Causes and first aid for convulsions in a child
Cramps in a child is a rather dangerous symptom. Few parents know exactly what needs to be done in case of development of a convulsive syndrome in a baby. But it is the quality of first aid that in many cases determines the outcome of the situation. In this article, we will explain why babies and teenagers experience muscle spasms and how parents act during an attack.
What it is?
Cramps medical science calls muscle contractions that are not subject to the will, which are involuntary or spontaneous spasms. Quite often, such cuts are very painful, painful and cause the child suffering.
As a rule, convulsive syndrome happens suddenly. Sometimes it covers the whole body, sometimes - its separate parts.
Muscular spasms are different. Their classification is wide enough. All seizures are divided into epileptic and non-epileptic. The former are various manifestations of epilepsy, the latter may speak of other pathologies.
By their nature, convulsions are:
Tonic. When they muscle tension is long, long-lasting.
Clonic. With them, stress episodes are replaced by relaxation episodes.
The most common among young patients are mixed - tonic-clonic convulsions. In early childhood cramps occur much easier than in adults. This is due to the age-related features of the functioning of the central nervous system in general and the brain in particular.
According to the prevalence of seizures are divided into several types:
Focal. They are small muscle tremors in a particular part of the body. Often, such convulsions accompany a state of calcium or magnesium deficiency.
Fragmentary. These spasms affect individual parts of the body and represent involuntary movements of the arm or leg, eye, head.
Myoclonic. This term refers to the spasmodic contractions of individual muscle fibers.
Generalized. The most extensive of muscular spasms. With them, all muscle groups are affected.
Tendency to convulsions is called convulsive readiness. The younger the child, the higher his readiness. The child may react with muscular spasms to adverse effects from the outside, to poisoning, to high temperatures.
Sometimes cramps are symptoms of the disease. Very often, children experience a single episode of convulsive syndrome. After this convulsions are not repeated. But the child still needs very close observation. Doctors found out that the majority of adults with the established diagnosis of "epilepsy" had convulsive seizures in childhood. Whether there is a direct link between children's convulsions and the subsequent development of epilepsy is not completely clear, but the observation of a child who has survived one attack should be continuous and close just in case.
Symptoms and signs
Convulsions are always the result of pathological disorders in the brain. Recognizing generalized convulsions in which the entire body of a child is shaken by convulsions is not difficult. It is much more difficult to notice other forms of convulsive syndrome.
Fragmentary convulsions look like separate muscle trembling. Quite often it is preserved even in a dream.Even the loss of muscle tone, excessive relaxation, a scattered gaze, mumbling, numbness are also forms of cramps.
In some diseases, the child may lose consciousness during a convulsive seizure. So, for example, febrile seizures occur. But with tetanus cramps, the child, on the contrary, maintains clarity of mind, even with a strong generalized attack.
The development of an attack always occurs in a certain sequence. In different diseases and conditions, this sequence may be different. Sometimes it is she who allows you to establish the exact cause of muscular spasms.
A generalized seizure is characterized by a sudden onset. During convulsions, the child tightly squeezes the jaws, may roll his eyes. Breathing becomes heavy or frequent, may stop for a while. Integuments change color towards cyanosis - turn blue. In some cases, the sphincters relax and the child may be described or crap oneself.
And even though convulsions look frightening and instill panic in their parents, they do not carry much danger by themselves. Much more dangerous consequences if convulsive syndrome is frequent. It affects the development of the brain, mental and intellectual abilities.
If an emergency is rendered incorrectly, the child may suffocate in a fit, choke on vomitus, get fractures.
Mechanism of occurrence
To understand what exactly is happening with the child, you need to be clear about how muscle spasm is born and develops. Normal muscle movements are possible only with the coordinated work of the brain and nerve fibers. The stability of this connection is provided by a variety of substances - hormones, enzymes, trace elements. If at least one of the links in this process is disrupted, then the transmission of a nerve impulse occurs incorrectly.
So, the wrong signals from the brain, overheated at high temperature, are not “read” by muscle fibers and febrile seizures occur. A lack of calcium or magnesium in the body makes it difficult to transfer impulses from brain cells to the nerve fibers, resulting in muscle spasm.
The nervous system of children is imperfect. This system is the most "loaded" in childhood, because it is the only one that is experiencing such rapid changes in the growth process of the baby.
