Bronchial asthma in a child: symptoms and treatment
Respiratory disorders, in which bronchial conduction is impaired, leads to the development of bronchial obstruction. With a long course, this condition turns into asthma.
What it is?
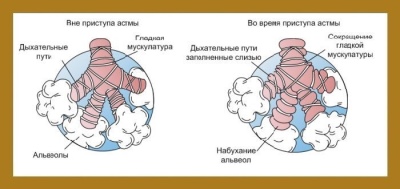
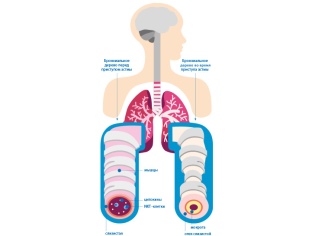
Several different causes lead to the development of respiratory disorders. In bronchial asthma, increased bronchial reactivity to certain substances occurs, which leads to the development of bronchial obstruction (blockage). The air with oxygen dissolved in it does not pass well through the narrowed bronchi. In the end, this leads to impaired air exchange between the blood, lung tissue and the environment.
After exposure to various provoking factors, there is a violation of bronchial conductivity. This condition is called broncho-obstructive syndrome. If this process lasts a long time, then the course of the disease becomes chronic. In this case, the bronchial obstruction syndrome becomes bronchial asthma.
According to statistics, this disease occurs in 10% of children. Boys are sick a little more often than girls. The peak incidence occurs at the age of 4-10 years.
Bronchial asthma is found not only in pediatrics. Adults can also get sick. The first signs of the disease can occur at any age.
The course of bronchial asthma is wavy. The periods of exacerbations are replaced by remissions. The duration of the quiet period may be different. It depends mainly on the state of the immune system and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases in the child. Weakened toddlers have much more exacerbations than children who undergo regular rehabilitation.
Risk factors
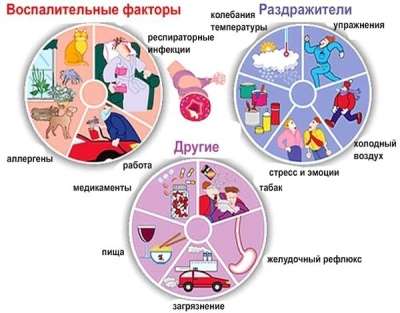
Different provocateurs can lead to the development of asthma. In some situations, the effect of several provoking factors at once has a more pronounced effect, leading to persistent broncho-obstructive syndrome.
Among the most significant risk factors are:
- Genetic predisposition. If one of the parents has asthma, then the risk of having a sick baby is 25%. In cases when father and mother are both sick, the risk of a child with respiratory failure is already 75%. Not all cases of genetic predisposition leads to the development of the disease. If the child does not act other adverse factors, then he may not develop the disease throughout his life.
- Contaminated air. Children who live near industrial plants and factories, as well as close to major highways, have a higher risk of developing asthma. The smallest particles of toxic products can be stored in the air for a long time. When they hit the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, they easily cause inflammation, leading to bronchial obstruction.
- Dust and household mites that live in pillows and blankets. These, at first glance, harmless factors often lead to the development of persistent symptoms of bronchial obstruction. The smallest mites are constantly in contact with the skin, causing severe allergies. Ultimately, this leads to a pronounced respiratory failure.
- Animals The most dangerous pets who live at home.Wool, fluff, and animal dander often becomes a source of a pronounced allergic reaction. It is manifested not only by the appearance of specific rashes on the skin, but also characterized by the presence of impaired breathing.
- Food products. Especially food cooked in an industrial way. In such products there are a lot of synthetic additives, dyes and aromatic components. Once in the gastrointestinal tract, they cause severe allergic reactions. This contributes to the development of systemic adverse symptoms: cough with sputum and wheezing during breathing.
- Household chemicals. Many synthetic products contain a fair amount of various perfumery additives and fragrances. These substances have a pronounced irritant effect on the organs of the respiratory tract. With prolonged contact with such products, the risk of developing bronchial obstruction in a child repeatedly increases.
