Brain cyst in newborns and infants
When making any diagnoses related to formations in the brain, parents have many different questions. Knowing the manifestations of such diseases in infants is very important. This will help prevent life-threatening conditions later on. Many parents are interested in brain cyst in newborns and infants.
What it is?
Cysts in the brain are cavities. Do not confuse them with tumors, they are completely different diseases. The cyst does not mean that the child has cancer. Various effects can lead to the development of this condition.
In some cases, cysts in the brain are not detected throughout life. The child grows and does not even suspect that he has any changes. In other situations, cysts cause the appearance of various symptoms that bring discomfort to the baby and disrupt his health. Such cases require treatment.
As a rule, a cyst in appearance resembles a ball. The size of education may be different. The contour of the cyst is regular and even. In some cases, the examination found several entities. They can be located at a considerable distance from each other or side by side.
Usually, one out of every three out of ten babies born doctors diagnose cerebral cysts. They appear in different places. In the cavity of the cyst is fluid. The small size of the formation, as a rule, do not cause any discomfort in the child.
If the cyst is not located near the vital centers, then this development of the disease is not dangerous.
The reasons
Various factors can lead to the appearance of cystic formations in the brain. In some cases, they can act together. Prolonged or severe exposure to various causal factors contributes to the appearance in the brain of various cavitary formations.
The most common reasons for their occurrence include:
- Various congenital pathologies. Usually they develop in the period of prenatal development. Pathologies of development of the central nervous system contributes to the development of pathological changes in the brain. Cysts in this case are congenital.
- Injuries received during childbirth. Too large fruit, the birth of twins contribute to the occurrence of traumatic brain damage in newborns.
- Infectionsarising from the mother during pregnancy. Many viruses and bacteria are able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Doctors often register brain cysts in newborns as a result of infectious diseases that have arisen during pregnancy. Viral or bacterial meningitis often the root cause of the formation of cavities.
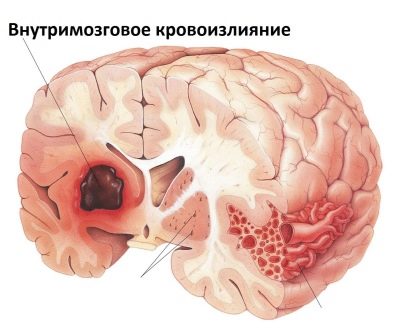
- Cerebral hemorrhage. May occur as a result of various causes. Often, various injuries and falls lead to the development of hemorrhage. Brain damage contributes to the formation of a cavity filled with fluid, which then becomes a cyst.
Kinds
The impact of various causes leads to the formation of cavities in the brain. They can be localized in its various departments. Currently, doctors have identified several possible localizations of brain cysts.
Given the location, all cavitary formations can be divided into several groups:
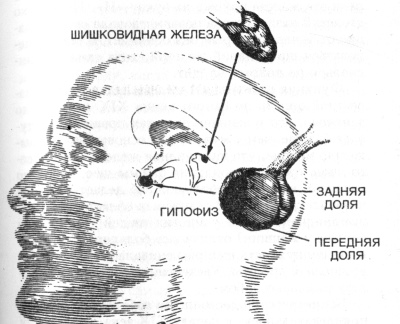
- Located at the level of the pituitary gland. Normally, this section of the brain is responsible for the synthesis of the elements necessary for the growth and development of hormones. When cysts appear in the child, various symptoms begin to appear. Usually without symptoms in this clinical form is not complete.
- Cerebellar. It is also called lacunar cyst. These types of cavitary formations are most often formed in boys. They are quite rare. With the rapid course of the disease can lead to the appearance of various motor disorders.
Mandatory treatment is required, as serious complications can occur - in the form of paralysis or paresis.
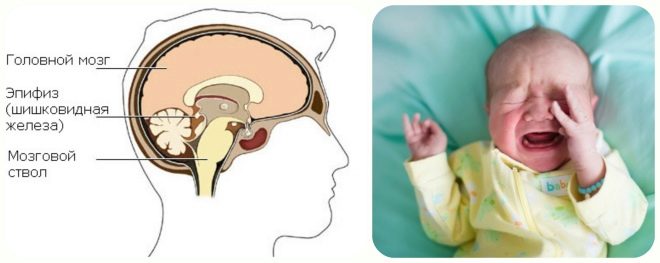
- Located next to the pineal gland. This organ is called the epiphysis. It performs in the body endocrine function. The epiphysis is well supplied with blood, especially at night. Violations in his work lead to a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which ultimately contributes to the development of cysts.
