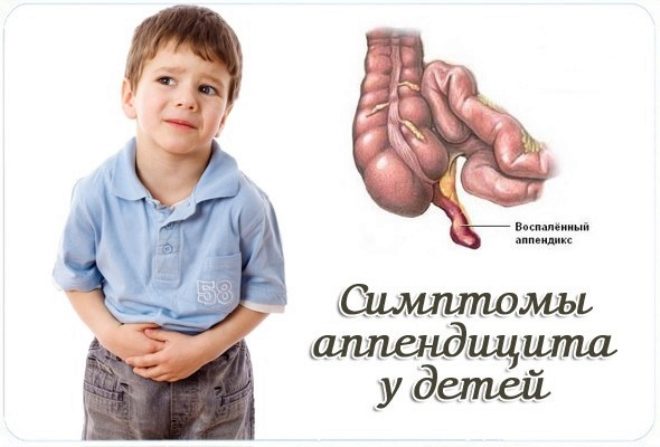
Appendicitis in children of different ages: symptoms and treatment
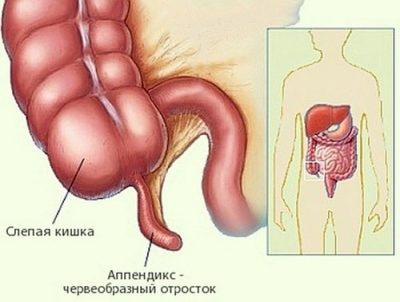
The inflammatory process in the final section of the cecum is called appendicitis. This disease occurs in people of different ages. They can easily get sick little kids and teenagers. Without timely medical care, this disease can be deadly or cause serious complications.
Causes and provoking factors
The causes of appendicitis can be completely different external factors. As a rule, inflammation occurs after hypothermia or reduced immunity. A child can also get sick with this disease if he has chronic diseases of the digestive system.
Improper diet low-quality products can also easily cause inflammation in the intestines. A large amount of untreated fiber may cause spicy inflammation of the final section of the cecum, causing disease.
In infants, the so-called mechanical (or obstructive) cause can be a common cause of appendicitis. In this case, the lumen of the intestine overlaps some kind of mechanical obstacle. In babies, this often results in ingestion of foreign components (swallowed toys or other objects) into the stomach, and then the intestines, as well as worms and other parasites, fecal stones. In infants who are prone to frequent constipation or untimely discharge of feces, fecal accumulations in the intestines may occur, which will cause inflammation of the wall of the cecum and even cause appendicitis.
The most rare cause of appendicitis may be congenital bowel disease. In this case, the baby is already born with a modified intestine. This can be an individual shortening of the length, as well as multiple bends or bends of the wall. In this case, appendicitis can also develop quite often when exposed to external factors.
Why timely diagnosis of appendicitis is important can be viewed in the next video.
Kinds
Like any inflammatory disease, appendicitis can occur in several forms. If the disease arose for the first time and proceeds with fairly severe clinical symptoms, this form is called acute. If after the treatment, in which the appendix was not removed, appendicitis recurs, then this form of the disease is called chronic. It requires removal of the appendix in order to prevent future dangerous symptoms.
All acute forms of the disease can be divided into several types:
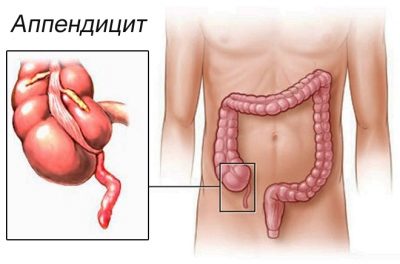
- Catarrhal form of the disease. In this case the disease proceeds as calmly as possible and, as a rule, does not cause life-threatening complications. In this form, the inflammatory process captures the wall of the cecum and provokes the appearance of the first specific symptoms of appendicitis. If a surgical operation was performed on time, the baby is completely cured.
- Phlegmonous form of the disease. It is already more dangerous, it can cause life-threatening complications. In this variant of the course of the disease, a strong inflammation of the intestinal wall is already occurring. Thrombosis of vessels supplying the cecum is also possible.