- Individual sensitivity to flowering herbs. Typically, asthma attacks with this condition have a clear seasonality. The baby’s well-being worsens in spring and autumn. It is at this time that weeds and meadow grasses bloom, as well as various trees and shrubs.
- High humidity and humidity in the room. This condition provokes the development of mold fungi. In wet and wet conditions, they quickly grow and multiply. Large colonies of mold fungi can cause severe respiratory failure in a baby.
- Infection with viruses and bacteria. Nowadays, doctors have increasingly begun to register a viral-induced form of bronchial asthma. The development of the broncho-obstructive syndrome often becomes a consequence of a viral infection in an often ill child with a reduced immunity. Also in some cases, and bacterial infections lead to asthmatic respiratory disorders.
- Ingestion of tobacco smoke. The effect of passive smoking on the development of bronchial asthma has been scientifically proven. If one of the parents constantly smokes in the apartment or room where the child is located, then the risk of developing asthma increases significantly.
- Strong physical exertion, leading to exhaustion. Excessive training, picked wrong, can lead to disruptions in the immune system. After prolonged stress, the child has respiratory problems and shortness of breath.
Causes
Bronchial asthma most often develops with a genetic predisposition originally present in a child. With additional exposure to adverse environmental factors, the disease course worsens and becomes chronic.
The development of asthmatic respiratory disorders lead to:
- Eating hyperallergenic foods. Most often it is: citrus fruits, chocolate, sweets, seafood, fish, honey and others. The ingestion of allergenic products in the body leads to the development of an allergic reaction. It can manifest itself in particular and severe bronchial obstruction syndrome.
- Inhalation of polluted air. Toxic industrial products and exhaust gases have a toxic effect on the epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract. These substances cause a strong spasm of the bronchi, which leads to a narrowing of their lumen and respiratory failure.
- Allergic diseases. Often these pathologies are secondary and develop as a background in concomitant chronic diseases. Persistent dysbacteriosis, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder dyskinesia and chronic hepatitis lead to the development of asthma.
- Drug use without prior advice of a doctor or picked wrong. All medicines can have side effects. Many of them can cause persistent bronchial obstruction.If the child has a genetic predisposition for bronchial asthma, this can lead to the development of the disease.
- Strong stressful situation or stress. Cases of the development of the disease after moving to a new place of residence, the divorce of parents, as well as the death of close relatives in early childhood are noted. Severe stress contributes to the production of an increased amount of hormones. They cause narrowing of the bronchi, which leads to respiratory failure.
- Improper treatment of chronic respiratory diseases. Frequent bronchitis, especially occurring with a pronounced broncho-obstructive component, ultimately leads to the development of asthma. If a child often has a cough and he has a cold up to 4-5 times a year, then parents should think about the presence of bronchial asthma in the baby.
Classification
All forms of allergic asthma can be divided into several groups. This classification is based on the causes of the disease. This division is very important in pediatric pulmonology. This classification helps doctors prescribe the correct treatment.
Taking into account the leading cause of bronchial asthma can be:
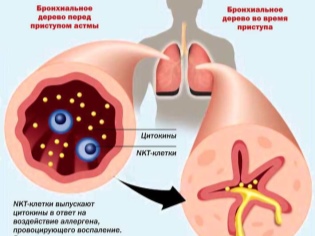
- Allergic. The development of this form of the disease results from the entry into the body of allergens that provoke the development of adverse systemic manifestations. In the presence of individual hypersensitivity to foreign substances in a baby, the level of immunoglobulins E increases. These components lead to a pronounced spasm of the bronchi, which is manifested by the appearance of cough.
- Non-atopic. In this form of the disease, a spasm in the bronchi occurs due to any exposure, but not an allergen. This variant of asthma develops as a result of severe stress, hypothermia, or as a result of excessive and improper physical activity.
- Mixed May occur as a result of exposure to both allergic and non-atopic causes. It is characterized by the appearance of numerous symptoms. The course of the disease is usually the most tranquil. The periods of remission can be quite long.
- Asthmatic status. This extremely dangerous emergency condition is highlighted in a separate form of bronchial asthma. During the life of the baby may experience several such attacks. This is an extremely serious condition in which the symptoms of respiratory failure increase sharply. In this case, emergency treatment is required.