That is why children often appear night cramps. In a dream, blood circulation slows down, muscles relax, impulses pass with great delay. Muscular spasm at night is also found in children-athletes whose muscles experience a heavy load during the daytime.
The brain in the event of a "failure" by all means seeks to restore the lost connection. The cramp will last as long as it takes him. After the impulses begin to pass, muscle spasms and convulsions gradually subside. In this way, a seizure may begin suddenly, but the reverse development of an attack is always smooth, phased.
Causes of development
The causes that cause child cramps are different. It should be noted that in about 25% of cases, doctors did not manage to establish the true cause, if the attack was a single one and did not recur. Muscle spasms, children often respond to fever with a high temperature, spasms are severely poisoned, some neurological problems can also cause increased spastic readiness.
Convulsions in children can occur on the background of dehydration, from severe stress. This concomitant symptom is accompanied by many congenital and acquired pathologies of the central nervous system. We will tell about the most common reasons in more detail.
Epilepsy
With this chronic pathology, the convulsions are generalized with loss of consciousness.Attacks are multiple, repetitive. Symptoms depend on the location of the epileptic focus, in which part of the brain there is a violation. The onset of an attack is preceded by the impact of a certain factor. Thus, in some adolescent girls, epileptic seizures occur only during menstruation, and in some young children - only at night or when falling asleep.
All the reasons why epilepsy develops in newborns and older children have not yet been studied, but among those identified a hereditary factor holds a special place — often children inherit the disease from their parents.
The likelihood of developing a disease in a child increases, if the expectant mother, during the period of gestation, took medications without a doctor's recommendation and urgent need, took alcohol and drugs. The risk is increased in premature babies and toddlers who received birth injuries. In preschool children, the cause of the development of epilepsy can be a severe infection, which resulted in, in particular, complicated meningitis or encephalitis.
Convulsions in different forms of epilepsy manifest themselves in different ways. Their duration can be from 2 to 20 minutes. Short-term respiratory arrest, involuntary urination can be observed. If you wish, you can recognize the first signs in infants. The crumb stops to suck and swallow, looks at one point, does not react to sounds, light, parents. Quite often, before the attack, the baby's temperature rises, there is an increased moodiness, refusal to eat. After an attack, one side of the body may be weaker than the other, for example, one arm or leg will move better than the other. This state passes in a few days.
Spasmophilia
This disease can cause seizures in children aged from six months to 2 years. In later age, tetany (the second name of spasmophilia) does not occur. Seizures with this disease have exchange causes. They are caused by a lack of calcium and magnesium in the body. This condition usually occurs with rickets. Spasmophilia can not be called a common cause, since it occurs in less than 4% of children prone to convulsions.
The greatest number of attacks is observed in children with rickets, as well as in premature babies with signs of rickets and rickets. The disease has seasonality. In most cases, convulsive spasms occur in the spring, when the intensity of sunlight becomes higher.
Spasmophilia is most often manifested by laryngospasm, that is, by spasm it reduces the muscles of the larynx. It does not allow the child to breathe normally, to speak. As a rule, an attack ends after 1-2 minutes, but there are situations when respiratory failure occurs. The manifestation of tonic convulsions of the hands and feet, facial muscles, as well as general eclampsia, when convulsions of large muscle groups with loss of consciousness, are characteristic of a certain form of the disease.
The danger of spasmophilia is rather ephemeral., because it is not proven that it provokes the development of epilepsy at an older age, and respiratory arrest and bronchospasm, life-threatening, occur extremely rarely during an attack.
Tetanus
This acute illness has an infectious nature. The child’s body, its central nervous system is affected by a very toxic exotoxin, which is produced by tetanus rods - bacteria that can be active only in an oxygen-deprived space, but warm enough and moist. Wounds, abrasions, burns and other damage to the integrity of the skin are such an ideal environment for them.
The risk of infection is higher in newborns (through the umbilical wound), in children from 3 to 7 years old, who more often fall and injured more often than in children living in the village, because the stick is found in large quantities in the soil in an area where there are feces of cows and horses , people. The tetanus mortality rate is highFor example, newborns die in 95% of cases.
Mandatory vaccination (DTP vaccination) reduces the likelihood of infection, and timely administration of tetanus toxoid after trauma on an emergency basis can additionally protect the child.
