Absences in children: from signs to treatment
Short-term loss of connection with reality, loss of consciousness without convulsions in children is perceived by parents as something unknown and strange. There were times when such phenomena were considered signs of obsession and unusual paranormal abilities. In fact, we are talking about absansy.
What it is?
The title was given to absans by the beautiful French word absence, which translates as “absence”. This refers to the lack of consciousness for some time. Absans in medicine is a minor seizure, very similar to epileptic, but not accompanied by convulsions. Clinical manifestations with such a convulsive seizure are called absans.
Such epilepsy without convulsions was known even to the doctors of antiquity, in particular, it was described by Hippocrates, who called the illness "a sacred disease." After the great doctor Hippocrates, a strange epilepsy, which is not associated with convulsions, but only manifested by loss of consciousness and a trembling of the eyes, was described by Swiss doctor Samuel Tissot in the XVIII century. A century later, absences were studied by the French psychiatrist Eskoliol and his students.
Until now, scientists and doctors argue, what is inherently absences. But for the most part, physicians agree that this is a separate epileptic form. She, of course, can accompany normal epilepsy, and can be observed separately.
Such seizures without seizures usually occur. in children after 4 years, most often at the age of 4-7 years, a little less at the age of 7-14 years, abscesses are very rarely started after 15 years. More common in girls and girls than in boys and young men. In infants up to a year, such a phenomenon is practically not encountered due to the immaturity of the cerebral cortex (the fact is that absansance requires a certain degree of maturity of the brain and nervous system).
The reasons
Doctors still argue about the true reason for the absences. So far, it is believed that the lack of balance between the processes of inhibition and excitation of the nerve cells of the cerebral cortex is to blame. Hippocrates suspected such a reason, and the research of his followers did not contribute anything essentially to the questions of the origin of absences.
The following factors can lead to the lack of a balance between braking and excitation pulses in neurons.
- Organic brain damage: transferred encephalitis, brain abscesses, as well as tumors and neoplasms. Such absences are called secondary, that is, occurred as a complication of the underlying pathology.
- Causes, medicine and science unknown and incomprehensible - these are idiopathic absansy. There is a version that they depend on genetic information and usually occur in children in whose family there were cases of epilepsy. There is also a version that similar abscesses can develop in children who have experienced episodes of febrile seizures at an early age (against the background of high heat), but this connection has not yet been reliably proven.
Absansy start under the influence of certain triggers, which also medical science has not been established for certain. It is believed that too frequent and deep breathing, which leads to hyperversions of the lungs, in particular, can cause an attack. Also provoke a paroxysm can flash of light, for example, a flash or bright salute.
It is believed that the likelihood of attacks is higher in children in a state of lack of sleep, as well as during periods of experience, stress and severe physical and psychological stress.
What is happening and the types of seizures
Absansy can rightly be considered the most mysterious pathology, since the mechanisms for the development of seizures are the secret behind seven seals. Many scientists believe that At the basis of such a non-convulsive seizure is the predominance of inhibition in the cerebral cortex, whereas convulsive epileptic seizure is usually associated with excessive neural excitation. The version of the importance of such seizures to compensate for certain processes in the children's brain also looks very reliable, which is why, in the majority of cases, there is no trace of absences to adulthood - the brain matures completely.
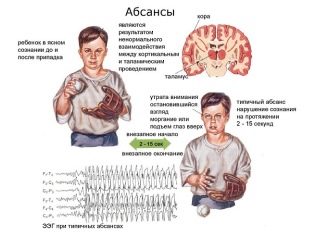
By themselves, abscesses are divided into simple and atypical. Simple (they are typical) occur with short episodes of a blackout - literally half a minute. Any other symptoms with typical absence are absent. In most cases, the child during such a seizure may continue the work he started before the attack, but his actions are very slow and inhibited. Difficult absansy (they are atypical) flow with a change in the state of muscle tone. The attack lasts from 5 to 20 seconds, they usually accompany an epileptic seizure.
Symptoms and signs
Typical and atypical abscesses occur in different ways. Simple, as already mentioned, are accompanied only by short-term loss of consciousness. The attack comes suddenly, nothing foretells him, there are no harbingers. It’s just that a child who was playing or was engaged in a conversation suddenly stops moving quickly, “becomes stone”, looks exactly in front of him, the mimic muscles do not contract, therefore The child’s facial expression does not change throughout the entire seizure. Baby can no response to external stimuli - voices, sounds, light. After about half a minute, the state normalizes. The child does not remember the attack, for him this half-minute seems to fall out of life.