- Gangrenous form. The most dangerous variant of the disease. During inflammation during this course of the disease, the intestinal wall dies away.This option can cause life-threatening complications: a breakthrough of the wall and the release of the entire contents of the intestine into the stomach (with the formation of peritonitis and shock). In this case, urgent surgery with removal of the organ is required. Only this measure will help save the baby life.
First signs
It is better for every mom to be familiar with the manifestations of this disease in order to easily recognize a dangerous problem at home. Determining this disease is not always easy.
Often parents think that the appendix is on the right side. However, this is not quite true. The vermiform process is very mobile. Anatomically, it can be located not only on the right. In 20% of babies, it is on the left side. Each 9 child out of 10 can even be located near the navel.
The onset of the disease can be quite non-specific. In many babies, the onset of the disease occurs under the guise of a common cold. In the first days, the body temperature rises to 37 degrees, weakness appears, less often chills. The child becomes lethargic, eats badly, refuses to play. Habitual activities do not give him any joy. The baby is sleepy, more often lies, sparing the tummy.
During the first two days, parents often cannot suspect appendicitis and begin to give the child medications for fever, as with flu or acute respiratory infections. However, despite the initiated treatment, the effect is not noticed. In the meantime, the child is getting worse. There are already more specific symptoms for this disease. Body temperature rises to 38-39 degrees. The child complains of pain in the tummy.
In the first two days, the pain begins in the area near the navel. Then she gradually goes down to the groin or in the right half of the body. The pain is significantly increased by changing the position of the body. A child may develop nausea or even vomiting. However, this is not a mandatory appendicitis symptom.
It is important to note the nature of pain in appendicitis. It may be different. Some babies feel pain in a moderate way, without sudden increases. Other - spasms. In this case, the pain increases first, then subsides a bit. As a rule, in most cases, violations of the chair does not occur. Only babies with chronic intestinal or stomach diseases can sometimes have constipation or diarrhea, but these are non-specific signs of the disease.
Is it equally manifest?
In children of different ages, the course of the disease can vary considerably. According to the latest scientific studies, the peak incidence occurs at the age of 10 years, 12 years. In most cases, infants are not at all affected by this disease. Kids up to 5 years old also get sick relatively rarely.
According to statistical medical data, every fifth person with appendicitis is a child aged 6 years, 7 years. More than half of all cases of inflammation of the appendix in children occur in the junior and middle school age. As a rule, these are children from seven to 14 years.
Since the body of a three-year-old child is markedly different, for example, from the body of a nine-year-old schoolchild, the course of the disease is also different.
Up to five years
For children of this age is characterized by the gradual development of the disease. Body temperature rises relatively low. Quite often, nausea or gagging can occur. Children often become moody, poorly eaten, very restless.
Babies up to three years old often have thirst and all the symptoms of dehydration. Skin and lips become dry. The baby begins to spare the tummy, does not allow to examine or touch. Crumbs in the first two years of life can also often appear constipated or very thin one-time stools.
Up to ten years
In children, body temperature rises to 37.5-38 degrees. In more severe variants of the disease - even up to 39 degrees. Toddlers are often sick, with vomiting or abnormal stool, as a rule, does not occur.
Characterized by severe pain in the abdomen. When viewed or trying to touch the tummy, it is greatly enhanced. The child tries not to lie on the injured side, as this greatly increases the pain.
Teens over 12 years old
In many cases, appendicitis at this age proceeds along practically the same scenarios as in adults. In the first couple of days, there are characteristic pains in the umbilical region with a gradual movement in the right half of the abdomen or in the groin. Often body temperature rises to 37-37.5 degrees. The pain is often paroxysmal, without severe spasms.
Violations of the stool, nausea or gagging are not characteristic. But quite often there are signs of dehydration. A child's appetite decreases or is almost absent, and weakness appears.
All symptoms of the disease are non-specific. Often, it is quite difficult to determine appendicitis yourself. In this case, you should definitely seek professional medical advice from a pediatrician.
