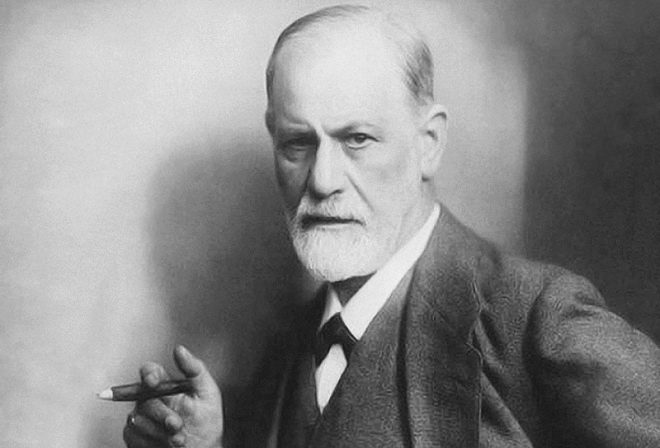Neuroses and tics in children
Childhood neuroses frighten and perplex parents, especially if such mental states are associated with the manifestation of tics. In search of causes and answers to their questions, adults bypass dozens of doctors, but it is often not possible to clarify the situation. The only thing that parents receive is a prescription for a psychotropic drug, which you don’t want to feed the child to adequate parents at all. In this article we will help you to understand what neurotic tics are connected with, what are the causes of neurosis and how to help a child without heavy medications.
What it is?
Under the concept of "neurosis" hides a whole group of psychogenic disorders. The bad news for moms and dads is that all neuroses are prone to very protracted, chronic course. And the good one is that the neuroses are reversible, and in most cases the child can completely get rid of such states.
Due to the fact that children are not always able to tell with words that they are disturbed or worried, a constant nervous tension is transformed into a neurotic state in which disturbances are observed both on the mental and physical levels. The child's behavior is changing, mental development can slow down, a tendency to hysteria appears, mental activity suffers. Sometimes, internal tension finds a peculiar way out on the physical level - this is how nervous tics arise. They are not independent disorders and always appear on the background of a neurosis or a neurosis-like state. However, the neurosis itself may well proceed without tics. Here a lot depends on the child’s personality, his character, temperament, upbringing features, state of the nervous system and other factors.
Neurosis practically does not occur in infants, but then the frequency of such disorders in children begins to grow rapidly, and in kindergarten age neuroses in varying degrees occur in about 30% of children, and by the middle school age the number of neurotics increases to 55%. Neuroses are present in almost 70% of adolescents.
Nervous tics in the majority - a problem exclusively children's. Few in the world of adults who suddenly under the influence of stress began to suffer tick. But there are adults who have taken out neurotic tics from their childhood, because most often the violation is laid in childhood.
Ticks of various species are most common in children aged 5 to 12 years. About a quarter of all neurotic children suffer from certain tics. In girls, physical manifestations of nervous conditions are 2 times less than in boys of similar age. Experts attribute this fact to the fact that the psyche of girls is more labile, it undergoes age-related changes faster and goes through a period of formation.
Neurosis and tics are disorders of higher nervous activity. Modern medicine believes that these conditions contribute to the emergence of various diseases and pathologies. There was even a whole direction - psychosomatics, which studies the possible links of psychological and mental states with the development of certain diseases.
Thus, it is believed that hearing problems most often occur in children whose parents were too authoritarian and suppressed the child, and kidney disease is characteristic of children, whose moms and dads often conflict with each other and often insult their child verbally and physically. Since neuroses are reversible states, the task of parents to start the process of reverse development as soon as possible, and for this it is necessary to find the cause of the child’s condition and give up all efforts to eliminate it.
The reasons
Finding the causes of neurosis in a child is always a very difficult task.But if you look at the problem from a medical point of view, the search area is significantly narrowed. Neurosis, and consequently, neurotic tics, is always associated with the development of a conflict - internal and external. The fragile children's psyche with great difficulty can withstand many circumstances that do not seem out of the ordinary. But for children such circumstances are very difficult, causing psychological trauma, stress, overstrain of the intellectual, mental and emotional sphere.
