Prevention of rickets in children
Rickets is among those childhood diseases that are easier to prevent than to cure. About what should be the prevention of this childhood disease, we will discuss in this article.
Features of the disease
The occurrence of rickets is always closely related to the deficiency of vitamin D in the body. Calcium and phosphorus metabolism is also disturbed, which can lead to rather sad consequences - the child’s bones are deformed due to the lack of minerals, and the internal organs - the lungs, kidneys, heart, liver, and spleen - suffer. Vitamin D is synthesized in human skin when exposed to sunlight. If the sun is not enough, if the child was born in late autumn or winter, the likelihood of rickets increases. At risk and premature babies, they are deficient in vitamin D and calcium to a greater extent as they grow at a faster rate.
The disease always develops in early childhood - from 2-3 weeks of independent life of the toddler, sometimes later. The treatment of the disease is quite long. That is why it is important to know what measures will help protect the child from the disease.
Who needs prevention?
Not so long ago, it was believed that the prevention of rickets is needed by all children, without exception. Now the doctors have somewhat changed the approach to this issue. And preventive measures are prescribed and recommended only to certain children. Among them:
- Premature babies (faster growth requires more vitamin D).
- Children living in the northern regions, where the number of sunny days per year is small.
- Babies who for a number of reasons cannot feed on breast milk and are fed artificially.
- Crumbs, born of a multiple pregnancy.
- Toddlers for whom parents do not provide proper care for social reasons.
- Children born in winter or late autumn.
Thus, if the child was born on time with a normal weight, if the mother has no problems with lactation and the baby is gaining good weight, if they walk with it every day even in winter, they do not have much need for vitamin D.
Taking medications containing such a vitamin is “just in case” very dangerous, since it can lead to an overdose, the consequences of which may turn out to be much more serious than rickets itself.
Thus, to engage in prevention without the knowledge of the attending pediatrician in any case is not necessary. All preventive measures must be approved by a specialist who believes that the child has a real risk of getting rickets.
Preventive measures before birth
Long before the birth of a baby, a mother can take care of minimizing the risks of developing rickets in an unborn baby. To do this, it must be properly and balancedly fed, without fail including in its diet fish, meat, fresh greens, eggs, cottage cheese and dairy products. To maintain the correct balance of vitamins and minerals in your own body, and thereby provide the unborn baby with the right amount, you can take special vitamin and mineral complexes that are specially made for pregnant women. "Elevit", "Materna".
Women under 30 years old, starting from the 31-32th week of pregnancy, should take drugs with a vitamin D content. The dosage, which is daily required future mother - 400-500 IU. The dose can be increased in the event that the woman lives in the conditions of the north, works at hazardous production. While waiting for a child, you need to walk a lot and often in the open air, using the opportunity to stay in the sun to the maximum so that vitamin D deficiency does not occur.
It is important to attend a consultation, follow all recommendations of an obstetrician-gynecologist, donate blood and urine, including to determine the level of calcium and phosphorus in the body.
Non-specific preventive measures
After childbirth, you can start the prevention of rickets as soon as the mother and the child return home from the hospital. Non-specific prophylaxis involves a large range of measures aimed at the harmonious development of the baby and the formation of its immunity. It is especially important to adhere to all these rules if the baby is born prematurely.
A child to meet the need for vitamin D is enough 20-30 minutes to be on the street, if it is summer and sunny. Walking in the winter is also of great importance, however, the amount of sunlight received by the baby will be less - after all, there are practically no areas of skin that are not covered by clothes. The child’s immunity should be strengthened from the first days of his life. For this, doctors recommend cool baths (according to the method of Dr. Komarovsky), obligatory daily restorative massage sessions, gymnastics.
This does not require special knowledge in the field of medicine; any mother and even father can master such massage and gymnastics.
During the massage, light stroking movements, slight pressure, circular movements along the back and tummy are used. Gymnastics consists of simple exercises that are allowed by age, starting from putting on the tummy and ending in a few months with coups, bending and unbending the arms and legs of the child in the joints. After the baby is given supplements, you need to start giving the baby calcined curd. Be sure to visit the pediatrician every month.
Only a doctor is able to notice the warning signs of the possible development of rickets, prescribe additional diagnostic examinations. This will provide an opportunity to quickly begin treatment, thereby minimizing the possible consequences of rickets.
Specific preventive measures
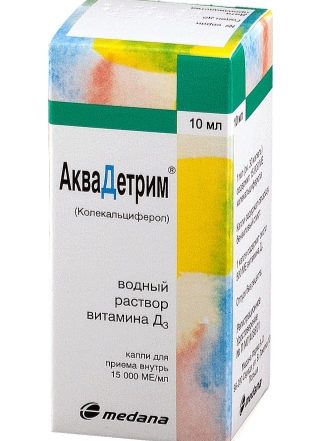
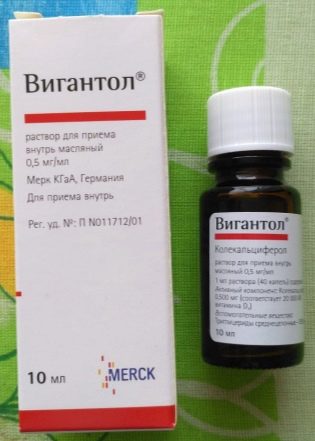
Specific prophylaxis includes taking prophylactic doses of vitamin D preparations («Akvadetrim», "Vigantol" other). For infants, the drug is prescribed at a dosage of 300-400 IU, for children after a year - 400-500ME. The dosage is very important to comply with, as an overdose of vitamin D causes serious consequences. Premature babies can have a prophylactic dose at the discretion of the physician, since the need for a drug for them is significantly higher than that of their peers who were born on time.
It should be remembered that taking vitamin D for prophylaxis only needs up to 3 years. And the last year (from 2 years to 3 years) vitamin give only from late autumn (from November) to early spring (until March).
Newborns and babies, as well as to the peanuts up to 2 years, the drug is prescribed systemically, throughout the year, breaks in the reception should be done only for the summer months.
A woman who is breastfeeding her newborn baby should also take vitamin D at a dosage of 400-500 IU. If the child is an artificialist, it is not necessary to feed him cow or goat milk, since the doses of calcium and phosphorus in these products do not meet the needs of the child’s body, calcium is leaching, and without it normal absorption of vitamin D is impossible.
To feed the baby is best milk formulas, which are fully adapted. This word is always indicated in the name of the food. After six months, the mixture that the crumb eats should be partially adapted (have the sequence number "2" in the title). The composition of these mixtures manufacturers in the required order of injected vitamin D. Refine how much, you can, after reading the composition of the mixture on the packaging.If the amount is not enough for the daily norm, with the permission of the pediatrician, you can add vitamin D to the desired amount.
Drug intake is also shown to children who have switched to complementary foods and supplements make up about two thirds of the daily ration.
Such drugs are not prescribed to children who have suffered hemolytic disease of the newborn, as well as children with congenital pathologies of the kidneys.
You can find out more information about rickets in children in the next release of Dr. Komarovsky’s program.