Diagnostics
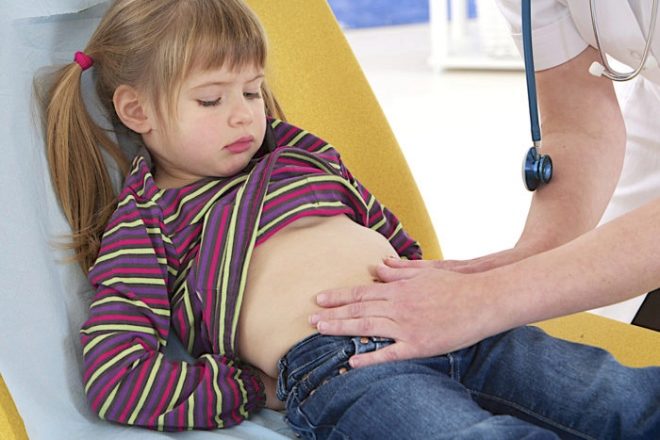
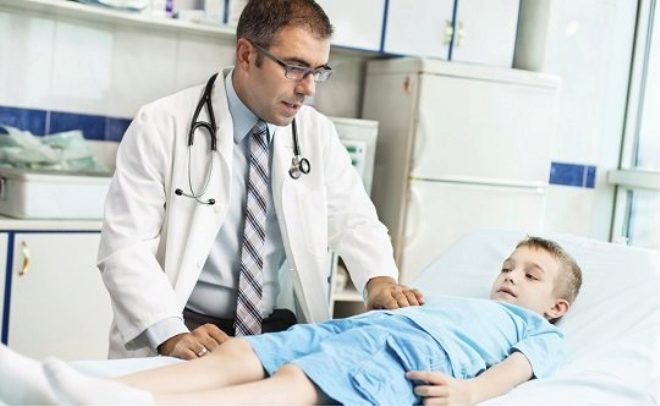
The appearance of the first symptoms of the disease is not yet one hundred percent method of diagnosis. Confirm appendicitis can only doctor. To do this, the doctor will first examine the baby, conduct all special medical tests, allowing with sufficient accuracy to confirm the disease at home.
For an accurate diagnosis, you need to take the child to the hospital. Without fail, he will make several tests. A blood test will show whether there is inflammation, as well as the severity of the disease.
In difficult cases, when the diagnosis of appendicitis is difficult to establish, doctors resort to additional methods of diagnosis. First, the surgeon will look at the baby. Then an ultrasound of the abdominal organs can be performed. This test will show the condition of the appendix, whether there is inflammation.
Before performing surgery to remove the appendix, the doctors will take blood from the baby for additional tests. This is necessary for future anesthesia and surgery.
Treatment methods
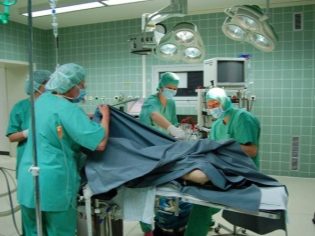
Inflammation of the appendix is a surgical disease. In most cases, when confirming the diagnosis, the inflamed organ must be surgically removed. Home mode in this case is extremely dangerous. Without the provision of timely qualified medical care, the baby may even die.
During his stay in the hospital, the baby will be given all the necessary urgent diagnostic tests and analyzes. After confirming the diagnosis, the operation to remove the appendix will be carried out in a fairly short time. Postponing an operation in many cases is very dangerous. This can lead to the development of peritonitis or septic shock in a baby.
Recovery from surgery usually lasts 10-14 days. At this time, the baby is assigned a special diet, sparing the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Vitamin therapy will help to quickly restore the child’s immunity. All physical activities (and even more so visiting sports sections) are allowed one month after the operation, not earlier. In this case, all physical activity should be introduced gradually. Raising heavy objects more than 5 kg is strictly prohibited (for three months).
Possible complications
The most frequent complications of appendicitis include:
- The development of peritonitis. If medical aid was rendered out of time or the disease proceeds in an aggressive and dangerous form, inflammation of the peritoneum may occur. This significantly worsens the prognosis and requires urgent surgery.
- Septic shock. In some cases, appendicitis can also be caused by bacteria or viruses. With reduced immunity, a child may develop shock. In this case, the blood pressure drops sharply and the pulse speeds up. The kid can even lose consciousness. The development of shock is a life-threatening event.
- Breakthrough of the wall of the cecum. If the disease is late suspected (or a surgical operation is not performed in time), due to severe inflammation, the intestinal contents may pour into the abdominal cavity. This is a very dangerous condition that can cause peritonitis or septic shock in a matter of minutes.
