Hydrocele in children
Mothers of boys very often after birth face a disease such as hydrocele. Often, parents are scared and do not know what to do and how to act if they discover the first signs of the disease in a child. Currently, this disease is perfectly cured by modern methods of medicine.
What it is?
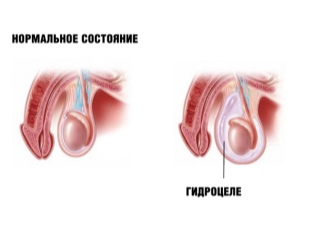
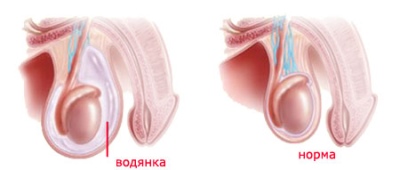
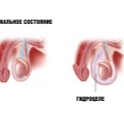
Hydrocele disease, or dropsy of testicles in newborns occurs quite often. The most common congenital form of the disease, which occurs immediately after birth. In infants there is an accumulation of fluid in the membranes of the testicles. This leads to the appearance of specific symptoms and manifestations of hydrocele in boys.
Dropsy of testicular membranes occurs most often on one side. As a rule, this form is more than 90% of cases. There may also be bilateral dropsy of the testicles, but in a much smaller number of cases.
According to statistics, every tenth boy born has a hydrocele. The disease can go away on its own, without additional treatment. However, in some situations even surgery is required.
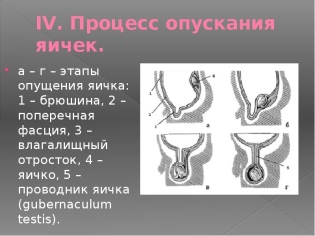
The laying of the genitals in the boy is still in utero. At about 22 weeks of pregnancy, the baby’s testicles begin to descend from the abdominal cavity to the pelvic area. This is quite a physiological picture of the normal development of the future male body. In some cases, even after birth, the testicles do not reach the scrotum, and remain also in the abdominal cavity.
With the passage of such a development as a result of exposure to various provoking factors may develop some disorders that lead to edema and the accumulation of serous fluid between the membranes of the testes. In this case, doctors detect a dropsy of the membranes, or hydrocele. This phenomenon is already a deviation from the norm and requires careful and careful observation of the baby, and in some cases even the appointment of special treatment.
Causes of
The edema of the membranes can be either on the right testicle or on the left one. All types of hydrocele are congenital and acquired.
Congenital
Meet immediately after the birth of the baby. Congenital or physiological variants of dropsy of the testicles occur more frequently when the following factors are affected during pregnancy:
Exacerbations of chronic maternal diseases, which lead to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure in the fetus.
Acute infectious diseases in which infection occurs during the descent of the testicles from the abdominal cavity to the pelvic region. Most often these are different types of viral and bacterial infections that a mother can get sick while pregnant. The risk is highest in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Violation of blood supply to the placenta and the threat of miscarriage. In this case, the full blood supply to the fetus is disrupted, which can also lead to a violation of the laying of the genital organs and improper lowering of the testicles during fetal development.
Premature birth or prematurity. Often in such children, the testicles simply do not have time to physiologically descend into the cavity of the small pelvis, and then into the scrotum. A baby is born with testicles that remain in the abdominal cavity. Even if they reach the scrotum, the edema and development of the hydrocele often develops.
Heredity. There are data that indicate an increased risk of having hydrocele in close relatives.
Infectious diseases of the urinary tract and genital organs in the fetus, developed during the pregnancy of the mother. Often associated with intrauterine infection of the future baby from the mother. In this case, besides hydrocele, the child may have symptoms of epididymitis or even inflammation of the kidneys and urinary tract after birth. Such diseases require mandatory consultation of the urologist.
Acquired
They are found mainly in babies after birth. There are much less. More common after traumatic injuries, as well as various diseases of the genital organs of boys, which develop after birth. Among the reasons that can also lead to the development of the acquired form of hydrocele, include testicular torsion or the development of complications after removal. inguinal hernia. Injuries to the scrotum can also cause symptoms of hydrocele.
