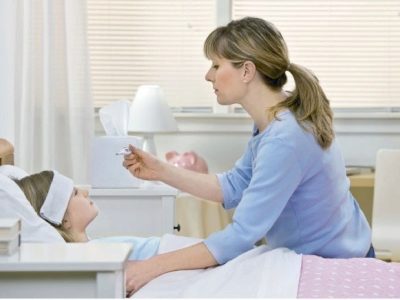
When to give antibiotics to a child at a temperature?
I have one lady I know who, every time her seven-year-old daughter begins to get sick, rushes to treat her with antibiotics. This mommy also has “favorite” drugs, which, according to her, “certainly will help from everything!”. The absurdity and frightening scale of the situation is that this mommy is not alone in her beliefs. More than 45% of parents, according to a poll conducted by VTsIOM sociologists, are confident that influenza and ARVI can be treated with antibiotics, and also believe that the high temperature of antibiotics is reduced as well as possible.
So let's see where the error lies. When, nevertheless, the doctor advises to take antibiotic medicines for hyperthermia (high temperature).
First you need to be clear about what “high temperature” means. For some, it is 37.1, and for others, 39 is transferred as 37. As for children's health, mothers and fathers tend to “exaggerate” the numbers, calling the “high” temperature increase for a beloved child up to 38 degrees.
There is a generally accepted standard of hyperthermia:
- Light heat - 38 -38.5
- Heat moderate - 38.6-39.5
- High heat - 39.5
- Heat, dangerous for life, extremely high - 40 and above.
Causes of childhood heat
High fever is not a disease, but evidence of the normal functioning of the body’s immunity. If the temperature rose, then the child’s body resists the invasion. Most often, no invitations come viruses. Therefore, acute viral diseases are the main reason why the thermometer crossed the mark at “38”, “39” and stopped somewhere between “39.5” and “40”. Thus, 90% of cases of high fever are viral infections.
It is not difficult to suspect that the baby’s well-being of the baby is at the root of the problem, it has a recognizable “handwriting”. A sharp and rapid increase in body temperature to 39 degrees or, conversely, low-grade fever around 37.5, dry cough, runny nose, feeling of aching muscles and joints, severe headache. Moreover, all these symptoms occur almost simultaneously, the condition worsens rapidly.
With flu and ARVI antibiotics can not be taken. First, because they do not have any effect on the cause of the disease - the virus, because they were created to fight other forms of life - bacteria. Secondly, attempts to knock down the "viral" temperature with antibacterial drugs will come out "sideways" - the virus will remain safe and sound, but the friendly bacteria that live in the intestines, stomach, in the genitourinary system, will die.
As a result, dysbacteriosis, thrush, allergies and who knows what other side effects of antibiotics will be added to the viral disease! In addition, antibiotics suppress immunity, and the child in the fight against the influenza virus, he will need more than ever.
In the next video, Dr. Komarovsky will explain why antibiotics should not be taken for long-term infections.
Another reason for a child’s high fever is a bacterial infection. It usually replaces the virus as a complication.But sometimes it is also independent. To recognize it, it takes some time and a certain skill. We can talk about a bacterial disease if:
- Recently, the child had a viral infection, it became easier for him, and then worsened again, and the repeated temperature is not inferior to the previous one and does not subside. If new symptoms appear. This is a sure sign of a secondary infection.
- If the temperature is above 38 degrees, it lasts more than 3 days in a child under the age of 3 months, and in a baby under three years of age, it stays at 39 degrees. These are good reasons to start taking antibiotics.
- If the temperature appeared later than the stuffy nose. A runny nose, in turn, appeared with a sore throat. Consistency and slowness of symptoms - a distinctive feature of the bacterial cold.
At this temperature, against the background of bacterial inflammation, the doctor, of course, does not immediately rush to prescribe antibiotics, with the exception of only children under three years of age. For them, prolonged heat can cause dehydration, intoxication and death. All children over 3 years old will most likely be prescribed antipyretics by a pediatrician. If the bacterial infection is severe and dangerous in itself (bacterial angina, pneumonia, meningitis, purulent otitis or sinusitis), without antibiotics, treatment is hardly possible.
How to treat correctly?
If a child has a viral infection, the treatment will in no way be directed towards reducing the temperature. The doctor will prescribe antiviral drugs that are allowed for children ("Kagocel», «Orvirem», «Rimantadine"," Anaferon "and others). Sometimes it is appropriate and antipyretic and painkillers, such as children's "Nurofen." In addition, symptomatic treatment will be prescribed: with a sore throat - rinsing, sprays, with a cold - drops or inhalation, with coughing- mucolytic drugs. The temperature will begin to decline as soon as the virus is blamed for the disease.
If the child has a bacterial infection, the temperature lasts from 3 to 7 days, there are obvious symptoms of inflammation, the doctor will recommend antibiotics.
If, within 72 hours after the start of taking antibacterial agents, the child does not get better, the temperature does not drop, then it is these antibiotics that do not help him, the bacterium is resistant to the medicine, and you will need to replace the drug with another one.
By the way, it is the body temperature that is an indirect indicator of the effectiveness of the antibiotic. If the medicine is chosen correctly, then the fever begins to subside within a day or two after the start of treatment. Although the antibiotics themselves are by no means antipyretic agents. This is a truth that every parent must remember.