Scientists and doctors are still arguing over how exactly the mechanism for the development of nervous activity is implemented. The difficulty of studying this issue is primarily due to the fact that the mechanisms are quite individual, unique for each child, because the child is a separate person with his fears, affections and ability to resist stress.
The most common causes of neurosis and neurosis-like states are:
- unfavorable situation in the family (scandals, quarrels, parents divorce);
- total mistakes in the upbringing of the child (hyper-care, attention deficit, permissiveness, or excessive severity and exactingness of the parents in relation to the baby);
- temperament of the child (choleric and melancholic are more prone to the development of neurosis than sanguine and phlegmatic);
- fears, phobias of the baby, with which he is not able to cope due to his age;
- overwork and overstrain (if the kid is not getting enough sleep, attends several sections and two schools at the same time, then his psyche is working “for wear”);
- psychological trauma, stress (we are talking about specific traumatic situations - the death of a loved one, the forced separation from one of the parents or both, physical or moral violence, conflict, severe fright);
- doubts and concerns about safety in the future (after moving to a new place of residence, after transferring a child to a new kindergarten or to a new school);
- age “crises” (in periods of active reconfiguration of the nervous system and psyche - at 1 year, at 3-4 years, at 6-7 years, during puberty - the risks of developing neuroses increase dozens of times).
Nervous tics develop in about 60% of pre-school age neurotics and 30% of schoolchildren. In adolescents, tics against neurosis appear only in 10% of cases.
The reasons for the development of involuntary muscle contractions for an erroneous command of the brain can also be different:
- postponed disease (after severe bronchitis, reflex cough may form in tick, and after conjunctivitis, the habit may persist in blinking often and often);
- mental shock, a situation that has caused tremendous psychological trauma (this is not about the long-term effects of stress factors, but about a specific one-time situation in which the nervous system and psyche of the child did not have time to “compensate” for the damage, because the effects of stress were many times stronger);
- desire to imitate (if a child observes tics with someone from relatives or other children in a kindergarten or school team, he can simply start copying them and gradually these movements will become reflex ones);
- aggravation of neurosis (if the negative factor that caused the neurosis does not disappear, but also increases its impact).
The true causes may remain unknown, since the field of the human psyche has not been sufficiently studied, and doctors cannot explain all the violations in the child’s behavior from a scientific point of view.
Classification
All childhood neuroses, despite the lack of scientific evidence on the causes and mechanisms of development, have a strict classification, designated in the international classification of diseases (ICD-10):
- neurosis obsessive states or thoughts (characterized by increased anxiety, anxiety, conflict needs and norms of behavior);
- fear neurosis or phobic neurosis (associated with a strong and uncontrollable fear of something, for example, fear of spiders or darkness);
- hysterical neurosis (destabilization of the child's emotional sphere, in which behavioral disorders, hysterical seizures, motor and sensory disorders occurring in a child in response to situations that the child considers hopeless are observed);
- neurasthenia (the most common type of illness in childhood, in which the child experiences a sharp conflict between the requirements for himself and the actual inability to meet these requirements);
- obsessive neurosis (a condition in which the child uncontrolledly makes certain cyclical movements with irritating methodic);
- food neurosis (neurotic bulimia or anorexia - overeating, constant feeling of hunger or refusal of food against the background of nervous rejection);
- panic attacks (disorders characterized by bouts of intense fear that the child cannot control and explain);
- somatoform neuroses (conditions in which the activity of the internal organs and systems is disturbed - heart neurosis, stomach neurosis, etc.);
- guilt neurosis (disturbances in the activity of the psyche and nervous system, which developed against the background of an agonizing and in most cases unjustified feeling of guilt).
