Symptoms and treatment of cystic fibrosis in children
In newborns and infants, various inherited diseases are often recorded. The course of some of them is very difficult and dangerous for the development of long-term consequences. These pathologies include cystic fibrosis.
What it is?
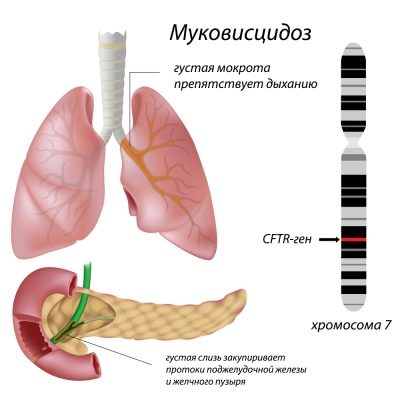
Congenital abnormalities in which congenital malfunctions occur in the work of different groups of endocrine glands are called cystic fibrosis. If translated from the Latin language, the name of the disease will be literally translated as "Thick mucus". This is a very capacious description of the essence of this congenital pathology. All glands that are responsible in the body for the formation of a secret (mucus), are not working effectively.
This feature is due to the presence of a persistent anatomical defect in the body, which arose at the stage of the birth of a small life in utero. The disease has a clear hereditary tendency. In families where children with cystic fibrosis are born, heredity is manifested quite clearly.
The disease develops quite hard. Exacerbations of the disease require compulsory treatment in the hospital with the introduction of various drugs. The first unfavorable symptoms of the disease in some cases appear already in children up to a year. They impose a significant imprint on the psyche of the baby, significantly disrupting their overall well-being.
Violations in this disease are formed at the genetic level. These changes are passed on from generation to generation. Most often, these disorders are associated with the presence of specific mutations that have occurred in the genetic apparatus. As a result, the work of all the endocrine glands is disrupted. They begin to produce a rather viscous secret that stagnates in the lumen of the organs and causes numerous disturbances in their work.
It is important to note that thick mucus is an excellent nutrient medium for the development of various microorganisms, including pathogens. This feature provokes an increased susceptibility to bacterial or viral infections in sick children. Reduced immunity only contributes to the rapid spread of pathogens throughout the body for a short period of time.
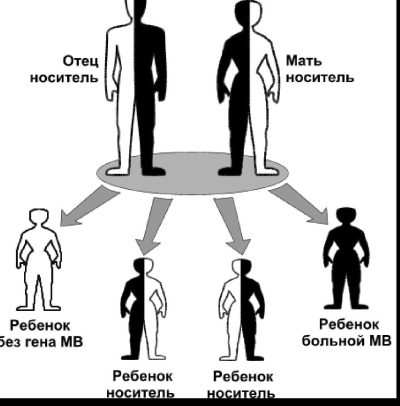
Scientists note that if both parents have the genes for a given disease, then the pathology may develop in a baby with a probability of 25%. It is not always the child can get sick. He may be a carrier and not at all aware of what is carrying such a damaged gene. In the future, he can pass it on to his children and grandchildren. Sometimes the disease develops after one generation.
To establish the presence of an atypical gene is possible only by conducting diagnostic tests. To detect cystic fibrosis in the carrier by external signs is impossible.
There is evidence that in the world there are more than ten million people who have the genes for cystic fibrosis. They do not even suspect the presence of this disease.
Causes of
Genetic damage leads to the development of the disease. They contribute to the violation of the outflow of secretions from the organs that produce it. The severity of the disease may be different. For most babies, the disease is quite severe. Lack of treatment can lead to life-threatening conditions and cause life-threatening consequences.
In some cases, the first adverse symptoms of the disease can be seen already in infants. They usually appear in the first few months after the baby is born.
The long course of the disease leads to a pronounced lag of the baby in physical and mental development from the indicators of the age norm.
Interestingly, officially registered cases of the disease are much higher in Europe and America. This can be explained by the presence of the best diagnostic tests and devices that allow to detect the disease at the earliest signs. In Russia, over the past few years, the diagnosis of this pathology has become much better. However, in some regions of the country, the disease is still detected by doctors rather late.
Clinical forms
Given the predominant localization of changes, doctors identify several variants of the disease. They can occur in babies in different ways and are accompanied by the appearance of specific clinical symptoms. Their severity depends on the initial state of the baby and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases of internal organs.
There are several clinical variants of the disease:
- Pulmonary form. Adverse symptoms of the disease begin to appear in the first months after the birth of the baby. This pathology is accompanied by impaired functioning of the respiratory, digestive and reproductive systems. Pulmonary variant of the disease occurs in approximately one in five children suffering from cystic fibrosis. A whole range of diagnostic procedures is used to diagnose the disease, including chest X-ray and laboratory tests.
