Hemorrhagic vasculitis in children: from symptoms to treatment
Hemorrhagic vasculitis is a disease that occurs most often in childhood. It can be a serious danger to the life and health of the child.
What it is?
Hemorrhagic vasculitis in children is quite widespread, and therefore the establishment of such a diagnosis a child should not be considered something out of the ordinary. The disease has several names - synonyms. Often it is called the disease of Schönlein-Henoch or allergic purpura. Sometimes there is such a name as capillary toxicosis.
The disease refers to hemorrhagic ailments. This is an allergic vasculitis, during which small blood vessels are damaged, which is manifested by a characteristic rash of a rich red color. Most often the disease affects children aged 5 to 14 years. In infants up to the age of three, the ailment is rarely diagnosed; only isolated facts are known to medicine.
Causes
Why hemorrhagic vasculitis develops, science is not known for certain, but studies have shown that the nature of the disease is mixed - infectious and allergic. A certain seasonal pattern has been observed: more often children fall ill in the cold and wet season - in the fall, in the winter and in the early spring. Since no precise reasons have been established so far, only the main predisposing factors that can lead to inflammation of the blood vessels and point hemorrhage to the skin can be identified.
- Infections. Most often, vasculitis occurs in a child who has recently suffered an acute respiratory infection. Not any rhinitis or bronchitis results in a hemorrhagic lesion. Hemolytic streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli were found in patients with vasculitis in the washes from the nose and pharynx. It is believed that the likelihood of hemorrhagic vasculitis is higher in children who have had adenovirus infection, herpes viruses of the first and second types.
- Medication. Sometimes the disease develops while taking certain medications. There is no exact list of them, but most of the registered cases of the disease occurred against the background of the administration of antibiotics of the penicillin group, the group of macrolides, against the background of the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs for arrhythmia. It is known that vaccines that are administered to children during vaccinations can also be a provoking factor, although the risk is only when the vaccine is given almost immediately after suffering an acute respiratory viral infection or flu.
- Allergy. The disease is more susceptible to children with allergies. In this case, the forms and types of allergies can be different - from food to allergies to cold. And these reactions can also manifest themselves in different ways - from a cold to rashes and eczema.
- Other reasons. There are external and internal factors that are believed to increase the likelihood of developing vasculitis in a child. This is freezing and hypothermia, or, conversely, too long exposure to sunlight, insect bites, skin injuries, diabetes mellitus in history, the presence of malignant tumors, severe liver disease.
In 65% of cases, it is not possible to establish the exact cause of the disease. Doctors believe that for the development of the disease should be a genetic predisposition. Genetics do not reject this assumption.
How is it developing?
The disease is of immune origin. It is believed that a disease occurs due to the fact that immune complexes are formed in the blood of a child, the activity of some proteins in the blood increases, the task of which is to repel the attacks of foreign organisms - viruses, bacteria. Proteins that belong to the complement system, are activated excessively and begin to move in the patient's blood.
At the same time, they somehow begin to be deposited from the inside on the walls of small blood vessels (venules, capillaries and others), gradually causing their damage. Local inflammation develops at sites of damage. The walls are becoming thinner, flawed. They begin the deposition of protein fibrin and thrombotic masses.
It affects not only the skin, but also the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the kidneys and joints.
Kinds
A disease always has three periods - initial, acute, and subsiding. The classification is based on the severity of the clinical course.
- Rheumatoid or articular form - the defeat of the large joints of the legs, accompanied by edema and point hemorrhages, while the functions of the joint itself are not impaired.
- Dermatoreumatoid form (skin and articular in the complex) - a red dot rash appears around the joints of the hands and feet, on the inside of the thighs, as well as on the face and pope. The development of joint deformity is not excluded. Red blood points can also be found on the mucous membranes.
- Dermatological (skin) form - red spots are formed only on the skin, and more often on the hands and feet. It happens more often in children as an allergy, as well as after SARS and flu.