Nervous transient tics that can develop on the background of any type of neurosis also have their own classification.
They are:
- Mimic - with involuntary repetitive contraction of facial muscles. These include facial tics, eyes, lips ticks and nose wings.
- Vocal - with spontaneous nerve contraction of the vocal muscles. A sound tick can manifest itself as a stutter, as well as an obsessive repetition of a certain sound, coughing. Voice tics are very common among children, especially preschool children.
- Motorized - while reducing the muscles of the limbs. These are twitching arms and legs, waving and bursts of arms, which are repeated often and have no logical explanation.
All ticks are divided into local ones (when one muscle is involved) and generalized ones (when a whole muscle group or several groups work during the movement). Also tics are simple (with an elementary movement) and complex (with more complex movements). Usually in children as a result of severe stress or other psychogenic causes primary tics develop. Doctors speak of secondary doctors only if tics accompany brain pathologies (encephalitis, trauma).
Quite rarely, but still there are hereditary tics, they are called Tourette syndrome.
It is not difficult to establish what kind of tiki in a child, it is much more difficult to find the true cause, including the connection with neurosis. And without this, full treatment is not possible.
Study history
The neurosis was first described in the 18th century by Scottish Dr. Cullen. Until the XIX century, people with neurotic and neurosis-like tics were considered obsessive. At different times, famous people stood up to fight obscurantism. Sigmund Freud explained the neuroses to the conflict between the true needs of the organism and the personality and the social and moral norms that have been invested in the child since childhood. He devoted a whole scientific work to this theory.
Academician Pavlov concluded, not without the help of his famous dogs, that neurosis is a disorder of higher nervous activity, which is associated with impaired nerve impulses in the cortex of the brain. The society has ambiguously perceived the information that neurosis is peculiar not only to people, but also to animals. An American psychologist Karen Horney in the twentieth century concluded that children's neurosis is nothing but a defensive reaction against the negative impact of this world.She suggested that all neurotics be divided into three groups - those who aspire to people, pathologically need love, communication, participation, those who try to distance themselves from society and those who act contrary to this society, whose behavior and actions are intended to prove to everyone that they can and much more successfully all the rest.
Doctors-neurologists and psychiatrists of our time hold different points of view. But in one they are in solidarity - neurosis is not a disease, rather, it is a special condition, and therefore its correction is both desirable and possible in all cases.
Symptoms and signs
Neuroses in children and possible accompanying tics have different symptoms, depending on the type and type of violation. However, all neurotic conditions are characterized by a group of signs that traces all children - neurotics.
Mental manifestations
Neurosis in no case can not be considered a mental disorder, since violations arise under the influence of external circumstances, whereas the majority of true mental diseases are associated with internal factors. Most mental illnesses have no sign of reversibility and are chronic, and neurosis can be overcome and forgotten about it.
With these mental illnesses in a child, there are increasing signs of dementia, destructive personality changes, and backwardness. With neurosis there are no such signs. Mental illness does not cause rejection in a person, the patient regards it as part of himself and is not capable of self-criticism. With neurosis, the child understands that he is doing something wrong, is not right, and this does not give him peace of mind. Neurosis causes inconvenience not only to his parents, but to himself, with the exception of certain types of ticks that the baby simply does not control, and therefore does not consider it significant.
You can suspect a neurosis in a child by the following changes:
- The mood of the child changes often., unexpectedly and without objective reasons. Tears can in a matter of minutes become laughter, and a good mood in a second can change to depressive, aggressive or otherwise.
- Almost all types of neurosis in children are characterized by pronounced indecision. It is very difficult for a child to make a decision on his own even just to decide which jersey to wear or which breakfast to choose.
- All children with neurotic changes experience certain communication difficulties. It is difficult for one to establish contacts, others feel pathological affection for the people with whom they communicate, others still cannot maintain communication for a long time, are afraid to say or do something wrong.
