Lactase deficiency in children (lactose intolerance)
A condition caused by the inability of the child’s body to digest lactose (milk sugar) is called lactose intolerance. Since the cause of this condition is the lack of the enzyme lactase in the body, the second name is “lactase deficiency”. What are the causes of this pathological condition and what should parents take if it is detected in a baby?
In newborns and infants
In newborns, lactase deficiency is usually genetically determined. To a greater extent, such congenital intolerance develops in carriers of Asian genes. Also in children younger than 6 months lactase deficiency is associated with an infection, allergies or other diseases associated with bowel disease.
Often lactase deficiency is detected in premature babies, as a result of the immaturity of their digestive tract.

In older children
Most often lactose intolerance develops in older children by the age of 9-12. In babies who are no longer breastfed, the amount of lactase in the body gradually decreases. Although among Europeans there are a lot of people in whose body lactase is normally produced until old age.
Among grown-up children, many do not tolerate milk sugar and do not suffer from it at all. They simply do not use dairy products to avoid the symptoms of intolerance. But for a young child, such a pathological condition can become a problem, since milk is the staple food at an early age.
Signs and symptoms
Hypolactasia (insufficient amount of lactase) can be identified by the following symptoms:
- Stomach ache.
- Nausea.
- Flatulence, bloating, rumbling in the stomach.
- Diarrhea, appearing one to two hours after drinking dairy products.
- Restless behavior after eating.
Classification
There are such types of lactose intolerance:
- Congenital A very rare condition in which a child loses weight quickly after birth, suffers from dehydration and risks dying. To confirm the diagnosis requires a biopsy of the intestine, but it is rarely prescribed to newborns, more often simply transferring the baby to a lactose-free diet for 4-6 months, after which they give the baby lactose in small quantities.
- Transient. Occurs in children who were born before the due date.
- Primary. Develops after feeding breast milk. This form of lactose intolerance is quite common. It is characteristic of people living in Asia, America, Australia, as well as on the African continent and islands in the Pacific Ocean. This is related to the nutritional history of people, because in the past people used animal milk mainly in European countries, in some parts of Africa and India. Such lactase deficiency is manifested by bloating, nausea, belching, diarrhea, vomiting. Symptoms may change throughout life. Someone reacts to a small amount of lactose, and someone is able to absorb more.
- Secondary. Appears as a result of intestinal lesions infection, allergies or other causes. For example, after gastroenteritis It takes the body several days or weeks (depending on age) to restore lactase production.
- Functional. Appears in a healthy child who is gaining weight, but is tormented by gases, frequent watery stools with a greenish tint. Analyzes that detect lactase deficiency in these children will be false-positive. The cause of this problem is the lack of crumbs from the back (rich in fats) of breast milk, as well as the still immature enzyme system.
Depending on the severity of the pathology, lactase deficiency is complete and partial.

Whether it is allowed breastfeeding with lactase deficiencyread in another article.
The reasons
The cause of lactase deficiency in newborns (the primary form of deficiency) is often a genetic predisposition.
The following causes lead to the development of the secondary form of this pathology, which is acquired:
- Inflammatory processes in the small intestine.
- Infected infections.
- Surgery on the stomach and intestines.
- The presence of celiac disease.
- Chemotherapy.
- Ulcerative development colitis.
- Crohn and Whipple diseases.
Here are the processes that occur in the body in case of problems with the digestion of lactose:
- Not digested lactose enters the large intestine, where water is also supplied by osmosis.
- This milk sugar is processed by bacteria that are found in the large intestine, resulting in the formation of gases.
- In the stool, undigested fatty acids appear, which are also formed as a result of the activity of bacteria.
- The mucous membrane of the intestine is irritated, which leads to an excess of mucus production.
- Since the feces pass through the intestines too quickly, its color becomes green.
- The result will be sour, frothy, greenish, loose stools, the research of which will reveal sugar (not digested lactose).
Differences between lactose and lactase
The similarity of the name often leads to confusion between these two words:
- Lactose is an important carbohydrate for the child, represented by the combination of two molecules - galactose and glucose.
- In order for the body to break down and digest it, it needs lactase. It is an enzyme formed in the small intestine.

If lactase is not enough, then lactose splitting does not occur, that is, it is not digested. That is why this condition can be called both lactase deficiency and lactose intolerance.
It is not allergic to milk.
Lactase deficiency is often confused with the development of allergies to dairy products. But these are completely different problems. Milk allergy is much less common with lactose intolerance and is a more serious condition with a risk of death.
If the baby has an allergy to milk, then it is contraindicated for him to use this product. Once in the body, even in small quantities, the milk will cause the baby to develop rashes, itching, difficulty breathing and other allergy symptoms.
But with a lack of lactase, the body is able to process a dairy product in a small amount, for example, if you drink milk in an amount of 100 ml at one time or eat yogurt up to 50 grams.
What to do?
If the baby has a greenish stool, it is fluid and frothy, the mother of the baby in breastfeeding is recommended:
- Ensure that the child is correctly attached and the breast is captured correctly.
- Try to feed for three to five hours from only one breast.
- Since often in this case, the mother has a lot of milk, the second breast at this time will have a little podtsezhivat.
We advise you to read the article about baby green feces.