Types of dropsy testicles
There are several different classifications that allow you to divide all variants of the disease into similar clinical groups. Most often, doctors use such, where the forms of diseases are divided according to the main provoking cause, degree of severity, variant of the course, as well as on the mechanism of the appearance of fluid in the scrotum.
According to the prescription of the onset of symptoms, hydrocele is:
Sharp Symptoms appear, as a rule, rapidly. After the action of a provoking factor, the development of manifestations of the disease increases in a few hours. The course of the acute form of the disease, as a rule, is accompanied by the appearance of pronounced symptoms that bring the kid a pronounced pain syndrome and strongly influence his health.
Chronic. The formation of this form of the disease takes several months or even years. With the development, as a rule, does not cause any adverse or discomforting symptoms. It occurs at an older age. For the treatment of this form of the disease, consultation of the urologist is required.
According to the mechanism of accumulation of fluid, hydrocele is:
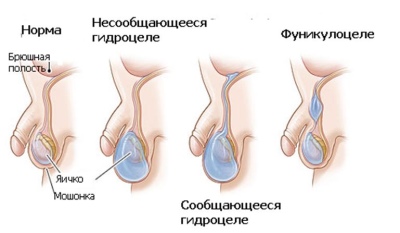
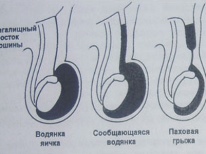
Communicating. In this case, during intrauterine development, there is no complete closure of the canal between the peritoneum and scrotum. Serous fluid can spread in various directions and cause disease. To determine this form of the disease, doctors identify a characteristic symptom: with a slight squeezing of the scrotum - its size is somewhat reduced. This is due to the fact that during compression, the fluid flows into the abdominal cavity.
Isolated Most often, as a congenital form. In this case, the opening between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum is closed, communication between two different cavities no longer occurs. In this case, all the fluid is between the membranes of the testes. This form is statistically less common.
Main symptoms
Every mommy who has a little boy grows up to know what a hydrocele looks like. Acquired forms of the disease can occur in babies at almost any age after any traumatic injury to the scrotum. At the slightest suspicion of the development of dropsy of the testicles, you should definitely show the baby to a pediatric andrologist. The doctor will be able to determine the disease at the earliest stages.
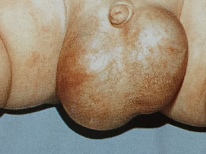
In most cases, with mild illness, symptoms that bring discomfort or pain to the baby do not develop. In newborns, the scrotum may be slightly enlarged or swollen. However, often for a long time this symptom remains unnoticed, since its manifestation is not too pronounced.
Suspect dropsy of the testicles of a baby should be if:
Slightly swollen and enlarged scrotum. In newborns, this feature is very difficult to identify.If the mother has speculated that the baby has some asymmetry or swelling of the scrotum - you should definitely show the child to a pediatrician or pediatric urologist.
Slight swelling. Usually dropsy of the testicles is one-sided. With a slight asymmetry in the scrotum, we can assume the presence of swelling of the testicular membranes.
Strong mobility of the skin of the scrotum. Determined only by a urologist. The presence in the membranes of serous fluid helps to improve the skin slip on the surface of the testicles. It is one of the specific signs of hydrocele.
Undisturbed urination. For most urological inflammatory diseases characterized by violation of the outflow of urine. The child may complain of some soreness or even a burning sensation when urinating. For dropsy of the testicles, this symptom is not characteristic. Urination for babies with hydrocele does not bring pain or marked discomfort.
The appearance of symptoms of intoxication with torsion of the testicle or the development of other urological complications of the disease. Often occurs after traumatic injury to the scrotum and infection with various viral or bacterial infections. In this case, the baby's temperature rises, appetite and sleep are disturbed, and pronounced weakness increases. Immediate hospitalization of the child is required.
In the chronic course of the disease - the development of the inguinal hernia. This form of the disease requires surgical treatment. In this case, treatment of edema of the testicles is performed and an inguinal hernia is removed during the operation.