The doctor will prescribe antibiotics during the long and protracted course of certain viral infections, such as rubella. Moreover, the temperature in these cases can hold on to the background of antibiotics.
Antibiotics for children
Most popular children's antibiotics:
- «Ampicillin»
- «Amoxicillin»
- Augmentin
- «Sumamed»
- «Flemoxine Solutab»
- «Flemoklav Solyutab»
- «Clarithromycin»
- «Azithromycin»
- «Cefotaxime»
- «Cefazolin»
- Cefix
- «Suprax»
- «Klacid»
- «Ceftriaxone»
Children called antibiotics, which are available in forms that are convenient for use by children. After all, to force a one-year-old crumb at high temperature to drink the medicine in pills is practically impossible. For children under 5 there are suspensions. You can buy them in the form of powder or granules, and then diluted according to the instructions with boiled cold water.
Children after the age of five can be given self-dissolving tablets. If the baby can not dissolve it, then it is easy to dissolve such a pill in a small amount of water and give it to drink in the form of syrup. Children from 7 years old can be given the usual pill in the shell, and adolescents from 12 years old can be given antibiotics in capsules.
From this year, all antibiotics in pharmacies are sold strictly according to prescriptions. This is done for a reason. The fact is that in recent years people have too often used antibacterial drugs for any reason and without it. They were available, did not require the mandatory appointment of a doctor, and everyone chose antibiotics for themselves and their children uncontrollably. This has led to the emergence of a huge number of new strains of bacteria, which are now resistant to the most popular antibiotics.
Microbes have developed their own protection. New drugs are released less frequently than old ones cease to be effective. The need to take away the "universal antibiotic pill" from the population has matured. Now, to buy antibiotics, you need to show the pharmacist the appointment of a doctor.
What illnesses are accompanied by fever and how to treat them?
Disease | Do I need antibiotic therapy? | Alternatives |
Flu, SARS | Not | Antiviral drugs, vitamins. |
Yes, if bacterial bronchitis | Expectorants, mucolytic drugs, inhalations | |
Pneumonia | In most cases, yes. | Not. |
Otitis | Yes - with purulent otitis or severe disease, as well as in children up to 6 months. | Ear drops with analgesic, antiviral, anti-inflammatory action. |
Sinusitis | Not. The exception is purulent sinusitis and severe disease. | Drops, physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, nasal gels, inhalations. |
Angina | In most cases, it is not, because more often the disease is viral. | Local anesthetics, antiseptics. Anti-inflammatory drugs. Rinse, inhalation. |
You can learn more about antibiotics for children, about when their use is necessary and how to take them properly to a child, by watching the following video.
What do parents need to know about temperature?
- If the doctor prescribed antibiotics, in no case can not combine their reception with antipyretics. The temptation to give your baby something to drink that quickly reduces fever is great. All parents want the baby to feel better as soon as possible. But such a decrease in temperature distorts the overall picture of treatment. If the antibiotic acts correctly and in the target, the doctor will be able to understand this by independently reducing the temperature without additional medications.
- If the antibiotic “works,” and the child has become noticeably better on the second or third day, his temperature has dropped, he looks more alert, you should not stop drinking or prick the antibacterial agent. The fact is that the surviving bacteria adapt to the antibiotic, and the next time the child will have to pick up a new drug, more potent. Bring the course, which was prescribed by the doctor, to the end. In addition, the disease can return, and then the unauthorized cancellation of antibiotics will trigger the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
- If the temperature of the toddler has risen in the background intestinal infection or food poisoning, the doctor is unlikely to prescribe you antibiotics. The exception is toddlers of up to a year who, due to diarrhea and vomiting, can quickly come to a critical stage of dehydration.
- Antibiotics can not be a means of prevention. You should not give them to a child simply because “someone got sick” in his class or group in the kindergarten, or at the first sign of a cold or fever.
- Starting to give antipyretic drugs is not desirable immediately, as soon as the child has a fever. Give your baby's immunity to try to cope with the disease. So the defense will be stronger.
- At high temperatures, the child must necessarily organize plenty of warm drinks. And no matter what kind of pathogen caused by fever. The smaller the child, the faster the thermoregulation processes take place.This means that the risk of dehydration increases as a result of severe intoxication. You can drink everything except sparkling water, sour juices and milk. Ideally in case of heat, give your baby crumbs with herbal teas, tea with honey, lemon, raspberries (if you are not allergic), compote or jelly.
- At high temperatures, you can not wrap a child in a "hundred clothes" and cover with a blanket on top. It is best to strip the child up to the panties and cover with a light sheet. The effects of overheating may be irreversible.
- If antibiotics are prescribed, take care to restore the baby’s body as soon as possible after such a powerful therapy. Ask your doctor to recommend the names of probiotics and prebiotics, drugs that will help you quickly and gently get rid of dysbiosis after antibiotics, restore the intestinal microflora for a full and healthy life of the child.
- When hyperthermia should not put the child banks and mustard plasters, bathe him in a hot bath, resort to alcohol-based compresses.
- Cool air in the room where the patient is, no self-treatment and parental love and caress. These are the three components of rapid recovery according to Dr. Evgeny Komarovsky.
In the next video, Dr. Komarovsky will give some tips to young parents on how to behave when the child’s body temperature rises.