The course of bronchial asthma can be different. This is influenced by several factors at once:
- the age at which the baby first showed signs of illness;
- immunity;
- the presence of concomitant chronic diseases;
- region of residence;
- the adequacy of the selected treatment.
All forms of the disease can be divided into several groups, taking into account the particular severity:
- With a slight episodic course. With this form of respiratory function is not observed. Attacks of impaired breathing occur less frequently than once a week. The period without seizures can be quite long.
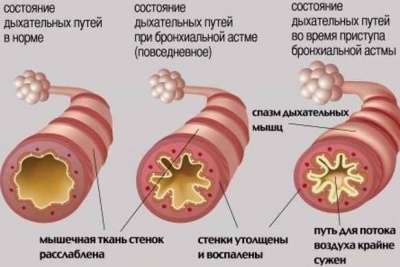
- With a slight persistent flow. Characterized by the appearance of bouts of impaired breathing several times during the week. Daily deterioration of health does not happen. When an attack occurs, breathing is disturbed, a hacking cough appears, and shortness of breath increases. Spirometry shows no abnormalities.
- With a moderate course. Impairment of well-being occurs almost every day. During such attacks, the child is disturbed by sleep, and severe breathing problems are observed, leading to severe shortness of breath. In the treatment of the condition requires daily use of bronchodilators. Spirometry shows abnormalities by 20–40%.
- With a heavy current. Dangerous development of several attacks in one day. Such deterioration may also occur at night. Therapy with short-acting bronchodilators does not bring a pronounced effect.To control the course of the disease requires the appointment of hormones. Spirometry shows a deviation from normal respiratory rates by more than 40%.
What is bronchial asthma in children, Dr. Komarovsky will tell in detail in the next video.
Symptoms
To recognize bronchial asthma at the initial stage is quite difficult. Quite often, parents believe that a child has just an allergy or broncho-obstructive bronchitis. In the interictal period, sometimes even an experienced doctor often cannot determine asthma in a child. Further development of the disease is manifested by the development of characteristic adverse symptoms that should alert the parents.
For bronchial asthma in the period of exacerbation is characterized by:
- The appearance of shortness of breath. She is an expiratory character. In this case, exhale is noticeably difficult. You can check for shortness of breath and at home alone. This is evidenced by the increased number of respiratory movements in one minute by more than 10% of the age norm.
- Cough with difficult expectoration. Mostly this symptom bothers the child during the day. At night, the cough is somewhat reduced. Phlegm with bronchial asthma is quite viscous, "glassy." If you try to cough up it, a child may even have a soreness in the chest.
- Increased heartbeat. Even in the absence of physical stress, the child has tachycardia. This symptom is usually associated with shortness of breath. The more pronounced it is, the greater the increase in the number of heartbeats per minute.
- The appearance of dry wheezing during breathing. In severe cases, such respiratory sounds become audible from the side, without using a stethoscope. Rattles are mostly dry and whistling. It is believed that in bronchial asthma, an accordion plays in the chest.
- The appearance of boxed sound during the percussion. This method is carried out to clarify the diagnosis. When fingers are tapped on the chest, a distinctive sound is heard, resembling strikes on an empty box. The appearance of this symptom is already manifested in the remote stages of the disease and indicates an increased filling of the lungs with air.
- The lack of effect of conventional drugs, used to eliminate cough. Only bronchodilators and hormonal agents have a visible therapeutic effect. In allergic bronchial asthma, antihistamines have a pronounced effect.
Symptoms of an attack
- The state of health of the child during the deterioration of the disease is greatly impaired. The kid becomes more capricious, scared. Some babies, especially in the first months after birth, begin to cry, asking for more in their hands. The kids almost completely disappear appetite, they refuse to eat.
- During an attack, the child develops expiratory dyspnea. To alleviate this condition, often the baby takes a forced posture. He leans heavily forward. The head may be slightly upturned.
- Often asthmatics during an attack try to lean their hands on a chair or even a railing of the bed. Such a forced position somewhat facilitates sputum discharge and improves breathing.