- Self-esteem of children with neurosis is not adequate. It is either overpriced and it cannot go unnoticed, or it is underestimated and the child does not sincerely consider himself capable, talented, successful.
- One and all children with neurosis from time to time experience bouts of fear and anxiety. And there are no objective reasons for alarm. This symptom can be expressed weakly - only occasionally the child expresses fear or behaves wary. It also happens that the attacks are pronounced, even panic attacks.
- A child with neurosis in any way can not decide on the value system the concepts of “good and bad” are somewhat blurred for him. His desires and preferences often contradict each other. Often a child even in preschool age shows signs of cynicism.
- Children with some types of neurosis are often irritable. This is especially characteristic of neurasthenics. Irritability and even anger can manifest themselves in the most simple situations of life - it didn’t work out the first time to draw something, shoelaces on shoes were untied, a toy broke.
- In children, neurotics almost no stress tolerance. Any little stress causes them to have bouts of deep despair or pronounced unmotivated aggression.
- Neurosis can talk excessive tearfulness increased touchiness and vulnerability.This behavior should not be attributed to the nature of the child, in normal these qualities are balanced and do not catch the eye. With neurosis, they hypertrophy.
- Often baby fixes on the situation that hurt him. If neurosis and tics were caused by the neighbour’s dog attack, the kid often experiences this situation again and again, fear grows and turns into a fear of all dogs in general.
- The performance of a child with neurosis is reduced. He gets tired quickly, cannot concentrate his memory for a long time, he quickly forgets the previously learned material.
- Neurotic children hard to carry loud sounds sudden noises, bright light and temperature drops.
- With all types of neurosis observed trouble sleeping - it is very difficult for a child to fall asleep, even if he is tired, often the dream is restless, superficial, the baby often wakes up, does not get enough sleep.
Physical manifestations
Since there is a connection between neurosis and the functioning of internal organs and systems, a violation cannot but be accompanied by signs of a physical nature.
They can be very different, but most often neurologists and child psychiatrists note these symptoms:
- The child often complains of headaches, tingling in the heart, irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath and pain of obscure origin in the abdomen. At the same time, medical examinations for the search for diseases of these organs and areas do not reveal any pathologies, the child’s tests are also within the normal range.
- Children with neurosis are often lethargic, sleepy, they have no power to perform any action.
- Children with neurosis have unstable blood pressure. It rises, then goes down, and there are bouts of dizziness, nausea. Often doctors make a diagnosis - vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- In some forms of neurosis, vestibular disorders are observed in children.difficult to balance.
- Problems with appetite peculiar to the vast majority of neurotics. Children may be malnourished, overeat, have a practically constant feeling of hunger or, on the contrary, almost never feel strong hunger.
- In children with neurotic disorders unstable chair - constipations are replaced by diarrhea, vomiting often occurs without any particular reason, indigestion quite often occurs.
- Neurotic very are sweating and more often than other children, they run to the toilet for little need.
- Often accompanied by neurosis idiopathic cough, having no valid reason, in the absence of any pathologies on the part of the respiratory system.
- When neurosis can occur enuresis.
In addition, children with neurosis are more susceptible to acute viral infections, catarrhal diseases, they have weaker immunity. In order to conclude whether a child has a neurosis or prerequisites for its development, it is necessary to evaluate not one or two separate symptoms, but a large list of signs of both physical and psychological properties together.
If more than 60% of the above mentioned symptoms coincide, you should definitely make an appointment to see a doctor.