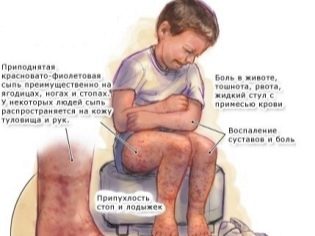
- Abdominal (abdominal) form - pains around the navel, the skin of the child is pale, his eyes sunk, children look very thin. Diarrhea is peculiar, blood may be admixed in the form of streaks in the liquid stool. Development of abdominal hemorrhage is not excluded.
By duration, acute vasculitis is distinguished, which lasts up to two months, and also protracted - lasting up to six months. Chronic forms of systemic vasculitis usually last more than 6 months.
By the nature of the course there are three degrees of the disease:
- easy - the rash is not extensive, the general condition of the child is satisfactory;
- average - a state of moderate severity, a rash plentiful, extensive, joints are deformed, there are all signs of arthritis on the background of hemolytic vasculitis, a stomach ache, red blood cells can be detected in the urine;
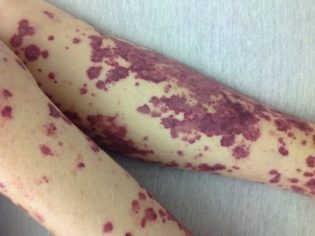
- heavy - A serious condition, an extensive rash, in some places they are combined with areas of necrosis, swelling of the throat, limbs, renal failure, a large amount of blood in the urine, stomach bleeding.
We should also note the vasculitis of the umbilical vessels in newborns. In this case, the symptoms of punctate hemorrhage are observed in the area of the umbilical wound.
Sometimes parents call any of these ailments hemorrhoidal vasculitis. This is an erroneous name. Hemorrhoidal veins (in the rectal area) usually do not suffer from systemic vasculitis.
Symptoms and signs
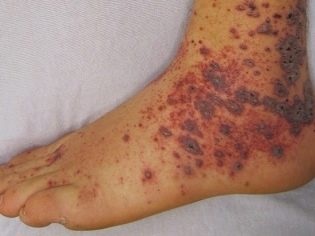
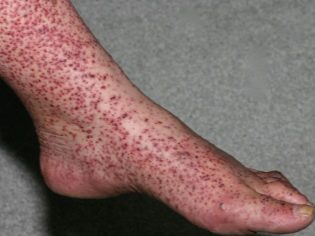
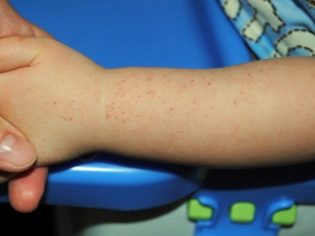
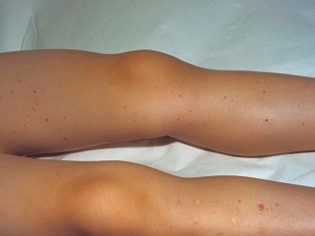
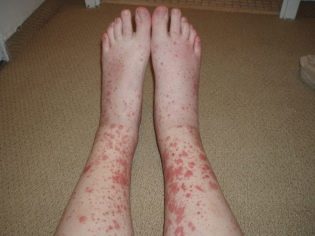
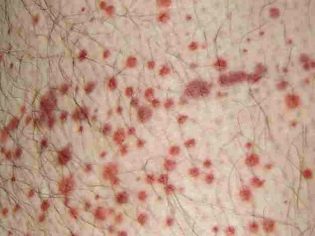
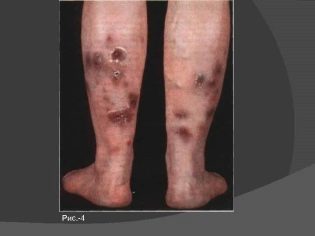
Allergic purpura in children usually begins with an increase in body temperature. The thermometer can show 37.0 degrees with a little, and 38.0 degrees or even higher. In some children, the temperature remains normal. Guessing the presence of vasculitis can be on the very first and surest sign - a characteristic red rash. It is spotted, the papules are usually small, if you press them with your finger, they do not disappear anywhere.
Another important distinguishing feature is the relative symmetry of the rash. It can be found on both shins, on both thighs, on two hands, around two identical joints (for example, knees). Less commonly, a rash appears on the body. If the disease is severe, foci of a necrotic nature, ulcers, form in the center of the papules.