- Shock (due to dehydration). When expressed symptoms of intoxication appear strong symptoms of dehydration. This leads to a large load on the heart and blood vessels. The baby may develop tachycardia or arrhythmia.
Complications of appendicitis can occur in almost any course of the disease. If a baby has chronic diseases, immunity is reduced, or he receives corticosteroid hormones, the risk of complications increases several times.
Principles of nutrition
After surgery to remove an appendix while still in the hospital, the baby will be prescribed a special, sparing diet. The first few days, babies are allowed to eat only pureed and low-fat foods. All dishes are prepared sparing method. As a rule, the menu includes only cereals, ground mucous soups and steam lean meat.
At discharge from the hospital, the attending surgeon makes recommendations to Mommy that you can eat the baby after the operation. Therapeutic diet is recommended to be followed for one to two months. This will allow the inflamed intestinal wall to quickly recover, a weak children's body will be strengthened.
The basic principles of clinical nutrition after surgery:
- Small portions of food. Babies should eat up to six times a day (in moderation). The volume and quantity of food is measured according to age tables. Overeating in the postoperative period is very dangerous! This can lead to re-inflammation of the intestines and provoke the occurrence of complications.
- The absence of very fatty, fried foods. All products containing smoked or marinade are also excluded. All food should only be lightly salted. Spicy and overly bright seasonings are prohibited. In the first month, you can add only a little salt in food. From the fifth week after the operation, you can add a little black pepper. You can add sugar, vanilla or a little cinnamon to sweet dishes.
- During the first two weeks after the operation, fresh fruits and vegetables can be eaten only after heat treatment. Raw fruit with the peel is strictly prohibited. Apples and pears are tasty after baking with a little addition of cinnamon or powdered sugar. Try to limit a large amount of crude fiber in the diet of the child.
- Enter fiber gradually.. The basis of the diet for the first two weeks for a baby is well boiled porridge, as well as meat products or poultry. You can use fish.
- Choose a gentle way of cooking. Grilling and cooking on the grill leave until the baby is completely cured. The most correct methods of cooking are boiling or cooking in a slow cooker, a double boiler.
- Use well boiled cereals as regular carbohydrates. No more than 1-2 times a week, you can add a little pasta or noodles. In the first two weeks after surgery, prepare non-dairy cereals. Adding dairy products can lead to a violation of the chair, to the appearance of diarrhea.
- Sufficient water intake. After severe dehydration, the children's body is in great need of water (to replenish lost reserves). Add fruit and berry fruit drinks, compotes, tea and plain boiled water to your child’s diet.
Prevention
Insure against appendicitis is almost impossible. At any age, this disease can be taken by surprise. but When the following conditions are met, the probability of appendicitis in your child can be somewhat reduced:
- Food Hygiene. Do not consume excessive amounts of coarse fiber. In fruits and vegetables, it is desirable to remove the skin before use.The peel contains a lot of fiber, which in large quantities can cause appendicitis.
- Prevention and control of helminthic invasions. Regularly take stool analysis for the presence of worms. This will allow to cure all parasitic diseases in a timely manner. Watch for babies under five years old, they often appear pinworms. Teach your child the right habits: be sure to wash your hands before and after meals, as well as before and after using the toilet. It is imperative to check whether the little ones washed their hands after walking on the street or visiting any public place.
- Watch out for scattered toys! Kids under three years old often pull all unfamiliar objects in their mouths to taste them. If foreign objects are swallowed, this can cause a blockage of the cecum and provoke appendicitis.
- All babies with immunodeficiencies and other diseases that significantly decrease their immunity should be sure to be observed by an immunologist. Active and strong immunity is a guarantee of excellent protection against various bacterial infections, which can also provoke appendicitis in a baby.
- Clinical supervision by a gastroenterologist in the presence of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If a baby has a disease of the digestive system that is not treated in time, then inflammation may occur at any time. Especially often appendicitis may occur in babies with chronic colitis or cholecystitis.
Treatment of appendicitis should be timely and quick. Delay in providing medical care for this disease is unacceptable! Only carrying out an emergency surgery will help in time to cure the disease and save the life of your baby. You can suspect the disease yourself, but you should definitely call an ambulance or pediatric doctor.
What can indicate a child's stomach pain, see the following video.