Tetanus cramps can be very strong, almost continuous, generalized. The first signs of the disease can be recognized by the characteristic shaking that occurs in the injured area. It is possible to distinguish them from ordinary startles by frequency and regularity. Following this sign, trisism occurs - the chewing muscles contract with a spasm, as a result of which the child’s facial expression changes - the eyebrows crawl up, the corners of the lips descend, it is very difficult to open or close the mouth.
At the next stage, cramps begin to reduce limbs and back, as well as the stomach. Muscles become tense, stiff, "stone". Sometimes a child literally freezes in unbelievable positions, often horizontally, relying only on two points - the back of the head and the heels. The back is arched. All this is accompanied by high fever, sweating, but the child with tetanus never loses consciousness.
Attacks can repeat rarely, and can be almost continuous, they are often provoked by light, sounds, voices of people. As recovery progresses, dangerous complications can develop. - starting from pneumonia and autorepractors to cardiac muscle paralysis, the development of acute respiratory failure.
Hysteria
A hysterical seizure differs from other causes of convulsive states in that it develops not because of viruses and bacteria, but solely against the background of a stressful situation. Children, by virtue of age, find it difficult to control their emotions, so hysterical convulsions are not uncommon for them. Usually they suffer from children from 2-3 years to 6-7 years. This is the period of the most active emotional development. Often, the first attacks occur in the so-called "critical years" - 3-4 years, and then 6 years.
The starting mechanism of a convulsive attack is always a strong emotion - resentment, anger, fear, panic. Often, to start an attack requires the presence of native people. The child may fall, but he always keeps the consciousness. Cramps are most often local in nature - hands move, toes are squeezed and unclenched, head is thrown back.
The child does not spell, does not bite his tongue, and generally rarely gets any mechanical injuries in the process of an attack.
At the time of the attack, the child responds quite adequately to the pain. If it is easy to prick him with a needle or a pin in his hand, he will reject it. Movement has the character of complex movements - the kid can cover his head with his hands, press his legs at the knees and do it rhythmically with an obsessive identity. There are grimaces on the face, possible uncontrolled strokes of the limbs. Attacks are quite long - up to 10-20 minutes, in rare cases, the child can fight in a hysterical fit for several hours. Rather, he understands what he is doing, but he cannot physically stop an already running process.
The attack ends abruptly. The kid abruptly calms down and behaves as if nothing had happened.. It is not drowsy, as it happens after seizures with epilepsy or after febrile seizures, it is not apathetic. Such cramps never occur during sleep.
Febrile
This type of seizures is peculiar only to children and only at a strictly defined age - up to 5-6 years. Muscle cramps develop on the background of high temperature during any infectious or non-infectious disease. Children from 6 months to one and a half years are most subject to such convulsions. Under the same conditions, at the same temperature, muscle spasms develop in only 5% of children, but the probability of their recurrence in subsequent illness with high fever is 30%.
Convulsions can develop against the background of acute respiratory viral infections and flu, with the eruption of milk teeth, with severe allergies and even with the reaction to the DPT vaccine. It is impossible to influence their development, Neither fever-reducing drugs nor constant temperature control reduce the likelihood of such an outcome.
It all starts about a day after the establishment of a feverish state.And simple cramps, which are expressed by trembling of individual limbs, and complex cramps that cover large muscle groups, the child loses consciousness. Actually, this is the first sign of a febrile attack. First, "brings" the legs, then the body and arms. The chin is thrown back due to the strong tension of the occipital muscle, the face stiffens. The skin turns blue, increases perspiration, possibly increased saliva secretion.
Short term breathing stops can occur in an attack.. After passing the peak, the symptoms develop in the opposite direction - the back and face are the first to relax, the legs are the last. After that, consciousness returns. The child is weak, after a seizure, he really wants to sleep.
Traumatic brain injury
Convulsions after a skull injury or intracranial injury may develop immediately or several days after what happened. Muscle spasms themselves are not a mandatory consequence of a traumatic brain injury, their nature and severity depend on what kind of injury was received and how seriously the lesion is. Parents should be alerted by changes in the behavior and condition of the child - lethargy, apathy, severe headaches, nausea and vomiting, loss of consciousness.
At the first symptom of convulsions (and they can be of any kind - from focal to generalized), you should immediately call an Ambulance and provide emergency assistance yourself.
