Treatment of diathesis on the cheeks in a child
Diathesis at an early age happens in many babies. Its most typical manifestation is skin lesions on the cheeks of a child. Why can the baby's cheeks turn red, can it be prevented and how to act when the redness has already appeared?
Symptoms
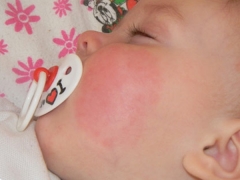
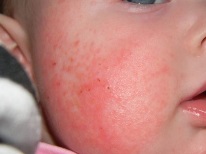
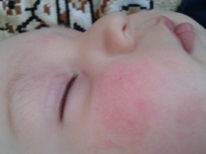
The diathesis on the cheeks appears reddish spots of different sizes. They, as a rule, strongly itch and give the baby great discomfort. This can disrupt the infant's sleep, as itching gets worse at night. Manifestations become more pronounced if the child is in hot and dry conditions. Also, redness may increase with the introduction of complementary foods.
Symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, rashes in other parts of the body, and diaper rash can also be associated with manifestations on the skin of the cheeks. At the age of 1 to 3 years, diathesis can also be manifested by coughing, sore throat, impaired stool, nausea, rash on different parts of the body. In children older than 3 years of age, diathesis on the cheeks is rare.
Kinds
Damage to the cheeks during diathesis can be:
- Dry - cheeks are red, flaky, itchy, covered with crusts.
- Weeping - cheeks become covered by intensely itchy blisters that burst and leave weeping wounds.
The reasons
Redness of the cheeks are a manifestation of diathesis, due to the tendency of the body of the baby to allergic reactions. Such a tendency may occur with a genetic predisposition of the baby, excessive consumption of pregnant allergen products, infections during gestation and many other factors that can affect the immunity and digestion of the baby.
In infants of the first year of life, diathesis on the cheeks is most often triggered by food in the diet of a nursing mother, allergies of crumbs to milk or lactose, the onset of feeding with juices and store puree. Children 1-3 years old red cheeks are after eating vegetables and fruits of red, citrus fruits, as well as cereals. In children older than 3 years, reddening of the cheeks may appear when eating chocolate, seafood, fish, peanuts, pickled and salted foods.
How to treat?
In some cases, the redness of the baby's cheeks passes without medical treatment, provided that the allergenic products are excluded from the diet of the mother and toddler. However, most children have to prescribe therapy, including not only diet, but also drugs.
Children are prescribed antihistamine drugs, drugs for dysbacteriosis, antibiotics (if the infection has joined), various local drugs. You can bathe the child in herbal decoctions, make lotions, lubricate the cheeks with various creams and ointments.
Diet
Feeding a child with diathesis should be given maximum attention. In the menu karapuza should not be products for which the child had a reaction in the form of red cheeks. Other allergen products should be given to the baby very carefully by writing to a food diary.
Possible strong allergens with which it is desirable for a child to meet peers later are:
- Cow's milk (whole).
- Cereals containing gluten.
- Red fruits, berries and vegetables.
- Citruses.
- Nuts
- Cocoa.
- Mushrooms
- Seafood.
Very carefully in the diet of the baby enter these products:
- Chicken.
- Fish
- Orange vegetables and fruits.
- Bananas.
- Legumes
- Cheese.
- Eggs
- Dried fruits.