Brain Tumor in Children: Symptoms and Treatment
Brain tumor - this diagnosis sounds scary. The sooner it is discovered, the more chances a child has for a normal healthy life.
That is why it is so important to know what signs accompany this pathology. In this article, we will tell you how to suspect a tumor in its early stages, find out whether new growths in the intracranial space are dangerous, as it seems, and whether you can count on a positive outcome of treatment.
What it is?
It's always hard to talk about childhood tumors. Do not like to do this, not only journalists and observers, but also the doctors themselves - too sensitive issue, because by and large the doctor can not answer the main questions of parents who are faced with the presence of such pathology in their child - why it happened and what is the prognosis for future.
In the occurrence of brain tumors in children (and in adults) there is still a lot of unknown. Nevertheless, there is information, and it is constantly updated, since up to 30% of the cases of all childhood tumors are none other than brain tumors.
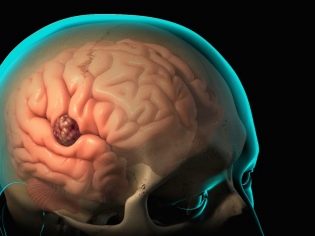
By brain tumors is meant a rather large group of neoplasms, both malignant (cancerous) and benign. Tumors develop due to the fact that in a certain organ the uncontrolled abnormal growth and division of cells begins.
Not so long ago, these cells were a natural component of the brain tissue, the membranes, but under the influence of certain factors, they begin to grow at an incredible rate, as a result they turn into a tumor. What cells began to grow, ultimately determines the type of education.
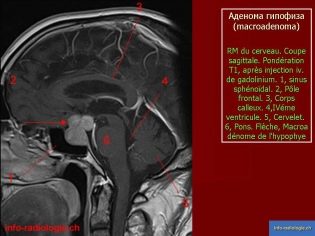
If cells of brain tissue grow, they talk about ependymoma or astrocytoma. Such tumors are most common - in about 60% of cases. If the cells of the meninge divide abnormally, meningioma is observed. Abnormal proliferation of pituitary cells leads to the development of pituitary adenoma.
When cells that are components of the cranial nerves inadequately divide, a neuroma develops. There are also diembriogenetic tumors that are formed in a child during the period of embryonic development, but they are very rare.
If the tumor appeared on its own and for the first time, they speak of a primary neoplasm, for example, of a primary neurinoma. If it is caused by the penetration of metastases from other diseased organs, then they are talking about a secondary tumor.
Features of pediatric tumors are that they may not manifest for a long time, because the children's organism has an incredible compensatory potential, it “smoothes” the pathology, levels the symptoms. That is why the tumor found in the child is sometimes quite large.
Symptoms and first signs
What will be the symptoms depends on which part of the brain the neoplasm appeared, which parts of the brain are subjected to compression, which cells are destroyed due to this. The earliest symptoms are called focal, these include the following.
- Change in sensitivity and perception. The child's susceptibility to pain, light, sound, and touch decreases or increases. Children older than 3 years may demonstrate a violation of the perception of themselves in space, for example, the baby cannot understand and explain how he holds his hand - up with his palm or down if he closes his eyes.
- Memory loss. A child begins to forget even those things that he knows perfectly well, may stop recognizing someone from his family, may forget letters and numbers if he already knows them. The memory of events, both distant and recent, also suffers.
- Movement disturbance. As the tumor grows, the signaling of the brain to the muscles worsens, resulting in complete paralysis; if a tumor of the brain stem, bone marrow develops, paralysis is local.
- Seizures and Spasms. At first, as a rule, small cramps appear, short in time, then epilepsy can develop.
- Impaired hearing. The child may lose the ability to hear, and may lose the ability to disassemble speech. If a tumor affects speech recognition centers, then all words turn into an incomprehensible noise for a small patient.
- Impaired visual function. If the optic nerve is clamped or impaired, the child partially or completely loses sight. It may not be the nerve that is struck, but the part of the brain responsible for analyzing what they see, and then the little patient stops recognizing familiar objects.
- Speech anomalies. With the defeat of the center of speech, the ability to speak in whole or in part is lost. Speech may persist, but become unintelligible mumbling.
- General deterioration. It is associated with the lesion of the vagus nerve by a growing tumor. Manifested in the form of bouts of severe dizziness, loss of balance, inability to stand up from a sitting position, as well as instability of blood pressure, bouts of severe weakness.
- Violations of motor coordination. This happens when the cerebellum is damaged. The symptom progresses rather quickly from small inaccuracies in movements to the complete impossibility of making a targeted movement, for example, taking a certain object from the table.
- Mental disorders. A child with a tumor, as it grows, changes in behavior, in reactions. Most often, children become aggressive, irritable and whiny. If the lesions are significant, self-identification may be lost. Many have visual and auditory hallucinations.
Secondary symptoms, appearing even when the tumor is quite large, are called cerebral. These include:
- severe headaches;
- persistent or regular vomiting;
- the inability to eat normally due to the fact that any substance falling on the root of the tongue causes a gagging attack;
- dizziness.
Babies of infancy and slightly older symptoms have their own characteristics. Most often in babies, the tumor manifests itself by changes in behavior: for no apparent reason, the child constantly cries, whines, moans, screams, makes tantrums, often vomits, there are signs of hearing or vision loss, a tendency to seizures and private nosebleeds.