The joints ache and suffer to varying degrees in 7 out of 10 patients. Such lesions can be short-lived, and after a few days everything goes away, and can be similar to arthritis. In this case, they swell up, hurt a lot, their mobility is significantly limited. The joints may fall ill at the initial stage, or maybe a little later.
The abdominal form of the disease is accompanied by complaints of the child in the abdominal pain, the rash may appear later, and may develop simultaneously with the pain. The nature of the pain may be moderate or severe, resembling intestinal colic. Disorders of the kidneys occur in every third sick person. You can determine this by the appearance of blood in the urine.
Other internal organs suffer less frequently. There are several cases of hemorrhagic pneumonia when a child has a cough with sputum with blood streaks, as well as several cases of hemorrhagic meningitis, when a hemorrhage has occurred in vessels of the brain membranes.
Possible complications
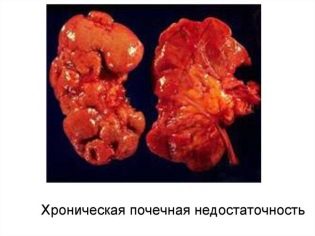
The most dangerous consequence of hemorrhagic vasculitis is persistent and irreversible kidney damage, manifested by renal failure. Internal bleeding is also dangerous - gastric, pulmonary, cerebral. The more blood loss from the affected vessels, the worse the predictions. But modern medicine can prevent many complications, reduce the risk of their development even in severe illness.
Lethal outcomes are possible, but mainly in rapidly developing forms of severe vasculitis, the so-called "fulminant".
Diagnostics
The diagnosis and treatment is provided by a rheumatologist. He will be helped by a nephrologist, if the child has impaired kidney function, a gastroenterologist and a surgeon, if the form of the disease is abdominal. Establishing a diagnosis of great difficulty is not on the external clinical picture, but the confirmation and features are determined after the following studies.
- Hematologic tests - complete blood count, in which there is an increase in the content of leukocytes and ESR, platelet growth, a large number of eosinophils, as well as biochemical blood tests. A coagulogram is also performed - an analysis of blood clotting factors to determine fibrin and a number of other characteristics.
- Urine test for the presence of blood, cylinders, protein.
- Fecal examination for hidden blood.
Also do ultrasound of the kidneys, stomach. In the case of a severe disease, a skin and kidney biopsy is performed.
Treatment
A child with acute forms of hemorrhagic vasculitis is shown bed rest and a special diet - you can not eat anything that even in theory can cause an allergic reaction. Water and salt are given in limited quantities.
In any form, blood thinning drugs are shown., for example, "Pentoxifylline", as well as fibrin disintegration activators - nicotinic acid. Heparin may be prescribed. This treatment helps to establish normal blood circulation, eliminates the likelihood of microthrombus formation.
When pain in the joints is recommended anti-inflammatory topical treatment. With the defeat of the kidneys use hormones - glucocorticosteroids, cytotoxic drugs.
Although the disease is generally considered to be allergic, use of antihistamines is considered ineffective.
But they are recommended for children with allergies, so as not to burden their condition, along with enterosorbents.
Projections for hemorrhagic vasculitis are ambiguous: light forms pass on their own, almost “on their feet”, without any consequences for the health of the baby. With severe and rapid form, death may come in a day. Transferred severe forms may require lifelong treatment, which will include the need for a kidney transplant, if your own fail.
Prevention of hemorrhagic vasculitis is quite complicated, because the true causes are not obvious. Parents are advised to treat the ENT organs for the child in time, and make sure that he does not have helminthic invasions. You should also avoid taking medication without prescribing a doctor and contact with strong allergens.
Reviews
According to parents, hemorrhagic vasculitis in children requires quite a long treatment - many spent in the hospital with a child from 4 to 8 weeks, until the manifestations of the disease disappeared completely.
The main thing, moms say, is to follow all the recommendations of the doctor, not only during therapy, but also after it, because life after vasculitis is closely related to dietary restrictions and medications.
More information about the treatment of hemorrhagic vasculitis can be found in the video below.