Diagnostics
Only a urologist or a pediatric andrologist can diagnose a hydrocele. To determine the form of the disease and conduct a differential diagnosis with other urological diseases, the doctor first of all conducts a physical examination of the baby. During this examination, the doctor can identify and determine all the symptoms of the disease, as well as exclude concomitant pathologies of the genital organs or identify complications.
In some cases, doctors resort to the appointment of additional laboratory and instrumental tests. They allow to detect the presence of complications, as well as to conduct a differential diagnosis with other diseases of the urogenital area.
Complete blood count is assigned to determine the presence of a viral or bacterial infection. Changes in the leukocyte formula suggest the presence of systemic inflammation, which quite often leads to the development of exacerbations of urological diseases in children. Accelerated ESR is also an early marker of inflammation in a child’s body.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and scrotum allows to detect the presence of free fluid between the membranes of the testes, and also gives a description of all the genital organs, taking into account their structure and anatomy. This method allows you to set even the smallest deviations from the norm. Ultrasound examination is necessarily assigned to all babies who are scheduled for surgical treatment of hydrocele.
Using the diaphanoscopy method, you can view the testicles on both sides. Streams of rays penetrate the skin of the scrotum well and reach the membranes. This method also allows you to make a conclusion about the presence of edema or fluid accumulation between the membranes of the testicle.
X-ray diagnostics in newborn babies and children of preschool age are attempted only in difficult diagnostic cases. High radiation exposure makes this method completely unsafe for the child's body. X-ray diagnostics is of an auxiliary nature and is used only in exceptional cases.
Effects
The danger of the development of terrible complications with hydrocele is quite high. Like any urological disease, dropsy of the testicles can proceed quite safely, and can cause terrible complications. The scrotum is highly stressed due to the large amount of fluid between the shells.Any traumatic injury or exposure to a provoking factor can lead to the appearance of adverse complications.
Most often, babies can experience various torsion or compression of the testicles due to the large amount of serous fluid. The addition of a secondary bacterial infection provokes infection in the scrotum and the development of inflammation. In this case, the skin in the groin area turns red, it becomes hot to the touch, and the pain syndrome increases. If inflammation has spread to the urinary organs, a violation of urine outflow or a burning sensation during urination may occur.
In the long-term period of the course of the disease, with delayed treatment or insufficient monitoring of the course of the disease, male infertility may occur in men who suffered from a hydrocele in childhood. Such situations require consulting an andrologist and drawing up a treatment plan that will help restore fertile function.
Treatment
For the treatment of hydrocele at home, there are many methods of traditional medicine. Some mothers say that they were able to cure the disease with sea salt or soda baths. However, there are no real positive reviews of such treatment, as well as reliable scientific studies that would allow the use of sodium chloride (table salt) for the treatment of hydrocele of the testicles.
To treat hydrocele should still under the clear guidance of the urologist. In this case, the risk of complications of the disease will be minimized. It is important to note that in most cases the hydrocele of the testicles passes independently by the age of two years. In this case, the liquid is completely absorbed, and the edema also goes away.
Usually, if the symptoms of the disease do not disappear by the age of two years, then doctors may recommend surgical treatment. Before embarking on such a therapy, urologists usually prescribe a course of medication. Usually drugs are prescribed for 3-4 months. If during the time of the conservative treatment, the symptoms have not diminished and there is no positive dynamics of the disease, then doctors recommend surgery.
Surgical operations can be divided into several categories:
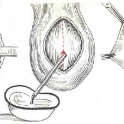
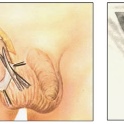
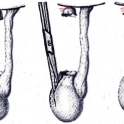
Winckelmann method. In this case, a midline incision is made on the anterior surface of the scrotum. The aspiration syringe removes all accumulated, excess serous fluid between all the membranes of the testicles. Then fixing seams are made. For this purpose, absorbable biological suture material is used. Accumulation of fluid after this procedure does not occur, as it easily penetrates into the underlying tissue. If a message is open between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum, then a reconstructive surgery is performed in parallel to remove it.
Bergman method. Usually performed with hydrocele of impressive size or pronounced strong swelling of the membranes of the testicles. In this case, surgeons excise the innermost envelope. A drainage is placed to remove the remaining fluid, the wound is sutured and an antiseptic dressing is applied to the incision site. Subsequently, the drainage is removed. The wound heals up quickly and only a small scar remains.