Manifestations of ticks
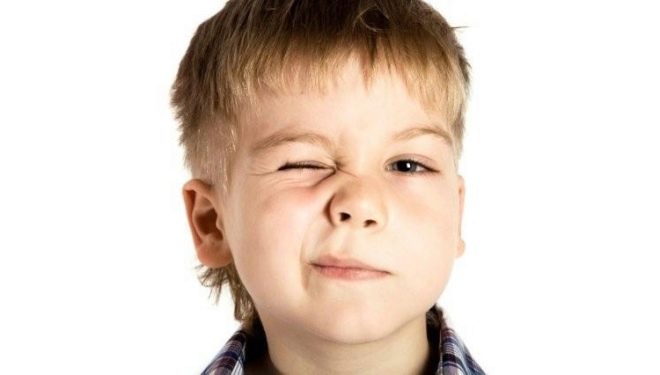
Nervous tics are noticeable to the naked eye. With primary ticks, all involuntary movements are local in nature. They rarely spread to large muscle groups. Most often, the child’s face and shoulders are involved (blinking, lip twitching, swelling of the wings of the nose, shrugging).
Tics are not noticeable at rest and only increase when the child is in a stressful situation.
The most common primary disorders are manifested as:
- blinking;
- walking in a closed circle or in a straight line here and there;
- gnashing of teeth;
- bursts of hands or strange movements of the hands;
- winding hair strands on a finger or pulling out hair;
- strange sounds.
Hereditary and secondary tics usually appear in a child closer to 5-6 years. They are almost always generalized (involving muscle groups). They are manifested by blinking and grimaces, uncontrolled shouting curses and obscenities, as well as constant repetition of the same word, including that heard from the interlocutor.
Diagnostics
In the diagnosis of neurosis there is a big problem - overdiagnosis. It is sometimes easier for a neurologist to make such a diagnosis to a child than to search for the true cause of the violations. That is why statistics indicate a rapid increase in the number of neurotic children over the past few decades.
Not always a child with poor appetite, sleep disorders or mood swings is neurotic. But parents require help from a specialist, and the doctor has no choice but to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. After all, it is incredibly difficult to refute the diagnosis of "neurosis", and therefore no one can blame the doctor for incompetence.
If a child’s neurosis is suspected, it is not enough for the parents to visit the local neurologist alone. It will be necessary to show the child to two more specialists - a child psychiatrist and a psychotherapist. The psychotherapist will try to make the most of the psychological situation in which the child lives; for children of middle and high school age, the method of hypnotic sleep can be used. This specialist pays special attention to relations between parents, between parents and a child, between a child and his peers. If necessary, a series of tests for behavioral reactions, analysis of the baby’s drawings, and research of his reactions during the game process will be carried out.
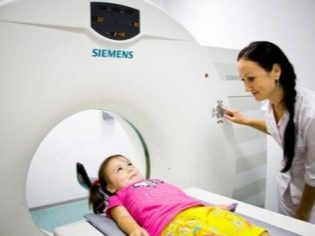
A psychiatrist examines a child for the connection of neurosis with impaired brain functions, specific tests will be used for this, an MRI of the brain can be prescribed. A neurologist is a specialist with whom the examination should begin and with which it ends then.
He summarizes the data obtained from a psychiatrist and psychotherapist, analyzes their conclusions and recommendations, assigns:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- radiography and computed tomography of the brain;
- electroencephalography.
The presence of neurosis as such can be judged in cases if:
- the child has not revealed any abnormalities in the brain or conduction of impulses;
- the child has no mental illness;
- the child does not have and has not had a head injury in the recent past;
- the baby is somatically healthy;
- neurotic manifestations recur for six months or more.
Treatment
The treatment of neurosis always begins not with taking pills, but with the correction of relations in the family where the baby lives and is raised. Psychologists and psychotherapists help in this. Parents should change their attitude towards the child, eliminate or correct their pedagogical mistakes, try to protect the child from severe stress, frightening and traumatic situations. Joint activities are very useful - reading, creativity, walking, playing sports, as well as the subsequent detailed discussion of everything that has been done, seen or read together.
If a child learns to formulate his feelings and emotions in a particular situation, it will be easier for him to get rid of traumatic memories.
A marriage that is bursting at the seams is not necessary to save for the sake of a child who has developed a neurosis about this. Parents should weigh well, as it will be better - without one of the parents who is scandalous, drinks, uses violence or with him.