- Intestinal form. Found in children's practice extremely rare. According to statistics, not more than 5% of all cases are recorded. This form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic symptoms associated with digestive disorders in children. Usually detected in infants with the introduction in their diet additional supplements.
- Mixed form. The most common option in children's practice. Accompanied by the combined lesion of almost all the endocrine glands. It provokes the appearance of numerous adverse symptoms of the disease. Treatment of exacerbations is carried out in the hospital with the use of specialized expensive drugs.
Some specialists also identify several forms of a genetic disease. These include the following options:
- atypical;
- erased;
- hepatic;
- electrolyte;
- with obstruction of meconium.
In 80% of cases, a mixed form of the disease is recorded. It is most difficult at all ages. To eliminate the adverse symptoms of the disease is very important timely diagnosis and preparation of the correct tactics of treatment. Treatment of exacerbations in this case is a hospital task. All babies with a genetic predisposition to the development of this disease must be observed at the doctor. Different clinical forms of the disease cause the child to have numerous adverse symptoms.
Most often, the first signs can be seen in a baby in the first months after birth. After their discovery, parents should immediately show the child to the doctor. The doctor will be able to establish the correct diagnosis and suggest the appropriate treatment regimen.
Symptomatology
Clinical manifestations can be truly different. Many of them appear at a very early age. However, some symptoms develop gradually. The course of the disease usually progresses. In some cases, the disease is aggravated by the addition of complications.
Among the most characteristic symptoms of the disease are the following:
- The development of meconium obstruction. It occurs in approximately 20-25% of cases. In this case, the intestine becomes blocked with meconium. In a healthy child, after birth, meconium (first stool after birth) comes out on its own.In babies with cystic fibrosis, this does not occur.
- The appearance of "salty" taste of the skin. Usually, this symptom is detected by parents of newborn babies when they kiss a child. Impaired gland function leads to the fact that the chemical composition of body secrets is changing. They increase the number of sodium chloride ions, which contributes to the appearance of a specific taste.
- Lag in physical development. Often develops in children with a long-term current disease. Typically, sick kids do not gain weight. It is important to note that their appetite is completely preserved or reduced slightly. Persistent deviations from the age indicators of the norm often accompany cystic fibrosis.
- Jaundice. Usually this symptom is characteristic of many newborn babies. However, it passes on their own and does not require the appointment of specialized treatment. In babies with cystic fibrosis, jaundice can be persistent. To eliminate this condition, complex treatment is required.
- Excessive stickiness and viscosity of all biological secretsproduced by the secretory glands. The presence of such mucus in the lungs provokes persistent productive cough. When joining a secondary bacterial infection in a baby, bacterial bronchitis or pneumonia may occur. Treatment of such conditions is usually long with the appointment of large doses of antibiotics.
- Violation of nasal breathing. The sticky secret contributes to the development of chronic rhinitis in the child - a cold. Most often this symptom manifests itself in babies with a mixed form of cystic fibrosis. Application in this case, the usual vasoconstrictor drops for the nose does not bring a pronounced positive effect.
- Impaired digestion. Usually manifested by pain in the abdominal cavity and a violation of the chair. In the intestines of babies suffering from cystic fibrosis, various "putrefactive" microbes easily settle. Their rapid development leads to the development of persistent pathological disorders. This is often manifested by constipation or diarrhea.
- Soreness after taking fatty and fried foods in the left hypochondrium. This symptom occurs due to the development of chronic pancreatitis, which occurs in intestinal and mixed cystic fibrosis.
- Dyspnea and development of breathing malfunctioning.. A prolonged and severe course of the disease can lead to the appearance of symptoms of respiratory failure in a child. This feature is extremely unfavorable. Normalization often requires hospitalization of the baby in the hospital.
- Changing child behavior. Such a serious disease will certainly cause some violations in the mental development of the baby. Typically, children suffering from cystic fibrosis learn worse and poorly learn the course of the school program. The exacerbation of the disease causes a marked deterioration in the child's well-being. He becomes nervous, whiny, refuses any contact.
- Some paleness of the skin. Attentive parents will notice that the skin of a baby with cystic fibrosis becomes pale. Some babies have pronounced signs of excessive dryness of the skin. They are easily exposed to any traumatic effects and can often suppurate.