- With a severe attack The baby has symptoms of respiratory failure. Lips become pale, and in some cases even bluish. Hands and feet - cold to the touch. The child has a paradoxical pulse. With this rhythm disturbance, the number of heart contractions during inhalation and exhalation changes.
- Some babies try to take a sitting position. It helps them breathe better. Even from the side can be seen the participation of auxiliary respiratory muscles when breathing. The baby breathes deeply and often. The condition is aggravated by severe coughing. In some cases, it even leads to the fact that the child begins to cry.
- After the attack, the baby feels overwhelmed. Some kids for a long time can not calm down. They have disturbed sleep. The duration of the attack may be different. With the late use of inhalers can develop a dangerous and life-threatening condition - asthmatic status. In this situation, it is impossible to cope with the elimination of adverse symptoms at home - medical emergency is required.
How does it appear in infants?
The course of bronchial asthma in an infant can also occur in different ways: from mild severity to the most severe. Infants often have asthma attacks on fermented milk products and mold fungi. The second in frequency is food allergies.
Usually, the first symptoms of asthma in an infant appear by the age of 5-6 months. At this time, the baby begins to receive new foods as food. If a child has individual intolerance or hypersensitivity to some substance, he may develop symptoms of bronchial obstruction.
A prominent symptom of bronchial asthma in an infant is the occurrence of cough. The baby starts coughing day and night. In some cases, shortness of breath joins. Even while in bed, without physical exertion, the child has an increase in the number of breaths and heart contractions per minute.
Babies start to suck badly, the effectiveness of breastfeeding decreases. Such kids lose weight and lag behind their peers in terms of physical development. Silent crying is also one of the symptoms of bronchial asthma in a baby in the first year of life. The child becomes lethargic, poorly asking for his hands. Some babies fall asleep poorly and often wake up during a night's sleep.
Diagnostics
In order to make a correct diagnosis only collecting anamnesis and examining a child by a doctor will not be enough. To identify persistent bronchial obstruction requires additional tests and examinations. Only carrying out various diagnostic tests will help to establish the correct diagnosis.
To diagnose bronchial asthma will require:
- General blood analysis. Increased leukocytes and moderate eosinophilia (increase in the number of eosinophils in the leukocyte formula) indicate increased allergization. Such changes are characteristic mainly for the allergic form of bronchial asthma.
- Sputum test. Detection of specific Charcot-Leiden crystals, Kurshman spirals, an increase in the number of desquamated epithelial cells, as well as an increased level of eosinophils indicate the presence of persistent bronchial obstruction.
- Conducting research on the ratio of blood gases. With a long course of bronchial asthma, there is a decrease in the content of dissolved oxygen and a slight increase in carbon dioxide. Such changes indicate the presence of severe hypoxia or oxygen starvation in the body.
- Spirometry Reflects indicators of external respiration. Assessment of forced expiration and general indicators of lung capacity helps to identify persistent bronchial obstruction in the body, leading to changes in the parameters of the respiratory function of the lungs. The reduction of these parameters is estimated as a percentage of the age norm.
- Conduct scarification samples. They help to identify all possible allergens that cause the development of bronchial obstruction in a child. The study is conducted only by an allergist. The test can be performed only in children older than five years.
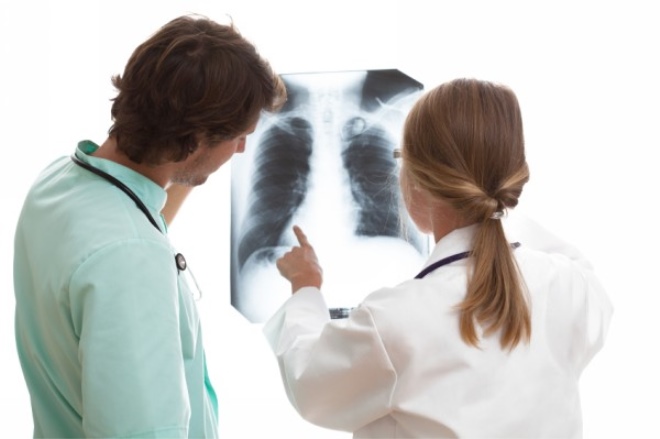
- Radiography of the chest. It helps to establish the secondary signs of bronchial obstruction: increased airiness of the lungs and a change in the diameter of the large bronchi.
