Organic brain damage (encephalopathy) in children
Brain cells are fragile and vulnerable. A variety of factors can affect their condition and vitality. Children's neurons are especially vulnerable. We will tell in this article what the diagnosis of “encephalopathy” means and what to do to parents if the child has such a pathology.
What it is?
Encephalopathy is called organic brain damage. This means that under the action of unfavorable trigger factors, neurons (cells of the nervous system) began to die. First, the metabolic processes in the neurons are disturbed, then, if the negative factor is not eliminated, the cells begin to die, and therefore the brain functions in particular and the central nervous system as a whole start to be disturbed.
Encephalopathy is of two types - congenital and acquired. Features of the diagnosis in childhood are that most often in children congenital pathology is detected, and the acquired forms of brain disease are characteristic mostly of adults and the elderly. Moreover, the diagnosis may sound in the first months of the child's life. Most often, the first signs become noticeable within a week after birth, if the child is full-term, and within 4 weeks if the baby was born before the obstetric period.
Detection of encephalopathy is not a sentence, but only an incentive to act. With timely medical response and compliance with all recommendations from the parents in 90% of cases, it is possible to compensate for the loss of cells and cure the child. Therapy will require a joint approach to the treatment of a pediatrician, a neurologist and other specialists.
The reasons
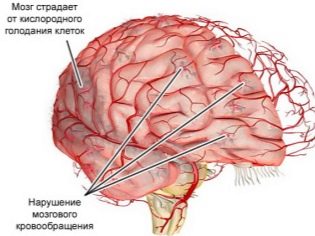
The most frequent causes of perinatal encephalopathy are the negative factors that influenced the fetus while it was still in the womb. The most dangerous are prolonged intrauterine hypoxia, as well as mother-borne infectious diseases and intrauterine infection of the baby. Damage to brain cells can also occur as a result of fast or prolonged labor, in which the child has experienced acute hypoxia, as well as birth injury to the head and neck.
Very often, encephalopathy closely coexists with other malformations, such as heart and vascular defects. Often, premature babies are susceptible to the disease. Encephalopathy acquired at an early age can develop due to trauma, for example, as a complication of traumatic brain injury, due to toxin poisoning, as a serious complication of an infectious disease that the child has had. Organic brain damage can occur with congenital diabetes, with adrenal insufficiency, in the presence of tumors in the brain.
Becoming a concomitant cause of the development of encephalopathy can malformations of the kidneys and liver of the baby.
Defeat in newborns can be anoxic, developed after a long resuscitation period (most common in preterm infants), residual-organic, in which some congenital factors are combined with residual, for example, after a difficult birth, focal and unspecified. Residual encephalopathy occurs in infants less frequently than in older children. Also common is the unspecified form of the disease, when the true cause of the death of central neurons cannot be established.
Symptoms and signs
The specific signs and manifestations of an organic lesion may be different, it all depends on how large the lesions are, which centers and parts of the brain were involved in pathological processes. Most often, the first signs of perinatal encephalopathy are:
- lack of cry after birth for a period set by obstetricians;
- faint cry after birth;
- Apgar score lower than 7/7;
- sluggish sucking reflex or lack thereof;
- sleep disturbances (frequent waking, restless sleep, sleep that is too long);
- nervous and hysterical crying or quiet monotonous frequent crying;
- heart rhythm disorder;
- drooping of the head and arching the back;
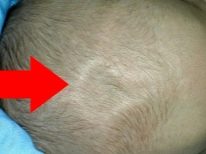
- pulsating and visually "swollen" spring;
- strabismus;
- plentiful and often regurgitation "fountain";
- excessive inhibition of the child, sluggish emotional reactions, as well as excessive excitability and activity;
- convulsions.
Not always signs are obvious and obvious. Quite often there is some one (two, three) trait, and they are expressed sluggishly, so parents can not even guess about the true origin of the problems in the behavior of the baby.
An older child in the case of resistant encephalopathy may begin to complain of systematic headaches, memory problems, dizziness, bouts of unconsciousness, loss of coordination of movements and balance.
Diagnostics
A pediatrician and a neurologist can suspect an acute brain organic disorder in a child. Confirming their concerns or refuting can modern methods of diagnosis, such as neurosonography, MRI, Echo EG, CT, EEG. When performing an ultrasound of the brain to the child, an additional Doppler study of the characteristics of the blood supply to the brain is required. This information allows you to set the lesions.
Additionally, the child is prescribed general blood and urine tests, hormone tests, and sugar levels. If necessary, carry out ultrasound of other internal organs (in case of suspected defects), and also recommend consultations of related specialists. Sometimes there is a need for puncture of cerebrospinal fluid.
It is impossible to make a diagnosis “by eye” in this case, and if some neurologist assures parents that the child has encephalopathy, but does not prescribe additional examinations, it is impossible to trust the diagnosis.
Treatment
It is said that nerve cells do not regenerate. In general, this is so, but in childhood the compensatory abilities of the body are greater than ever, and therefore proper care and adherence to the recommendations prescribed by a doctor help to level out the “losses” - healthy cells take over the functions of dead neurons.
The treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the organic damage. If it is an infection, then treatment of the infection begins, if the cause was poisoning with toxins, detoxification therapy is carried out. If encephalopathy is caused by hypoxia, vitamin therapy, oxygen masks, medications to improve cerebral circulation, as well as vascular agents are recommended for treatment. At the same time, massage, therapeutic exercises, water procedures are recommended, and physiotherapy is recommended for children who have come out of infancy.
Where the treatment will take place - at home or in the hospital, depends on how severe the lesion is. In severe cases, the baby is placed in intensive care, artificial respiration is performed, hemodialysis is performed. Treatment of encephalopathy is always quite long, so parents should be patient.
In addition to drugs that are designed to mobilize compensatory capabilities, funds are assigned to relieve individual symptoms. When convulsions is carried out anticonvulsant therapy, with vomiting prescribed antiemetic treatment.
In the most severe cases, the child is treated promptly, but neurosurgeons have to resort to services, fortunately, quite rarely.
During treatment, the child should receive adequate nutrition, he is shown walking, hardening.
Forecast and possible consequences
As already mentioned, the vast majority of cases of perinatal encephalopathy respond well to treatment, provided that the diagnosis is made in a timely manner and the treatment is correct. The likelihood of future consequences is minimal.
In the case of second and third degree encephalopathy, the consequences of the death of central neurons for future health can be quite noticeable. Among them are the occurrence and development of hydrocephalic syndrome, systematic migraines, dizziness, fainting, paralysis and paresis, asthenia, various neuroses and hysteria, epilepsy, impaired hearing and vision, difficulty with social adaptation, deviant behavior.
Severe forms of encephalopathy often lead to the death of a child, the development of cerebral palsy, a wide range of mental disorders, idiocy, dementia.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent organic brain damage in the child must be taken during pregnancy. It is important to be registered in the antenatal clinic, in time to pass all the necessary tests. In the case of an infectious disease in the period of childbearing, it is important to urgently receive qualified medical assistance.
During pregnancy, a woman should avoid situations that are dangerous for the child from the point of view of hypoxia development by all possible methods - do not smoke or take alcohol and drugs, avoid strong stress, do all the prescribed ultrasounds and CTGs, take longer to walk in the open air, take vitamins eat full. After childbirth, it is important to avoid the action of toxic substances on the baby, as well as to prevent infections with influenza and ARVI.
For information on how to treat encephalopathy in children, see the next video.