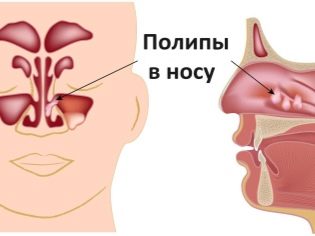
- The growth of polyps in the nose. Often occurs as a remote consequence of the disease. It is registered mainly in adolescence. Rapidly growing polyps in the nasal passages can significantly impede nasal breathing, which also contributes to the deterioration of the child's well-being.
- Excessive dryness in the mouth. Violations in the glands lead to the fact that significantly disrupted the process of formation of saliva. This contributes to the appearance of difficulties in the child with the ingestion of food, especially solid. This condition causes a decrease in appetite and body weight.
Diagnostics
To determine the presence of positive signs of the disease can be already at 8-12 week of fetal development of the baby. You can also suspect the disease by screening.
To establish the diagnosis, a special DNA examination is carried out, allowing the baby to detect the presence of the mutant cystic fibrosis gene.
In complex diagnostic cases, reanalysis is required. This is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. In addition to laboratory tests, doctors study the features of family history. They conduct a genetic survey of the parents of the sick child, and also establish the likelihood of their having sick babies in the future.
For prenatal diagnosis, several tests are used:
- Quantitative determination of the level of trypsin in dry blood. Used as one of the diagnostic tests for cystic fibrosis.
- Sweat test. To do this, determine the amount of sodium ions and chlorine in the sweat. To this end, the baby is pre-performed electrophoresis with the introduction of pilocarpine. This chemical can activate the sweat glands. The test can be conducted to all babies older than a week from the moment of birth.
- Carrying out coprogram. Allows you to establish the presence of functional disorders of the digestive system. A large number of undigested food components with a significant content of fat and muscle fibers indicates the possible presence of cystic fibrosis in the child. This laboratory test is not specific and has a secondary meaning.
- Conducting a comprehensive examination of the chest. These include: radiography, spirometry and physical auscultation. In the presence of wet cough, sputum bacteriological examination is also carried out. Such a complex of diagnostics helps to exclude bronchopulmonary diseases similar to cystic fibrosis.
Treatment
Unfortunately, there is no cure for cystic fibrosis. If the child has clinical signs of the disease, then you can only slightly reduce their severity. Therapy in this case is not aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, as this is impossible, but at reducing adverse events.
Nutrition plays a very important role in the treatment of this dangerous disease. It should be very high in calories. Usually, the total caloric content of a therapeutic diet for babies with cystic fibrosis is 10-15% higher than usual.
The emphasis in nutrition is on the inclusion of protein products. They may be of different origin.
The entry of high-quality protein into the daily diet of a sick child is very important. Various protein molecules are needed to build your own body cells. In childhood this is necessary, as it ensures the growth and development of the baby. In the food pyramid, the proportion of complex carbohydrates decreases slightly. Fats from the diet are not excluded. From the food should be removed all vegetables containing large amounts of unprocessed coarse fiber.
To preserve the water-electrolyte balance requires the mandatory use of a sufficient amount of water. As a drink, any fruit and berry compotes, fruit drinks or juices are suitable. For babies with signs of pancreatitis or suffering from an intestinal form of cystic fibrosis, too sweet liquids should be diluted with boiled water.
Drug treatment helps to cope with various functional symptoms of the disease. So, in case of enzymatic insufficiency of the pancreas, means are used to help eliminate this deficiency. These include: Pancreatin, Panzinorm, Creon other.
Drugs are prescribed taking into account the child’s age and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases of internal organs.
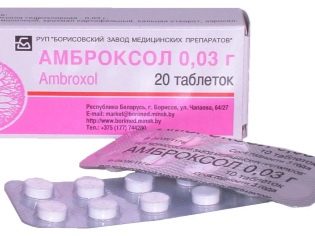
To improve breathing drugs are used with a bronchodilator effect. They help to remove sticky phlegm from the respiratory tract. These include: Ambroxol, Bromhexine, ACC, Fluivort other. They can be administered in the form of sweet syrups or tablets. In some cases, more indicated inhalation with the introduction of aerosol forms of existing drugs.
If a bacterial infection is attached that worsens the course of the disease, antibacterial agents are prescribed. Usually selected drugs from the group of cephalosporins or fluoroquinolones. They are assigned to the exchange rate. Treatment of bacterial complications is carried out in stationary conditions under the regular supervision of medical professionals.
Kids with cystic fibrosis should be in the dispensary at the doctors throughout their lives. The development of the disease requires regular and close monitoring. Usually, with adequate treatment of exacerbations of the disease, the course of this pathology is highly controlled.
Currently, the life expectancy of babies with cystic fibrosis has increased several times.
About what is cystic fibrosis, see the following video.