- Arachnoid. Located in the arachnoid membrane. Normally, it covers the brain outside and protects it from various injuries. Most often, this type of cyst occurs as a result of injury or inflammation of the meninges due to infectious diseases.
- Dermoid. Revealed extremely rare. They are registered in babies in the first year of life. Inside the cyst is not a liquid component, and the remnants of embryonic particles. In some cases, you can find the beginnings of teeth and bones, various elements of the sweat and sebaceous glands.
- Vascular plexus cysts. Arise in the period of prenatal development. Most often, these cavities are registered already at the 28th week of pregnancy. After birth can stay for a lifetime. Usually the child has no adverse symptoms, everything proceeds without any clinical changes.
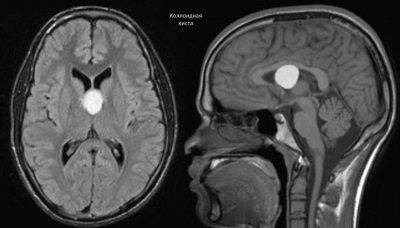
- Interstitial cysts. Located in the crease of the pia mater, which is located in the zone of the third ventricle of the brain. Often detected only by magnetic resonance imaging.
- Pseudocyst. Inside the cavity is spinal fluid. The disease is usually asymptomatic. The child does not change health and behavior. In some cases, there are several pseudocyst, which is a consequence of polycystic.
- Subarachnoid. Located in the subarachnoid space. Often occur after various traumatic brain damage or after car accidents. May occur with the appearance of adverse symptoms. With severe course of the disease and the rapid growth of education, surgical treatment is carried out.
- Cysts in the ventricle of the brain. Located in the cerebral collectors of cerebrospinal fluid. Most often, these cysts are formed in the zone of the lateral ventricles. The rapid growth of the formations leads to symptoms of intracranial hypertension.
- Subependymal. The most common cysts in infants of infancy. Inside the formations is the cerebrospinal fluid. Abdominal formation occurs due to hemorrhages under the membrane of the brain and rupture of blood vessels. Usually, this condition occurs during birth trauma. They can be of various sizes - from 5 mm to several centimeters.
- Retrocerebellar. Formed inside the brain, not outside, like many types of cysts. The formation of the cavity occurs as a result of the death of the gray matter. Various provoking causes may lead to the development of this type of cyst: trauma, infectious diseases, hemorrhages, and others. Such cavitary formations usually proceed quite hard and require treatment.
- Parencephalic. This condition is extremely rare in children's practice. Characterized by the formation of several cavities in the brain - of various sizes.
Symptoms
The manifestation of clinical signs depends on the initial localization of the cavity formation. If there are several cysts, they are located in different parts of the brain, then a child may develop a variety of symptoms that make diagnosis much more difficult.
The most common clinical manifestations of cystic formations include:
- Headache. It can be different in intensity: from easy to unbearable. Pain is usually the maximum after waking up or active games. To identify this symptom in babies of infancy is a difficult task. It is worth paying attention to the behavior of the child, which changes significantly with the appearance of a headache.
- Change the state of the baby. In some cases, the child becomes more inhibited. He has increased drowsiness, there are pronounced problems with falling asleep. In children, the appetite is getting worse, they are sluggishly applied to the chest. Sometimes babies completely refuse breastfeeding.
- Increase in head size. This feature does not always appear. Usually the size of the head increases with the expressed size of cysts. If a child has such abnormalities, an additional examination is required to exclude abdominal formations in the brain.
- Strong pulsation and bulging of fontanel. Often this symptom is the first sign of a cavity in the brain, which has already led to the appearance of intracranial hypertension.
- Movement disorders and coordination disorders. Usually, these unpleasant clinical signs appear in the presence of a cavity formation in the cerebellum of the brain.
- Vision disorders. Often, when looking at closely spaced objects, the child appears double vision. This pathological condition arises as a result of squeezing by a growing cyst of the optic nerve.
- Disruption of sexual development. It occurs as a result of the presence of a cyst in the pineal gland - the pineal gland. Violation of hormone production leads to a pronounced lag of the child from age norms. In some cases, the opposite situation occurs - excessively early puberty.
- Bouts of epileptic seizures. This condition appears when a cyst occurs in the area of the meninges. To eliminate the adverse symptoms, a special treatment is required, and in some cases even surgery.
Diagnostics
It is rather difficult to suspect the presence of a cyst in the brain of a newborn baby. To establish the diagnosis requires additional examinations. These studies are conducted on the recommendation of a pediatric neurologist. If the development of a cyst was preceded by injury or brain damage, then you should consult a neurosurgeon.
