features
- The shelf life of the drug in liquid form is 2 years, and ointment - 3 years.
- The optimum temperature for storing liquid Dioxidine is from 15 to 25 degrees Celsius.
- Store ointment should be at a temperature below +20 degrees.
- If the storage temperature drops below +15, crystals may appear in the solution. Such a drug should be heated in a water bath so that the whole sediment dissolves again, and the medicine itself becomes transparent.
- The opened ampule of "Dioxidin" should be used immediately. If the medicine is applied to the nose, then each time a new ampoule is opened for instillation. This can be avoided if the medicine is poured from an open ampoule into a bottle from under the drops for the nose or into a syringe, and then measure the desired amount for one procedure.
Reviews
On the use of "dioxidine" for children there are different reviews. In many of them, mothers confirm the good efficacy of this remedy for purulent infections, and also praise the drug for its low cost and widespread availability. In other reviews, parents note the appearance of an allergy to such a remedy or the lack of a therapeutic effect.
There are also negative opinions from mothers who do not risk using Dioxidine for a child, fearing its toxic effects. They are supported by many pediatricians (including Dr. Komarovsky), preferring to prescribe antibacterial drugs approved in childhood for children, which are now being produced by a wide range of pharmaceutical companies.
Analogs
“Dioxidine” and “Dixin” can serve as a substitute for “Dioxidin”, since they contain the same active substance and are produced in the form of a solution used for external treatment and for injections. Other antiseptic and antibacterial agents can be used instead of "Dioxidine".
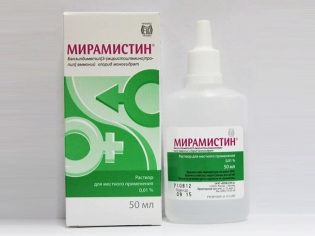
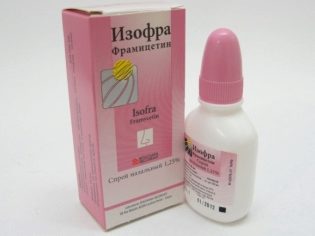
It can be replaced "Miramistin", Drug"Polydex», «Protargol», «Chlorophyllipt», «Chlorhexidine», «Izofroy"And other medicines that are prescribed for adenoids, rhinitis, otitis, and other pathologies. As they include other active ingredients and can have side effects, they should not be used without consulting a doctor.