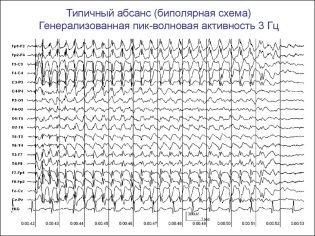
Such paroxysms can be repeated several times a day, and several times a month. With high frequency typical attacks reach a frequency of several dozen per day. Each lasts no more than half a minute, a child with open eyes is in a detached state, external stimuli do not remove it from an attack. Such typical attacks on the electroencephalogram are marked as peak-wave with a certain frequency - 3 Hz.
With atypical absences, the child not only loses consciousness for the time of the attack, but also occurs other phenomena, for the particular baby each time the same. For example, with the same movements of the lips, tongue, some specific repetitive gesture, constant correction hairstyle. That is, the child continues to act, even when unconscious, which is why such paroxysms often go unnoticed for a long time.
Very often, atypical absansy occur on the background of changes in muscle tone. The child can move his head back with his eyes rolling, or he can bend back and at the same time keep his balance at the expense of the leg laid back. If the tone changes in the direction of the hypotonus, the fall is still unavoidable, since the muscles, regardless of posture, quickly weaken.
Often such attacks are accompanied by taste, auditory or visual hallucinations. The child remembers the attack itself, but regards as something unusual what had just happened to him and that he cannot explain.
A complication of absences may be the development of resistant epilepsy. This happens about every third child with periodic absences. If you fall during a complex attack, the child may be injured. Sometimes the presence of absences leads to deviations in the mental and mental development of the child.
What to do?
If parents notice such “oddities” for a child, it is important to turn in time to a pediatric neurologist who will help determine whether there are abscesses and what is their reason. A neurologist examines a child, but with non-epileptic absences (idiopathic), no neurological abnormalities are usually detected by examination.
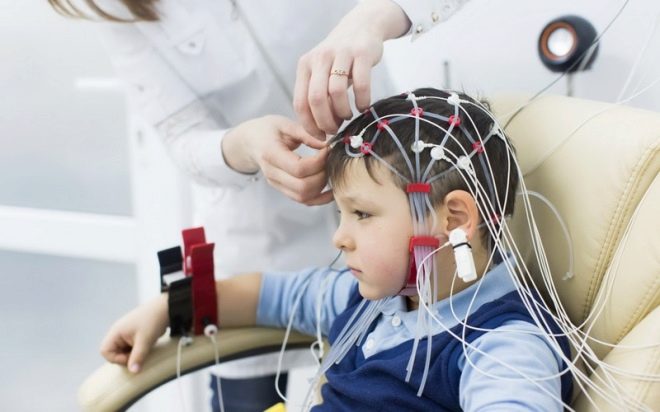
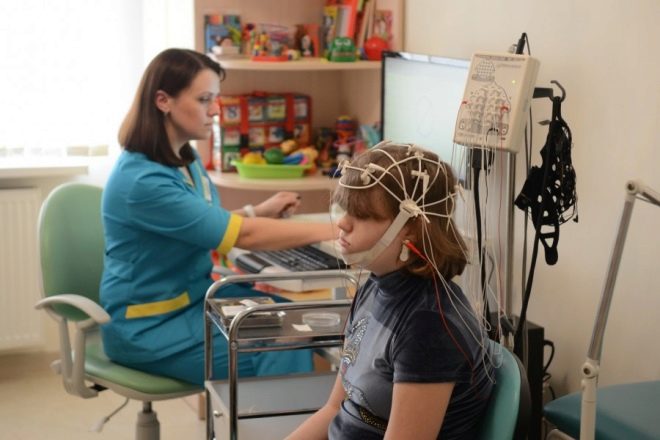
The child is recommended to undergo an EEG (electroencephalogram), in some cases it is recommended to perform an MRI scan of the brain to exclude tumors and organic lesions.
Treatment is prescribed only after the doctors can determine whether the child has major diseases or not. From this, in fact, will depend on therapy. Children with simple absences are recommended to take valproic acid drugs - in about 75% of cases, treatment is effective.
Complicated absences require the use of anticonvulsants. Antiepileptic therapy lasts as long as the doctor deems necessary, the dosage then decreases gradually. Usually for the abolition of the drug need indications, for example, the absence of attacks for 2-3 years.
Folk remedies, conspiracies, osteopathy for absences does not exist, parents should not forget about this.
In most cases, forecasts are favorable: abscesses remain in the past when a child grows to the age of 18-20 years. If the first attacks appeared in adolescence, then the probability that a person will “take” them with him into adulthood is estimated at about 25-30%. Alas, the forecasts are not too favorable, if the absences are manifested too early, they recur, if they proceed with a lag in mental development, impaired memory, thinking.
About children's absansa more tells the specialist in the video below.