Should I give antibiotics for intestinal infections in children?
Intestinal infections are an unpleasant reality. More often this ailment affects children, not adults, and, like an epidemic, includes large children's groups (whole groups in the kindergarten or groups in children's health camps). This is familiar and understandable to all parents whose children attend preschool and school institutions. Intestinal infection in a child is much more severe than in an adult. In addition, it is fraught with dehydration and even death for the baby.
Many parents, faced with such a problem in a child, are wondering whether it is possible to take antibiotics for intestinal infections. To answer, you need to understand that an intestinal infection is not just one specific disease, it is several completely different diagnoses. And they also need to be treated differently.
Do I need antibiotics?
Antibiotics for intestinal infections prescribed, if the causative agent of the disease - the bacterium. If the cause was a virus or food poisoning, antibiotics are not needed. They do not just not help to cope with the disease, but can seriously harm.
Antibiotics, which are not capable of destroying the virus during rotavirus or enterovirus infection, will rather quickly “crack down” on beneficial intestinal microflora, and the body of the crumb will lose the last “defenders” during viral diarrhea and vomiting. And severe intoxication and dehydration after diarrhea and vomiting can be fatal, especially for young children.
A bacterial intestinal infection, or as it is also called, “dirty hands disease” develops if bacteria are introduced into the body of a child. This is mainly due to unwashed hands, dirty vegetables, unsuitable for drinking water, as well as during the contact of the child with infected people or animals. Bacterial is considered dysentery, blue pus bacillus, salmonellosis, cholera, typhoid fever, botulism.
Intestinal infection caused by a virus is the familiar rotavirus, adenovirus and enterovirus to all parents. Most often these are seasonal diseases, and they attack children in the fall and spring.
Food poisoning most often occurs in the summer when foodstuffs deteriorate faster due to hot weather.
If a child has diarrhea, he sweats heavily, throws him into a fever, begins vomiting, and in the stool a large amount of mucus and even blood impurities - all this indicates the presence of a bacterial infection of the intestine, and the issue of antibiotics is quite rational.
Indications
Typically, treatment of intestinal infections do not begin immediately, but after establishing the type and family of the pathogen. But even if tests confirm that the disease is of bacterial origin, not all cases, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics to the child.
Mild forms of intestinal infection do not need potent antibacterial drugs, with minor disorders the child’s immunity is quite able to cope with treatment based on antidiarrheal and anti-emetic agents.
According to statistics, the doctor prescribes antibiotics for intestinal ailment in every fifth case (about 20% of the total number of children with a bacterial infection need powerful antibiotic therapy).
Antibiotics are necessary in the following cases:
- Infections of the heavy course. These are dysentery, typhoid fever, salmonellosis, cholera, etc.
- With a difficult course of infection. For example, with liquid stools more often 10 times a day at the age of 3 years.If adults are prescribed antibiotic therapy in a serious condition, then antibiotics are shown to the child with a moderate severity of the ailment.
- If the baby has blood in the feces. This is a sign of intestinal inflammation. And without antibiotics, such inflammation cannot be cured.
- With a state of immunodeficiency child.
- If the child has a tumor in the body.
Treatment
Treatment with antibiotics for intestinal infections will definitely be complex. Doctors apply the same approach to viral infections; you will be prescribed a complex of drugs for rotavirus.
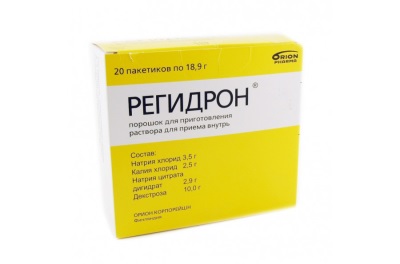
The doctor, in addition to antibiotic therapy, may prescribe antiemetic, antidiarrheal drugs, as well as means to normalize the balance of water and salt in the body in order to avoid dehydration, for example, "Regidron».
