Osteoporosis in children: symptoms and treatment
There are children who fall from a bicycle and a swing, play professional sports and do not get hurt, bruises and abrasions do not count. And there are children who are quite insignificantly hit or lose their balance, and they need to put another plaster. Often the cause of increased fragility of children's bones is such a disease as osteoporosis. In this material we will describe in more detail how to recognize it and how to treat it, as well as how to prevent the development of this pathology.
What it is?
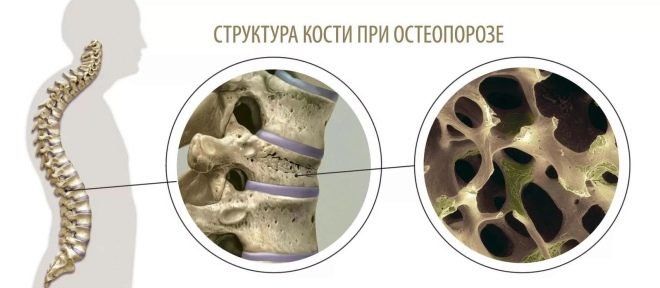
Osteoporosis is called a decrease in bone density. If an insufficient amount of calcium is deposited in the bones of the child, the metabolism is disturbed, the bone becomes more porous, more fragile. Even a minor injury can cause a fracture. The more pronounced the impairment of mineralization, the more severe can be traumatic fractures of bones and vertebrae.
The disease belongs to the category of diseases of the bone tissue. It is widely distributed in adults and the elderly. But in children it is mostly primary, it can develop for no apparent external reasons.
A child of any age can get sick - both a year and 2 years old, but most often, according to medical statistics, children from 8-10 to 14-16 years old suffer from osteoporosis. Doctors tend to see in this the effect on the bone metabolism of hormones, which are activated during puberty and shortly before it. Girls are sick more often than boys.
For a long time osteoporosis was detected already when a fracture occurred. Today, medicine has many diagnostic methods to determine the state of a decrease in bone mineralization even before a serious injury occurred.
Causes
Rarely, osteoporosis is congenital. It is due to genetic causes, hereditary features of the structure of bones. A child, in whose family older relatives often have fractures, is more likely to have a predisposition to osteoporosis or pre-existing problems with bone metabolism.
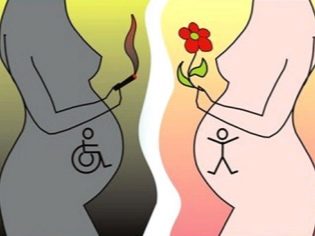
Fetal factors can affect the onset of osteoporosis at an early age - the harmful habits of a pregnant woman during a child's birth, the state of fetal hypoxia, the disease of a pregnant woman and various pathologies of the pregnancy itself. Osteoporosis is susceptible to children born from multiple pregnancies, as well as premature and low birth babies. The cause of osteoporosis in a child up to 3-5 years old may be a congenital violation of mineral metabolism and metabolism.
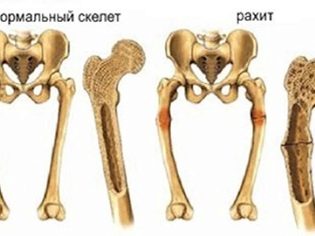
Vitamin D deficiency in the first year of life, the presence of diagnosed and confirmed rickets is a frequent and regular cause of osteoporosis in a child. Some pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, in which calcium absorption is impaired, can also serve as a starting mechanism for disruption of bone mineral density.
Juvenile (adolescent) osteoporosis can occur as a result of malnutrition, bad habits, systemic diseases, low physical activity, kidney and liver diseases.
Symptoms
The difficulty of osteoporosis lies in the almost complete absence of symptoms. Pain usually occurs when the bone structure is seriously damaged.
Parents and doctors may suspect this ailment in a child due to a number of characteristic and common signs:
- fractures and bone fractures occur frequently, for injuring a small enough impact on the bone;
- spinal curvature, posture change, limb curvature;
- lack of growth (a child with osteoporosis always grows much more slowly than his peers);
- excessive growth rates (children who grow too fast are also at risk for developing osteoporosis);
- the presence of asymmetrical skin folds on the body;
- inclination to caries;
- systematic headache, complaints of fatigue;
- dry skin, brittle nails and weak hair;
- propensity to convulsions.
If such symptoms are observed, parents should definitely visit the pediatrician and consult with him. Only a full range of laboratory and instrumental studies will help establish whether there is a basis for disturbances and anxieties.