By the method of the Lord. This option of surgical treatment is most in demand in babies of the first months of life, as it is the most benign among other urological interventions. It can also be used in older patients, but with a slight swelling.
Ross method. In this case, close the message between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum. This hole is sutured in layers, all serous fluid is aspirated. After which the wound is sutured, and antiseptic dressings are applied. This surgical technique is mainly used in babies of any age, as well as adults. The method is shown in the reported version of dropsy of the testicles.
The choice of surgery is coordinated with the operating urologist.After an ultrasound scan of the scrotum and auxiliary laboratory tests, the doctor can determine which surgical tactics are best used to treat a particular child. It directly depends on the amount of damage, the amount of serous fluid between the membranes, the age of the baby, as well as the presence of comorbidities or complications.
All surgical interventions are carried out in the urology department of multidisciplinary hospitals. Usually such procedures are routine. Every day, doctors operate on a huge number of boys with hydrocele. The duration of the operation, as a rule, is 25-35 minutes. Postoperative complications are rare. Compliance with all recommendations after the operation can reduce the risk of secondary infection and prevent possible adverse effects.
Local anesthesia is most commonly used. The use of anesthesia is resorted to in exceptional cases: in case of severe course of the disease or the presence of concomitant urological pathology, which requires a longer surgical procedure.
Previously, an aspiration method was used to treat hydrocele — the liquid was removed by a puncture method. Currently, this method of treatment was refused, since the risk of mechanical damage to the testicular tissue is very high. Also during this manipulation, you can carry a bacterial infection and even cause suppuration.
Possible complications after surgery
It is important to note that surgical procedures for removal of dropsy of the testicles are planned procedures and are very safe for the child's body. The risk of postoperative complications is less than 5-10%.
Among the adverse effects that may occur in a baby, after carrying out such a procedure are the following:
The development of postoperative bleeding.
Secondary infection of the open wound, and the development of suppuration.
Inflammation of the internal seminal ducts. Such an inflammatory process can lead to the development of chronic urological diseases that can lead to infertility. Often this pathology is bilateral.
Atrophic changes in testicular tissue. This occurs as a result of circulatory disorders in the scrotum.
The development of pain in the groin area, as well as increased pain when moving or changing body position
Hygiene after surgery
In order to prevent the development of adverse complications that may occur after surgery, the following preventive measures should be observed:
Do not touch the post-operation wound with dirty or untreated hands. So you can bring a bacterial infection and even cause suppuration.
After surgery, you can not take a bath for a week. Water should not be completely expelled at the wound site.
The place of the postoperative scar must be treated with special disinfectants or antibacterial agents, which the urologist will recommend.
If pain occurs during the first two weeks, then analgesics should be used. When increasing the pain, be sure to show the child to the urologist. Perhaps the baby has a postoperative complication.
To eliminate residual serous fluid, doctors may prescribe diuretics. Diuretics can help cope with the elimination of even the residual amount of serous secretions between the membranes of the testes.
Regular medical check-ups at the urologist. All babies who underwent surgery to restore the normal functioning of the testicles are shown to undergo consultations with a doctor of the appropriate profile every month within six months after surgery. In the future, it is enough to appear to the urologist once a year.
Strengthening immunity and prevention of hypothermia. For a baby who just underwent surgery, it is better to choose warmer clothes for walking outside. Overly wrap the child is also not worth it! Give preference to light and at the same time warm clothing that does not hinder movement.
Wearing underwear made from natural materials. All synthetic products, as a rule, badly let in air and “do not breathe”. Wearing such underwear can lead to a violation of the air exchange of the genital organs and even contribute to the appearance of complications. Choose products from natural fabrics that are easy to wash, and they dry quickly.
Hydrocele is one of the most common urological pathologies in newborn boys. Modern methods of treatment can eliminate the adverse symptoms at any age without harm to men's health. Edema of the testicles is well treated and in most cases does not cause dangerous disorders in babies.
Explanations about hydrocele or dropsy of the testicle tells urologist Alexey Kornienko.