- Bronchoscopy. It is used in limited cases, mainly for differential diagnosis in order to exclude similar diseases occurring, as well as bronchial asthma with symptoms of bronchial obstruction.
Complications
The development of adverse effects of bronchial asthma depends on many factors. The most important of them is timely diagnostics and correctly prescribed treatment. With an inadequately selected treatment regimen, the child may experience numerous adverse effects of the disease.
Among the most frequently recorded complications of bronchial asthma:
- Development asthmatic status.
- Sudden onset of symptoms acute respiratory failure.
- Spontaneous pneumothorax. In this condition, a capsule ruptures, covering the outside of the lungs. This condition usually occurs during a severe attack.
- Shock buildup. The development of acute respiratory failure leads to a sharp drop in blood pressure. This condition is extremely unfavorable and requires emergency treatment and hospitalization in the hospital.
- Pneumonia. Appears when joining the inflammatory process of bacterial flora. It is characterized by a rather heavy course. Antibiotics are required to eliminate symptoms.
- Pulmonary emphysema. Developed in asthmatics with experience. It is characterized by increased air content of the lung tissue. This significantly reduces the respiratory function of the lungs, which leads to symptoms of respiratory failure.
- Formation of cardiovascular failure. It is an extremely unfavorable complication. In this condition, the appointment of several types of drugs, including cardiac glycosides.
Treatment
According to the clinical guidelines for the treatment of asthma, the therapy of different forms of the disease should be graded. Modern medical standards provide for the gradual administration of drugs.
Selection of necessary drugs is carried out only after a comprehensive examination of the child. Before you choose the required inhalers or pills, you must accurately identify the form of bronchial asthma and determine the severity of the disease.
Treatment of a child with asthma is carried out by a pulmonologist. In case of an allergic form of a child, it is imperative to show an allergist. This doctor will help to make a more individual treatment, taking into account the peculiarities of the immune system.
Treatment in the pulmonary clinic is carried out only in difficult cases of the disease. In case of a mild course, regular visits to the clinic and outpatient consultations with doctors are quite sufficient.
The treatment of bronchial asthma includes several basic principles:
- The appointment of symptomatic agents. In this case, medications are used only during an attack, in order to eliminate the acute adverse symptoms of the disease. Typically, various inhalers are used for these purposes.
- Selection of basic therapy. These funds are already assigned to a permanent reception. They help prevent new seizures and improve the course of the disease. Monitoring the effectiveness of drugs is carried out using spirometry. At home, a special portable device, a peak flow meter, is perfect for this purpose.
- Exclusion from everyday life of all types of allergens. Compliance with a hypoallergenic diet, the use of special bed linen, as well as the limitations of games with soft toys will help prevent new attacks and the development of asthmatic status.
- Use special air humidifiers. These devices help create an optimal indoor climate. Too dry air irritates the airways, causing breathing problems and new asthma attacks.
- The use of antitussive and expectorant drugs. These tools help to eliminate pronounced coughing. In the absence of allergies in a child, also medicinal herbs are suitable: coltsfoot, thyme, calendula, and others. Phytotherapy should be used only after consulting a doctor.
- Restriction of games with animals. For a child suffering from bronchial asthma, it is better not to make fluffy home friends. The wool and down of animals can adversely affect the health of the child and cause him new seizures.
- Regular disinfecting treatment. To clean the visit, where the child is located, should be daily. Use caustic and too aggressive chemicals for this should not be. It is better to choose detergents that do not contain pronounced aromatic additives. The best option is household chemicals that have special markings about the safety of use, even in children's rooms.
- Strengthening immunity. To do this, perfectly fit active walks in the fresh air, exercise therapy complexes, breathing exercises, as well as a variety of hardening. Properly harden the child should be from the earliest years of his life. Hardening should be regular. The complex of these measures will help strengthen the weakened immunity of the baby, which will help reduce asthma attacks in the future.