Reflexes can also be disturbed - swallowing, sucking.
Recognizing the pathology by a combination of symptoms is impossible without diagnosis, but the appearance of such symptoms, or at least one of them, should be a good reason to postpone all cases and plans and go with the child to see a doctor.
Why is it important to do it urgently? Because in the case of tumors, it is important to have time in time - to diagnose in time, start treatment in time. According to statistics from the Ministry of Health, over the past three decades, the number of children with brain tumors has increased significantly - almost 3.5 times. In 15% of cases of all tumors we are talking about cancer.
The reasons
Since the causes of the development of a tumor are not known for certain, not a single doctor will take the liberty of even suggesting why the child began an uncontrolled division of more recently healthy brain cells. But after all, something needs to be said; the doctor cannot answer the honest “I don't know” parents.
Therefore, the occurrence of a tumor process is usually attributed to the reasons that explain everything that cannot be explained - poor ecology, radioactive contamination, genome-modified food, toxins, or at least genetics, if it turns out that someone from the relatives of the child also suffered from a brain tumor or had problems with tumors.
It is believed that various craniocerebral traumas that a child could have gotten in a fall, in a fight, while playing sports, can provoke (indirectly) the growth of brain cells under the influence of an abnormal immune response.
The risk group for the probability of cerebral neoplasms includes children with HIV infection, as well as children who, for some other medical reasons, are prescribed drugs that suppress the activity of the immune system (immunosuppressors).
Diagnostics
If you find suspicious signs in your child, such as weakness, lethargy, irritability, fatigue, frequent and severe headaches, behavioral changes, and systematic vomiting that are not related to other causes, you should immediately contact a neurologist or pediatrician.
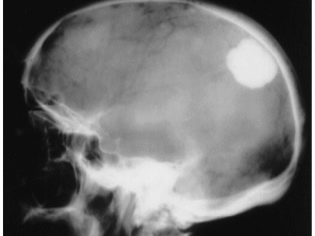
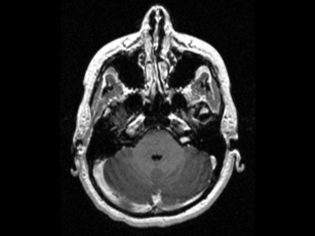
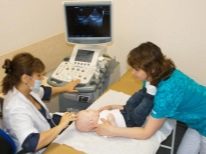
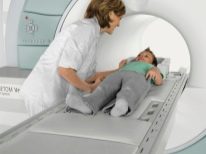
For primary diagnosis using methods such as EEG, Echo EG, CT, MRI, babies up to one and a half years old perform neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain). When a neoplasm is detected, PET-CT is performed; this technique makes it possible to assess the degree of malignancy. The exact cellular nature can be established by histology.
Treatment
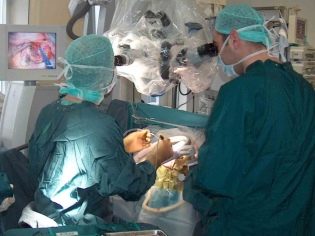
Conservative treatments are aimed solely at relieving certain symptoms, such as constant vomiting or severe headaches. The medications do not eliminate the cause of these symptoms. Therefore, the most effective is surgery, during which doctors remove the tumor.
If the tumor is small and grows slowly, stereotactic radiosurgery can be applied, in which the tumor is exposed to radioactive radiation. But usually, full recovery does not occur: the tumor only ceases to develop, and sometimes slightly decreases in size. If the neoplasm is growing quite intensively, then this method is not suitable for treatment.
After surgery, and sometimes before it, and after, conduct courses of radiation proton therapy, as well as courses of chemotherapy. The treatment is very serious and long lasting. It will require parents to mobilize forces, both physical and moral.
Much depends on them - the child needs constant support, love and care, as well as a firm parental belief in a positive outcome of treatment.
On this long and difficult path, they will meet different people - attentive and cynical doctors, representatives of different religions who will encourage them to pray, as well as healers, false healers, magicians and wizards who will offer non-repayable assistance in healing a child and drugs. "
It is at this moment that the temptation to start watering the child with aviation kerosene, a mixture of vodka and oil according to the Shevchenko method, mouse droppings can prevail over common sense. It is necessary to refrain from such “treatment”, having trusted the doctors. Believe me, they want your babies to be healthy as much as you do.
Forecasts and consequences
Benign tumors are considered most favorable for prediction. With their convenient location and accessibility, tumors in children are quite quickly removed. The downside is that no one will guarantee that a benign education will not appear again, and this may require a repeat operation.
Spinal bone marrow tumors, subtentorial, localized in the middle section, operate much harder. If the tumor is malignant, and also difficult to reach, the prognosis is unfavorable.
It is very difficult to say something about the long-term consequences, because not only the tumor itself can harm the child, but also the methods of its treatment, especially in the age periods when certain brain skills are formed - in newborns, at 6 months, at 11-12 months, at 3 years.
Survival statistics are compiled for a five-year period. It states that between 60 and 75% of children survive.
More information about the diagnosis of brain tumors in children can be found in the following video.