Hemophilia in children
Such a serious disease, such as hemophilia, is inherited and is manifested by frequent bleeding and hematomas. Why does it appear in a child, how can it be detected and can it be cured?
What is it?
Hemophilia is a disease in which a person often and long-term bleeding occurs.
The reasons
The disease is genetically transmitted from parents to children. The disease manifests itself predominantly in men because it is associated with the transfer of a gene that is linked to the X chromosome. Women with such a transfer of the gene become carriers.
In girls, hemophilia can appear extremely rarely - if the father is sick, and the mother has the disease gene. Also, in some patients, hemophilia is not detected in relatives. Scientists explain the disease in them by gene mutations.
A gene that is afflicted with hemophilia is responsible for blood clotting, in particular, for the presence in the child's blood of certain substances involved in coagulation (they are called coagulation factors).
Taking into account which factor is missing, the following types are distinguished:
- hemophilia A is the most common and is associated with the absence of factor VIII;
- hemophilia B - for this type, there is no factor IX in the child’s body;
- hemophilia C is the rarest type that is now referred to as coagulopathy.
The symptoms of all these pathologies are the same, however, determining the type of the disease is very important for treatment.
Disease progression
Due to the absence of a specific coagulation factor, the process of formation of a blood clot is disturbed when the vessels are damaged. In this case, hemorrhage in hemophilia is represented by the hematomatous type, which is delayed.
Immediately after the vessel is damaged, blood platelets are responsible for blood coagulation, forming a primary blood clot. However, this thrombus cannot stop the bleeding completely, and since the formation of a final thrombus is impossible due to the lack of the necessary clotting factors, the bleeding is resumed and lasts for a rather long time.
Depending on the severity of hemophilia, it can be:
- light - bleeding appears only in case of injury and medical procedures);
- moderate - hematomas are extensive, the disease manifests itself in childhood);
- severe - the disease is detected in the neonatal period).
Symptoms
The main symptoms of hemophilia in a child are:
- Bleeding
- Hematomas.
- Hemarthrosis.
The disease is primarily manifested by excessive bleeding. A patient periodically has bleeding of different localization. A feature of such bleeding is their inconsistency with the severity of the damaging factor, as well as the appearance over time, and not immediately after the injury. Due to such bleeding during dental and other medical procedures, as well as injuries, the child loses a lot of blood. If bleeding from the gums or from the nose begins, then the usual methods can hardly stop it.
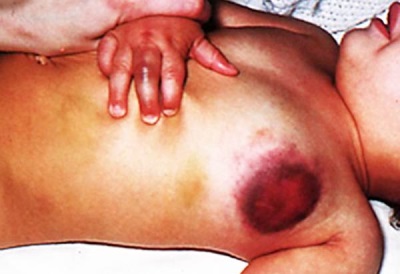
With a slight injury in patients with hemophilia, large hematomas appear. The blood in them for a long time does not thicken. It is also very common for children to develop hemarthrosis (bleeding inside the joints), in which the joint swells, hurts, ceases to function. In most cases, the knee, elbow, and ankle are affected.
The disease is often accompanied by indigestion. Blood may be present in the urine and feces of hemophilia patients.
In children of the first months of life, the disease often manifests itself in the form of cephalhematome - hematomas appear on the head and can occupy a large area.
Another symptom that occurs in newborns is bleeding from the umbilical cord. Moreover, in most infants, hemophilia may not manifest at all, since blood clotting during the first months of life is provided by the substances found in the breast milk.
Complications
The disease is especially dangerous with the sudden appearance of bleeding in the tissues of the brain or spinal cord, as well as hemorrhages in other important organs. With a severe form of the disease in 10% of newborns appear cerebral bleeding, threatening their lives.
Also among the complications of the disease include the appearance of chronic pain, arthropathy, contractures, anemia, pseudotumor. Hematomas can squeeze arteries, nerves, intestines, causing necrosis, sensitivity disorders, obstruction and other problems. In case of retropharyngeal bleeding, the baby may suffocate.
In addition, a patient with hemophilia is constantly at risk of contracting diseases transmitted through blood, because he is forced to receive drugs from donor blood.
Diagnostics
- Anomaly can be diagnosed before the baby is born.
- In a newborn, the idea of the presence of hemophilia may be caused by prolonged bleeding from a cut umbilical cord, as well as the appearance of hematomas.
- In older children, suspicion can be caused by frequent bleeding from the nose, extensive hematomas during a fall, non-absorbable bruising for a long time, and the appearance of hemarthrosis in large joints.
To identify hemophilia, adults are asked about family genetic diseases, and laboratory tests are carried out, among which are blood clotting tests.
The first studies will reveal the lengthening of the clotting time in the normal prothrombin and thrombin tests. After them, clarifying analyzes are performed, which determine the level of coagulation factors.
Treatment
For the treatment of hemophilia, the replacement of the missing clotting factors is used. With the help of an injection into the patient's blood they inject factors that are not produced by him. Drugs are made from donor blood. With type A disease, it is possible to transfuse fresh blood, since factor VIII is destroyed during prolonged storage. For treatment of type B, canned blood can be used, since the ninth factor is not destroyed during storage of the donor material.
If a child develops hemarthrosis, depending on its severity, prescribe rest and immobilization, hematoma puncture or surgical treatment.
Probability of transmission by inheritance
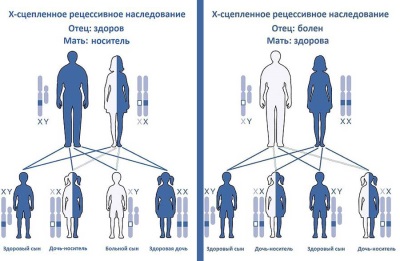
If the mother is healthy, and the father has hemophilia, then in such a family all the boys will be healthy, and all the female children will become carriers of the disease gene.
If the father is healthy, and the mother has a hemophilia gene, then the sons can be both healthy (if the son gets a healthy X chromosome) or sick (if the son has an X chromosome with the disease gene). Daughters in such a family can be either completely healthy or become carriers of the disease-causing gene.
Care Tips
Although the disease cannot be cured, thanks to proper therapy, the health of people with hemophilia can be maintained at a satisfactory level. All children who have been diagnosed with hemophilia are put on dispensary registration. Their parents are told about the features of patient care, as well as how to provide first aid to the child for bleeding.
It is important to create all the conditions for the normal development of the baby, as well as to prevent bleeding. Children with this disease can not work physically, so you should focus on intellectual work.
Do not confuse hemophilia and hemophilic infection, from which children are vaccinated at an early age. These are different diseases and vaccines for hemophilia does not exist. As for vaccination with hemophilia, it is not canceled, but rather recommended. However, injections to a sick child can only be done subcutaneously.