Drug therapy
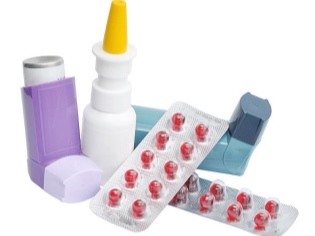
As a basic treatment, various groups of drugs are used. Among them:
- Mast cell membrane stabilizers. Helps to reduce the number of pro-inflammatory biologically active substances that appear during allergic inflammation. The effect does not come immediately. It usually takes from 14 days to several months to achieve the effect. These drugs include: Ketotifen, Kromogen, Kromoheksan, Nedokromil, Intal and others.
- Antihistamines. Helps to eliminate swelling from smooth muscle cells of the bronchi. This helps improve sputum discharge and reduce inflammation. They are prescribed by an allergist. To control asthma fit: Suprastin, Loratadine, Zyrtec, Claritin other.
- Hormonal. Appointed in severe asthma, as well as in cases where the previous treatment regimen was ineffective. They have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. With long-term use can cause side effects. May be administered in the form of inhalers or tablets (for severe).
For symptomatic treatment and elimination of adverse, acute symptoms of bronchial obstruction, drugs with a bronchilitic effect are used. They help to quickly eliminate bronchial spasm and improve breathing.
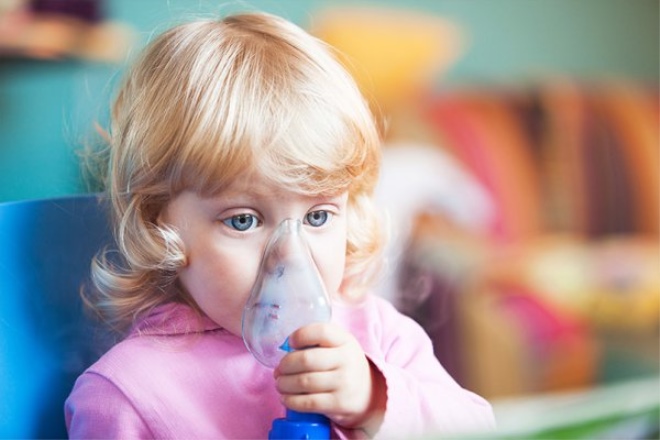
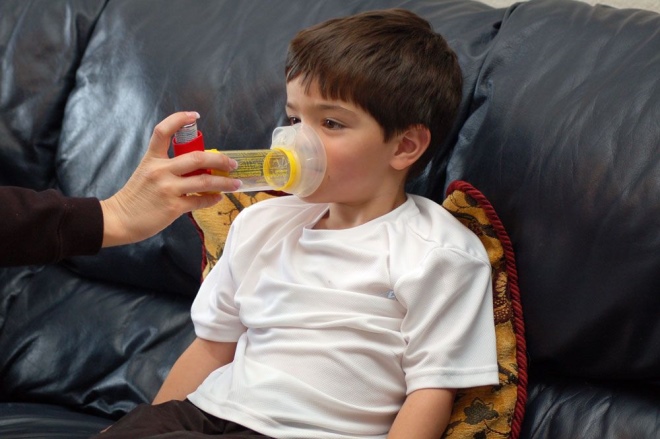
These funds are assigned as aerosols, which are produced in the form of various inhalers, spacers and nebulizers. They help to distribute the active substance as quickly and efficiently. The smallest particles of medicine reach the bronchi in the shortest possible time. Usually the effect is achieved within the first 5 minutes from the moment of use.