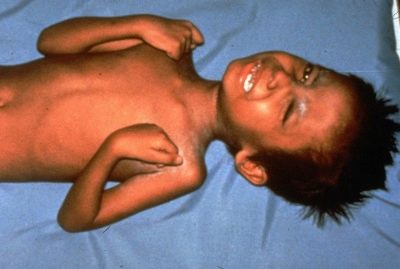
Organic lesions
Congenital organic lesions of the central nervous system can be accompanied by convulsions - microcephaly, hydrocephalus, underdevelopment of brain lobes and so on. Doctors will be obliged to warn parents of such a probability, since the majority of such pathologies become obvious in the first hours and days after the birth of the child.
Often convulsions occur against the background of existing diseases of the musculoskeletal system (paralysis, cerebral palsy). During meningitis and enfetsalita convulsions are accompanied by numerous neurological symptoms. They start 1-2 days after the onset of the disease and usually have a frightening adult generalized nature.
Convulsions of different types and intensity, but usually generalized, are accompanied by toxic brain lesions in case of poisoning with poisons. Quite often, the child loses consciousness. This is preceded by other signs of poisoning - vomiting, diarrhea.
First aid
The algorithm for providing emergency care is quite simple. Parents must first call an ambulance and fix the time of the onset of the attack. It will be necessary to gather all the will into a fist and, in anticipation of the doctors, notice all the details of what is happening with the child - what kind of convulsions are in, how often do they recur, does the child react to external stimuli, is he conscious. All this information is useful to the doctor to quickly make the right decision to establish the possible causes. If it is difficult to determine the nature of convulsions, You can remove what is happening on the video and show it to the doctor later.
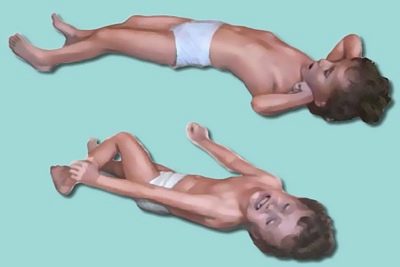
The child is placed on a firm and level surface in the universal position of “salvation”: the position of the body is on the side so that the child does not choke with saliva or vomit. If the legs are not tightened, then you can leave everything as is. Under the head, put a roller folded towel.
The mouth of the child is cleaned of mucus using a scarf or cloth. If the reason is not known for certain, then just in case it is worth taking precautions that are important during an epileptic seizure. A wooden object (spoon or knife handle) is inserted into the child between the teeth, necessarily wrapping it with a cloth. You can simply tie a knot on a towel and insert it into your mouth. This should protect the tip of the tongue from involuntary biting.
Be sure to open the windows, balcony doors that provide fresh air.This tactic of the actions of parents in the event of convulsions in a child is exhausted. The rest is the business of doctors.
What not to do:
Giving a child to drink during cramps.
Do not try to give your baby any medications.
Stretch your teeth apart and shove an iron spoon into your mouth. This can cause teeth to break, and debris gets into the respiratory organs.
Unclenched spasms of the limbs, as this can lead to fractures, muscle tearing and muscle tearing from the bones.
Drench or spray baby with cold water, try artificial respiration, heart massage and perform other resuscitation if the breath is saved.
Treatment
The tactics of stopping an attack by an ambulance team that arrived will depend on what kind of seizures have occurred, and from the probable cause. Most often, when generalized, infantile children's convulsions are administered "Seduxen". Dosage of this drug or «Relanium» for total muscle relaxation is calculated based on the age of the baby.
With affective-respiratory convulsions, which are manifested in children with breath holdings, with febrile convulsions of a simple type of baby can be left at home. With other attacks - epilepsy, toxic convulsions, tetanus, urgent hospitalization is required.
Treatment usually requires emergency administration of anticonvulsant drugs, cleansing the body with intravenous saline, mixtures of vitamin and mineral solutions. In tetanus, tetanus toxoid is administered to the child. In case of hysteria, the child is shown neurological and psychiatric care with the use of nootropic drugs and sedatives.
Usually, hospital stay is not limited to treatment. A child is observed at a dispensary, sometimes anticonvulsant drugs are prescribed for long periods.
The kid after a history of convulsions shows taking multivitamins and microelements, walks in the fresh air, measures to strengthen the immune system, good nutrition.
About what to do with convulsions in children, see the following video.