Treatment of lactose intolerance is usually reduced to the exclusion of this disaccharide from the diet or to the use of drugs containing lactase. At the same time, the symptoms are treated and the cause is eliminated (if lactase deficiency is secondary).
Breast-fed babies Lactase preparations are often prescribed, as it is undesirable to reduce the amount of breast milk in a baby’s diet. If such drugs cannot be used, the child is transferred to a low-lactose mixture (first, partially, keeping the maximum of breast milk in the diet of the baby, which will not cause symptoms of lactase deficiency).
When feeding a baby with a mixture Such a product is selected in which there will be a maximum amount of lactose that does not cause clinical manifestations of deficiency. You can combine the usual mixture and lactose-free or transfer the crumbs to the sour milk mixture. If the lactase deficiency is significant, the child is given only a low-lactose mixture.
In the preparation of complementary foods for a child with lactase deficiency, it is not milk that is used, but a lactose-free mixture, and after a year dairy products are replaced with low-lactose analogues.
If hypolactasia is secondary, then a low-lactic diet is kept during the period of treatment of the underlying pathology. Products with lactose injected gradually over 1-3 months after recovery.
We recommend to see list of lactose free mixtures.
Required tests
There are several ways to determine the presence of intolerance to milk sugar:
- Coprogram. The analysis determines the amount of fatty acids, as well as the pH reaction. If there is lactose intolerance, the reaction of feces will be acidic, and the concentration of fatty acids will increase.
- Identify carbohydrates in feces. Most often used to identify lactose intolerance, but often false-negative or false-positive. The method reveals carbohydrates, but can not show exactly what is milk sugar. Its results are taken into account only in conjunction with other analyzes and clinical manifestations.
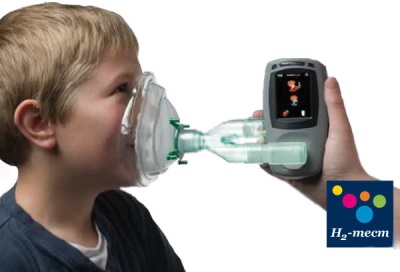
- Hydrogen breath test. A very common method is to use a special device that checks the air exhaled by a person after consuming glucose. The test is not used for children under 3 months.
- Lactose curve. Blood sampling is done on an empty stomach in the morning, then lactose is used and after a few hours a blood test is performed again. Based on the results build a graph, which is called the lactose curve. The method is not very informative, and its use in an infant poses some difficulties.
- Intestinal biopsy. This is a very accurate method for making a diagnosis of lactase deficiency. It consists in taking small areas of the mucous membrane of the small intestine. On these microscopic sites determine the activity of lactase. The method is rarely used because of its trauma and the need to use general anesthesia.
- Genetic research. Helps determine primary failure. The disadvantage of the method is its high cost.
How to live with it?
The prognosis in people with this pathological condition is usually favorable. Most of those who can not tolerate milk sugar, do not consume dairy products at will (not wanting questions, they say that they simply do not like them).
Lactose is not in such products:
- Vegetables;
- Vegetable oils;
- Pasta;
- Rice;
- Fruits;
- Raw fish;
- Eggs;
- Honey;
- Raw meat;
- Vegetable and fruit juices;
- Nuts;
- Cereals;
- Legumes;
- Soy drinks, soy meat and bean curd;
- Tea.
Recommendations for lactose intolerance:
- On sale you can find milk in which there is no lactose. Sugar in this milk is already split into galactose and glucose, so this dairy product can be consumed with lactase deficiency.
- If there is lactose intolerance, you should eat more of those dairy products in which this carbohydrate is already fermented. Such products are hard cheeses, yoghurts and other dairy products.
- Chocolate milk is a good choice, as cocoa has the ability to stimulate lactase production, which improves milk absorption.
- Milk with lactase deficiency is recommended to drink with meals. Excellent if milk is combined with cereals. The volume of servings of milk at one time should be up to 100 milliliters.
- Remember that milk sugar is present in skimmed milk. In such milk, fat is removed, not lactose.
- Lactose is available not only in milk, but also in other products - products for diabetics, confectionery, sauces, bread, margarine, cream, condensed milk, chips and many others. Even if the list of ingredients is not written that the product contains lactose, the presence of this carbohydrate can be judged by other components - the presence of milk powder, whey or cottage cheese.
- You should also be aware that lactose is included in some medicines. Milk sugar can be found in nope, bifidumbacterin, motilium, cerukale, enape, contraceptive and other drugs.
- Lactose is one of the important components of nutrition for children. It must be added to the milk mixture, in order to bring their composition to women's milk.