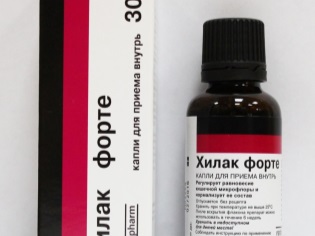
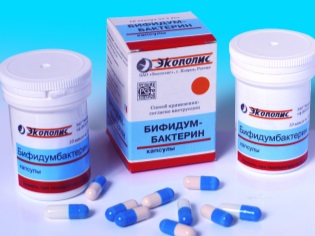
In addition, in the treatment of intestinal infections, the doctor will definitely recommend giving the child bacteriophages.Baktisubtil"," Hilak Forte "," Lactulose ","Bifidumbacterin"," Laktiale "to restore the natural protection of the intestines and the prevention of dysbiosis.
Drug List
The most effective "fighters" with microorganisms - the causative agents of intestinal ailments are antibiotics of the cephalosporin group. But physicians first prescribe tetracyclines (children older than 8 years) or penicillins, and if they do not have the desired effect, then go to the "heavy artillery" - cephalosporins.
Antibiotics - tetracyclines for the treatment of intestinal infections:
- "Doksal". An antibiotic that quite effectively deals with intestinal microbes of different origin. But this drug is contraindicated in children under 8 years of age, since it forms specific chemical compounds that are “deposited” in the baby’s bone skeleton and in the enamel of still forming teeth. Children from 9 to 12 years old (provided that their weight does not exceed 45 kilograms) are prescribed a daily dose of 4 mg. per kilogram of body weight on the first day of illness, and then 2 mg. per kilogram of weight (two daily intakes). The drug is available in tablets, capsules and forms for injection. In case of severe intestinal infection, the antibiotic is prescribed precisely in injections, but then it is recommended to switch to tablet forms.
- "Tetradox". Antibiotic produced in capsules. This remedy is contraindicated in children under the age of 9 years. The dosage of "Tetradox" is determined by the doctor strictly individually, necessarily taking into account the age of the child, his body weight and the severity of the disease.
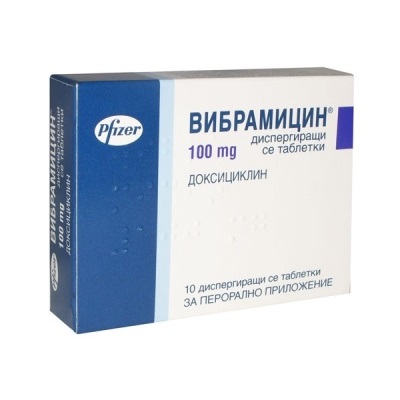
- "Vibramitsin". Antibiotic, which is also not recommended for children under 8 years old. The dosage regimen and dosages of this drug are the same as those of Doksal.
Antibiotics –Penicillins for treating intestinal infections:
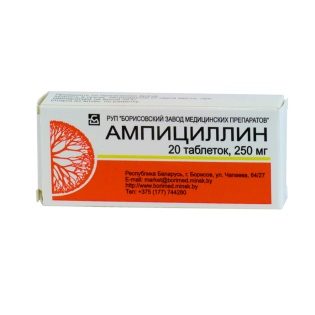
- «Ampicillin». An antibiotic is prescribed to children from 1 month. If the infection of the baby is quite severe, the doctor will recommend an individual dosage of the drug in the range from 50 to 100 mg. per kilogram of body weight of the child. The resulting amount will have to be divided into several equal receptions per day. If the child’s weight has passed for 20 kilos - he can use the adult dosage (from 250 to 500 mg times a day.
- "Monomitsin". An antibiotic that can cope with most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including those that are resistant to acid. They, without dying in the stomach, "get" to the intestine. For children, the drug is prescribed at the rate of 4-5 mg per kilogram of child's weight. The total daily amount is divided into 3 doses. Not recommended for babies up to a year.
Antibiotics - cephalosporins for the treatment of intestinal infections:
- “Klaforan”. Third generation antibiotic. It is not recommended for children under 2.5 years. Children whose weight has not reached 50 kilograms are given injections at a dosage of 50-100 mg per kilogram of weight every 6-8 hours. For severe infections, the doctor may increase the dose by half. For children weighing more than 50 kg, the dosage is identical to that of an adult.