The following groups of drugs have a bronchodilator effect:
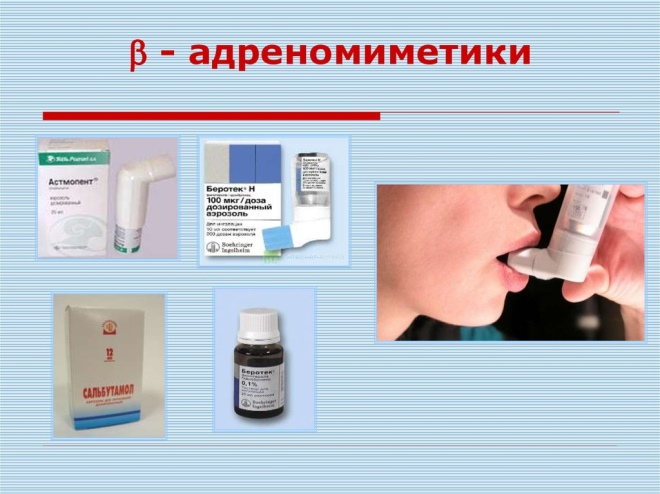
- Adrenomimetics. Block adrenoreceptors, which are located on the surface of bronchial cells. May be short and prolonged. Preparations based on salbutamol eliminate bronchial spasm in 5-10 minutes. Foradil, Serevent and Valmax help eliminate obstruction in the airways for 10-12 hours.
- Anticholinergics. Have a pronounced effect. May cause systemic adverse effects. Often greatly reduce blood pressure. These include: Atropine, Atrovent, Platyfillin and others.
- Xanthines Are not drugs of choice. Appointed only with the ineffectiveness of previously selected therapy. Often used in combined bronchial asthma treatment regimens. These include: theophylline, Euphyllin other.
- Combined. The combination of anticholinergic and adrenergic mimic allows you to achieve a quick effect and keep it for a long time. These include: Berodual, Ditek, Intal Plus, Symbicort, Seretid and others. Assigned to 1-2 inhalations per day. With prolonged use, you may need a dose adjustment or replacement with other drugs.
Diet
Medical nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of bronchial asthma. The diet is of particular importance in allergic form. In order for a child to not have new bouts of the disease, he should follow a hypoallergenic diet regularly. It was developed by the Union of Pediatricians for the treatment of various diseases in which there is a tendency to develop allergic reactions.
Children suffering from bronchial asthma should completely eliminate highly allergenic foods from their diet. These include:
- Red varieties of meat and poultry.
- Tropical fruits.
- Vegetables and fruits are yellow, orange and red.
- Seafood and sea fish.
- Citrus.
- Honey.
- Chocolate.
- Sweets and fizzy drinks.
- Industrially prepared food with a high content of spices, as well as preservatives and dyes.
In babies with lactase intolerance, an attack of bronchial asthma can occur after eating dairy products and cow's milk. In such cases, it is better to switch to using goat curd and cheese. These products will be safer for an asthmatic baby.
The optimal menu of a child with asthma should contain hypoallergenic protein products, cereals and enough fiber. As proteins fit: chicken breast, rabbit, turkey (in the absence of allergy to chicken eggs). On the side, you can cook porridge or mashed potatoes, made from potatoes or cauliflower.
It is possible to include all cereals in the children's diet. Restrictions can only be barley and oat porridge in case of gluten intolerance. As the fiber will suit any vegetables and roots of white and green flowers. Dessert can be apples and pears. Try to choose the green varieties grown in the region of residence.
Harbingers of a quick attack
Before a severe sudden deterioration of health begins, the child has some borderline symptoms. They are also called "aura." Before the development of an asthmatic attack, a child may experience severe sneezing, sore throat, and runny nose.
The baby is growing anxiety. In some cases, even panic. The behavior of the child may change. He becomes more silent, refuses to make contact. Many kids try to be in their own room, as this brings them more peace of mind.
The appearance of dry cough indicates the transition of the border state in a real attack. In the next few hours, all the symptoms are aggravated. Cough begins to grow and there are numerous dry wheezing and shortness of breath.
After a few hours, the child has a strong heartbeat and general weakness increases.
Emergency care in a seizure
To successfully stop sudden deterioration, parents should know what to do and how to help their baby. To do this, use the following tips and action algorithm:
- Do not leave the child alone when he has the first signs of deterioration of health. The older child should be asked about what is bothering him and where it hurts.
- Pay attention to whether the child has shortness of breath. To do this, count the number of respiratory movements in one minute. It's very easy to rate: watch the ribs move as you breathe. If the number of breaths is more than 20 per minute, then this indicates the presence of shortness of breath in the baby.