However, it should be remembered that one parent, who is calm, self-confident, who loves and appreciates the baby, is better for the child than the two shaken and suffering parents.
Very much in the treatment of neurosis falls on the shoulders of the family. Without her participation, the doctor will not be able to do anything, and the pills and injections will not bring any result.Therefore, drug treatment is not considered the main type of therapy for neurosis. Neurologist, psychologist, and psychotherapist, who have interesting methods to help neurotic children, are ready to help their parents in their difficult task.
Types of therapy
In the arsenal of the psychotherapist and child psychologist there are such methods of correction of the baby's condition, like:
- creative treatment (specialist sculpts, draws and cuts together with the baby, at the same time talking to him and helping to sort out a complex internal conflict);
- pet therapy (treatment through communication and interaction with pets);
- play psychotherapy (classes according to special methods, during which the specialist will carefully observe and evaluate the child’s behavioral and psychological reactions to stress, failure, excitement, etc.);
- fairy tale therapy (understandable for children’s understanding and entertaining way of psycho-correction, which allows the child to adopt patterns of correct behavior, set priorities, determine personal values);
- autotraining (physical and mental relaxation method, excellent for teenagers and children of senior school age);
- hypnotherapy (method of correction of the psyche and behavior by creating new attitudes during immersion in trance. Only suitable for older children and adolescents);
- psychotherapist group classes (allow you to adjust the neuroses associated with difficulties in communication, in adapting to new conditions).
Good results are brought by classes in which children are present with their parents. After all, the main type of therapy for neurosis, which has no equal in effectiveness, is love, trust, and understanding between the child and his family members.
Medicines
Medicines for the treatment of simple and uncomplicated types of neurosis are usually not required. The doctor may recommend herbal preparations with a calming effect: «Persen, Pharmacy collection motherwort. The child as an aid can be given tea with melissa, mint, motherwort, make baths with the decoctions of these herbs.
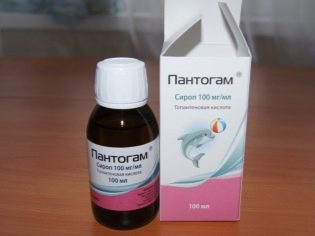
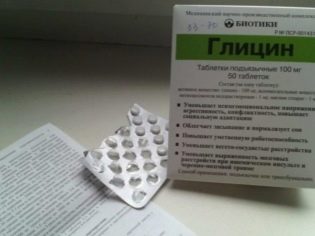
In some cases, the doctor prescribes nootropic drugs. «Pantogam», «Glycine». They require systematic and long-term use, because they have the accumulative property of action. To improve cerebral circulation prescribed «Cinnarizine» in the age dosage. If laboratory tests show a lack of calcium or magnesium in the child’s body, which also contributes to neurological disorders, the doctor prescribes accordingly. "Calcium gluconate" or its analogs, as well "Magnesium B6" or other magnesium preparations.
The list of drugs that can be prescribed for nervous tics is much longer. It may include antipsychotics and psychotropic drugs. A prerequisite for the appointment of such powerful and serious preparations - tics should be secondary, that is, associated with impaired activity of the brain and central nervous system.
Depending on the nature of tics and other behavioral features (aggressiveness, hysteria or apathy) "Haloperidol", "Levomepromazine", "Phenibut"," Tazepam ","Sonapaks». For strong, convulsive tics, the doctor may recommend Botox and botulinum toxin preparations. They allow you to "turn off" a specific muscle from the pathological chain of nerve impulses for a time during which this connection may cease to be reflex. Any medication for serious neurotic disorders must be prescribed and approved by a doctor, self-medication is inappropriate.
Most of the neurotic children are helped by drugs that contribute to the establishment of a normal sound sleep. After a few weeks, the child becomes more calm, adequate, friendly. Doctors do not recommend the use of strong hypnotic drugs for children's neurosis.It will be enough light drugs or homeopathic remedies like drops "Bayu-Bay", "Dormikind"," Little hare ".