Diagnostics
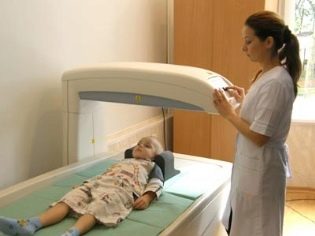
Radiography helps to establish changes in bone tissue. It shows the centers of bone thinning and suggests the presence of osteoporosis. But to establish the appropriate diagnosis of a single X-ray is not enough. Densitometry data is needed - only this study allows us to establish with great accuracy the fact of a decrease in bone mineral density.
Densitometry is carried out with the help of a special apparatus installed in a separate room. The study is considered safe and painless. Either by ultrasound or x-ray method, the doctor takes a “snapshot” of the bones, and a special program in the device calculates bone density. As a result, the doctor can tell if there is a violation of the mineralization, and how strongly it is expressed.
The biochemical blood test, which shows the quantitative content of calcium and other minerals in the blood plasma, complements the diagnostic picture.
Treatment
Most cases of acquired osteoporosis in children are successfully treated. With innate forms, things are somewhat more complicated, but they are not considered a sentence either. Treat the disease taken in a complex with the use of physiotherapy, gymnastics, correction of nutrition and drugs.
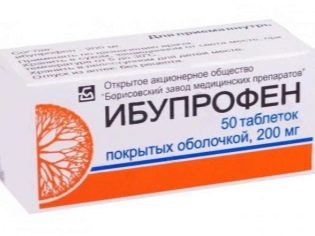
Of the medications prescribed painkillers, if the thinning of the bones in children is already manifested by pain. Most often, anti-inflammatory drugs with an anesthetic effect, such as Ibuprofen, are preferred.
Calcium and vitamin D3 supplements are considered obligatory, the doctor calculates the exact dosage based on the patient's age and the degree of mineralization impairment.
In severe cases, hormone therapy is recommended, aimed at the formation of new bone tissue, but due to the fact that hormones are used potent, modern doctors resort to such an appointment very rarely, when there is no other way to correct violations or osteoporosis continues to progress, despite therapeutic measures.
The child is prescribed a diet with a predominance of protein foods and foods enriched with calcium and phosphorus. Dairy and fermented milk products, fish, meat, fresh greens, eggs, peas and germinated cereals are recommended.
Gymnastics and physiotherapy are recommended after the bone tissue has already been slightly restored with drug treatment. Experts recommend practicing exclusively in the office of physical therapy under the supervision of a doctor, because improper exercises at home can cause injury. After 2-3 courses of physical therapy in the clinic, parents will be able to work with the child on their own.
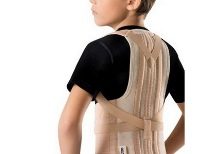
Teenagers with osteoporosis are advised to wear a special orthopedic corset, since their disease is more intense, even successful treatment does not guarantee that the posture will not continue to deviate from the norm.
Implications and predictions
The exact mechanisms for the development of osteoporosis in childhood are currently poorly understood, data are insufficient to state that the prognosis is favorable.Sometimes doctors encounter inexplicable childhood osteoporosis, which progresses despite the best efforts of doctors and parents. In such cases, prognoses are classified as doubtful, and the risk of disability resulting from severe vertebral or bone injury is high.
Timely diagnosed minor deviations in mineral density can be corrected until complete recovery. True, recovery time will take quite a lot: the treatment cannot be considered fast, sometimes it lasts for years.
Prevention
Prevention of osteoporosis should be dealt with even during pregnancy - to observe the recommendations of the doctor, not to smoke and not to take alcoholic beverages, to monitor the balance of nutrition. After birth, it is important to provide the baby with enough vitamin D to avoid rickets. The child must be given mandatory vaccinations, which are designed to protect against diseases whose complications can be osteoporosis.
The baby’s nutrition must be complete and sufficient; it must meet the needs of the growing organism in calcium and phosphorus. It is forbidden to arbitrarily assign diuretic drugs to the child and their long-term use, this often leads to a critical decrease in the level of calcium that is washed out with urine.
To prevent problems with bone tissue from childhood, it is necessary to harden and strengthen the musculoskeletal skeleton, to teach the child to play in the fresh air, to play sports.
Prolonged sitting at the computer or in front of the TV does not contribute to the formation of healthy bones and normal metabolism, including minerals.
About why children and adolescents develop osteoporosis, see the next video.