For the diagnosis of cavitary formations use:
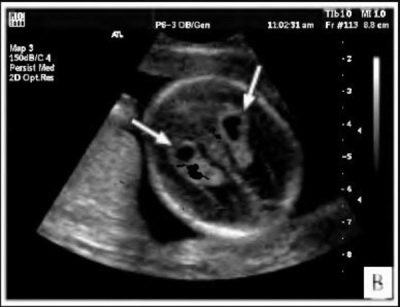
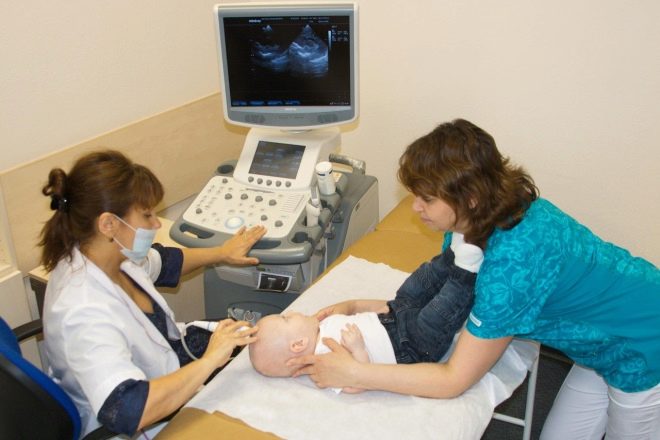
- Brain ultrasound. In neurology, it is also called neurosonography. This method is quite safe and can be used even for babies in the first months of life. From the survey there is no pain. 15-25 minutes is enough to determine the diagnosis.
- Computed tomography (or CT). The study gives a high radiation exposure. It should not be performed for screening cystic formations. This method is used only in difficult clinical cases where diagnosis is difficult. The study provides a complete picture of the abnormalities and anatomical defects present in the brain.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI). Feedback after this study is very positive. In most cases, it was with the help of MRI that it was possible to establish the presence of cystic lesions in the brain. The method has a high resolution and allows you to successfully identify cysts, even the smallest size.In complex diagnostic cases, they resort to the preliminary introduction of contrast, which makes it possible to establish the diagnosis more accurately.
Effects
Usually, cysts are asymptomatic and do not require intervention from doctors. However, in some cases with adverse localization, complications and consequences of their presence in the brain can occur. Neurologists deal with the treatment of such conditions. When it is impossible to conservative treatment resort to performing surgical operations.
The most common complication of abdominal cavities in the brain (especially in newborn babies) is a lag in physical and mental development in the future. In some cases, the child has visual and motor (motor) disorders.
One of the complications is also a congenital or acquired hearing loss - due to the presence of a cyst in the brain.
Treatment
The pediatric neurologist makes up the tactics of treatment - after the child has revealed signs of cystic formations in the brain. Usually babies are observed in such doctors throughout their life. Regular examination allows you to control the growth and development of cysts.
It is possible to treat cystic masses in the brain conservatively and with the help of surgical operations. The choice of therapy remains with the attending physician. No one will operate the infant immediately. First, a waiting tactic is applied. The doctor assesses the well-being of the child using special diagnostic methods. If there are no violations in the child’s behavior, then there is no need to perform the operation. Usually, conservative therapy is reduced to the appointment of drugs that have a symptomatic effect.
With increased intracranial hypertension, diuretic and vascular medications are prescribed. They help to improve the outflow and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid - and thus lead to a normal increased intracranial pressure.
If a cyst has arisen after bacterial meningitis, then the prescription of antibacterial drugs is required. In some cases, they are prescribed in the form of injections or droppers. Treatment of such forms of the disease is usually carried out in the hospital. After recovery from an infection, as a rule, the cyst that is formed changes significantly in size. After a while, it can completely dissolve and disappear.
If the child has an immunodeficiency state, immunostimulating drugs are used. They are appointed by the course, often as intramuscular injections. Typically, this treatment is combined with the appointment of multivitamin complexes. Combined therapy helps to improve the immune system and leads to recovery.
When traumatic injuries of the meninges or after some birth injuries, doctors are forced to resort to the appointment of surgical treatment. Usually operations are performed at an older age. Newborns and babies only watch. If the course of the disease is swift, and the adverse symptoms substantially disturb the child's well-being, then the decision on the need for surgical treatment can be made earlier.
You will learn about brain cyst in the next video.