- Help your baby take a comfortable position. Do not lay the child on his back, if he is uncomfortable and breathe. Such a situation can only aggravate the development of an attack.
- Provide air flow. If the room is too stuffy, then open the window or window. Try to prevent the child from catching a cold at this time.
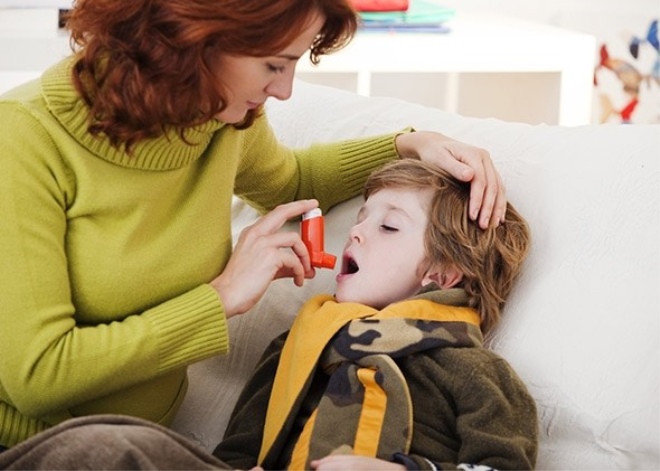
- Use an inhaler recommended by a doctor to relieve symptoms. Usually, to eliminate the attacks used drugs that have a quick effect. Often used for this inhalers based on salbutamol.
- If, despite using the medicine, the baby continues to have shortness of breath, there was a pronounced cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle and blood pressure decreased markedly, then this is a reason to call the ambulance brigade.
- Do not use 3-4 or more inhalations at once in an attempt to achieve the effect. Such irrational use can only lead to the development of a dangerous condition requiring hospitalization of the baby in the hospital. Large doses of adrenomimetic block receptors, which further prevents the bronchi to work fully. To eliminate this effect may require the introduction of hormones by the intravenous route.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation measures in the interictal period will improve the course of the disease, as well as significantly affect the prognosis. If bronchial asthma was registered in a baby for the first time and for a long time only proceeded in a mild course, then competent rehabilitation will help almost to bring recovery, and in some cases even make a diagnosis.
Rehabilitation measures include:
- breathing exercises;
- massotherapy;
- physiotherapy techniques (ultrasound treatment, speleological chambers, ultraphonophoresis, hydrotherapy, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis with medicinal bronchodilators and others);
- Spa treatment;
- complex therapeutic exercise.
All these methods together help to achieve a pronounced therapeutic effect. To achieve stable remission of bronchial asthma, rehabilitation should be carried out regularly during the entire period without exacerbations. An individual scheme of rehabilitation measures is drawn up for each child. Effectiveness control is assessed using spirometry and other examinations.
Pulmonary sanatoriums
Immunity strengthening and sanitation of bronchial tubes are important components of basic treatment and rehabilitation of bronchial asthma. Rest with the child in the pulmonary sanatorium would be an excellent option for improving health. You can go to rest at any time of the year. Choose a sanatorium should be based on the profile of services provided.
In Russia, there are a great many different health resorts that treat and rehabilitate babies with asthma. Usually they are located in close proximity to the sea or in the beautiful pine forests. The air in such places has a pronounced therapeutic effect on the respiratory organs. Trips to the pulmonary sanatoriums are usually designed for 21 days.
Young patients with disabilities due to bronchial asthma with severe bronchial obstruction can get free accommodation and treatment in such health centers. Usually vouchers are issued every year. During treatment in a sanatorium in a child, indicators of external respiration improve, and immunity is restored.
Prevention
In order for the child not to have new bouts of the disease, you should follow a few simple recommendations:
- Regular use of properly selected inhalers to relieve seizures.
- Compliance with a hypoallergenic diet.
- Conducting daily wet cleaning of the children's room.
- Careful selection of bed linen, mattress, pillows and blankets. They should not be made of materials that can cause allergic reactions in the baby.
- Implementation of rehabilitation activities in the interictal period.
- Exception from the daily life of all possible allergens.
- Regular visits to the pulmonologist and allergist.