Physiotherapy and massage
Massage is useful for all children with neuroses. It is not necessary to turn to the expensive services of specialists, because therapeutic massage for such violations is not shown. Enough will be a relaxing massage that any mother can do on their own at home. The main condition - not to do toning techniques that have the opposite effect - exciting and invigorating. Massage should be just relaxing. When carrying out such an impact, it is necessary to avoid pressing, tingling, deep kneading.
Relaxing effect can be achieved with gentle strokes, circular movements with hands without effort, light rubbing of the skin.
In the presence of nerve tics of a primary nature, additional massage techniques can be added for a place affected by involuntary muscle contraction. Massage of the face, hands, shoulder girdle should also be relaxing, non-aggressive, measured. It is enough to do a massage once a day, in the evening, before bathing. For kids, it is important that the massage gives them pleasure, so it is desirable to hold it in a playful way.
For secondary ticks, professional medical massage is required. It is better to turn to a good specialist who, in a few sessions, will teach the mother or father all the necessary techniques, so that they can then conduct the course treatment of the child on their own. Among physiotherapeutic methods, acupuncture is quite often and quite successfully practiced. There is no age limit for the method, however, provided that the child is somatically healthy.
Do not underestimate the effect of physical therapy. Children in 2-3 years may already attend such classes with their parents. A specialist in drawing up a lesson plan for a particular child will take into account all motor manifestations of neurosis, will teach special exercises that will allow you to relax and strain the necessary muscle groups in order to save the child from the manifestation of ticks.
A child with neurosis and tics will benefit from swimming. In the water of a child, all muscle groups relax, and the physical load on them during movement is uniform. It is not necessary to record the child in the professional sports section, it is enough to visit the pool once a week, and for the kids it is enough to take a swim in the large home bath.
About what treatment is recommended for this type of disorders doctor KomarovskySee the next video.
Prevention
Avoid the development of neurosis in a child will help measures that maximize prepare the child’s psyche for possible stressful situations:
- Adequate education. A child should not grow in greenhouse conditions so as not to grow up as a weak-willed and insecure neurasthenic. However, excessive severity and even parental cruelty can also disfigure the child’s personality beyond recognition. You should not resort to blackmail, manipulation, physical punishment. The best tactic is cooperation and constant dialogue with the child from an early age.
- Family well-being. Not so important, in the full or incomplete family grows baby. Of greater importance is the microclimate that prevails at home. Scandals, drunkenness, tyranny and despotism, physical and moral violence, swearing, shouts - all this gives fertile ground for the development of not only neuroses, but also more complex mental problems.
- The mode of the day and food. Supporters of the free regime are more often faced with neurotic disorders in their children than parents, who have taught the child to observe a certain daily routine since birth. Especially important is the regime for children of primary school age, who are already in a state of severe stress - the beginning of school requires their endurance and patience. Food for children should be balanced, rich in vitamins and all necessary trace elements.Fast food should be mercilessly limited.
- Timely psychological assistance. Just to protect the child from stress and negative effects on the psyche will not work, no matter how hard the parents. However, they should be sensitive enough to notice the slightest changes in the behavior and mood of their child, to react in a timely manner and help the baby to understand what happened. If your own strength and knowledge for this is not enough, you should contact a psychologist. Such specialists today are in every kindergarten, in every school, and their task is to help the child, regardless of his age, overcome a difficult situation, find the right solution, make an adequate and informed choice.
- Harmonious development. The child must develop in several directions in order to become a whole person. Children whose parents require only sports records or excellent study at school have a higher chance of becoming neurotic. Well, if a child combines sports with reading books, with music lessons. At the same time, parents should not exaggerate their demands and harass the child with their inflated expectations. Then failures will be perceived as a temporary test, and the experiences of the child about this will not overpower the compensatory abilities of his psyche.