- Cefabol. A powerful antibiotic with a fairly extensive list of side effects.Manufacturers do not recommend giving it to children under 2.5 years old, but pediatrics have developed the practice of using Cefbol in children from 1 month, if their condition requires urgent and strong antibacterial therapy. In children from 1 month. up to 12 years, the daily dose is from 50 to 180 mg per kilogram of weight. The drug is made injections 4-6 times a day. For children weighing more than 50 kg, the dosage is according to the adult scheme.
- "Rocephim". Third generation antibiotic. Newborn babies give it to 20-50 mg per kilogram of body weight once a day. Infants, children aged 2 years, and children older (up to 12 years), the doctor will prescribe an individual dose in the range from 20 to 80 mg. drug for every kilogram of baby's weight once a day. Teenagers over 12 years old, the drug can also be taken 1 time per day, 1-2 g (at the discretion of the doctor).
- «Ceftriaxone». This antibacterial drug should be used with great caution in the treatment of premature babies. It is better if such treatment takes place in the hospital under the supervision of a physician. The medicine has its pros and cons. Plus the fact that it can be taken by children of any age only once a day. A minus is that neither in tablets nor in suspension, "Ceftriaxone" is not available. Only injections are possible. Children over 12 years old - 1-2 grams. drug. Newborn crumbs up to 2 weeks the maximum dosage is 20-50 mg. for every kilogram of weight. Children up to 12 years old have a daily dosage of 20 to 75 mg per kilogram of body weight.
Other antibiotics for the treatment of intestinal infections:
- «Furazolidone». An antibiotic representing the nitrofuran family. Available in tablets, granules for suspension and powders. Contraindicated in children under 1 year. Usually prescribed in a dosage of 10 mg. for every kilogram of child's weight, the amount received is divided into 4 doses per day. Recommended for babies in the form of a suspension.
- «Ersefuril». Another antibiotic is nitrofuran. Children from 1 month give the drug two or three times a day, 100 mg. Babies from 2.5 years old and adolescents up to 14 years old are prescribed 100 mg each. three times a day. Adolescents 14 and over take 200 mg in 4 doses (every six hours). The drug adolescents can be given in capsules, and children - in the form of a 4% suspension.
- "Intrix". This antibiotic, synthesized in France relatively recently, has no analogues by active ingredient. The antibiotic is available in capsules. Manufacturers claim that the drug is contraindicated in children under 14 years old, however, pediatricians use “Intetrix” to treat intestinal infections, however, the dosage is set individually for each child. At 2 years, at 4 years or at 7 years a single dose will be different.
- «Phthalazole». This is a real "long-liver" among intestinal antibiotics. They have been treated for such diseases for more than half a century. Modern pediatricians claim that there is no need to give Ftalazol to children under 3 years old, especially since many new and more effective antibiotics have now appeared. However, all experts agree that "good old" Ftalazol is quite safe for children. The daily dose of antibiotics for children under 3 years old is -0.2 grams per kilogram of body weight; children over 6 years old can be given 0.4-0.8g. per kilogram of weight. Antibiotic is available only in pills.
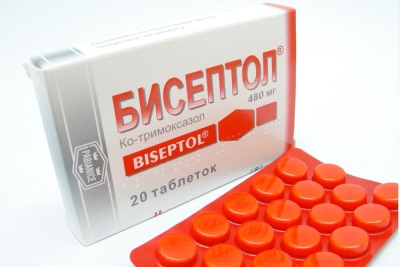
- "Biseptol". This antibiotic is available in tablets, injectable powders and suspensions, or a ready-made solution for oral administration. The drug can be given to children from one and a half months. Babies can be given 5 ml of suspension or ready-made solution once a day. Schoolchildren under the age of 12 are given 460-480 mg twice a day.
Also, a doctor may be appointed "Azithromycin», «Clarithromycin"Or a relatively young drug" Lekor. "
General rules for the treatment of antibiotics of gastrointestinal infections in children:
- The average course of therapy is from 3 to 14 days. The doctor will determine the duration of treatment in each case, based on the severity of the symptoms, the diagnosis and age of the baby. When an improvement occurs, it is not worthwhile to reduce the dosage yourself or to stop taking the drug at all.Surviving bacteria will become resistant to this type of antibiotic. And the next time you will be difficult to find an effective drug.
- When treating with antibiotics, the child must comply diet, drink more fluids.
You can learn about intestinal infection by watching Dr. Komarovsky’s video: