Use of Oxytocin during and after childbirth
Sometimes during labor, doctors decide to stimulate the process with medications to make labor easier and faster. There is a lot of controversy about the need to induce and stimulate childbirth, and many women are very afraid of this. They are especially afraid of the introduction of "Oxytocin", because of such a drug there are many negative reviews from mothers who mention the harmful effects on both women and children. Therefore, during pregnancy, future mothers are often interested in whether Oxytocin is really dangerous and when its use is justified.
What it is?
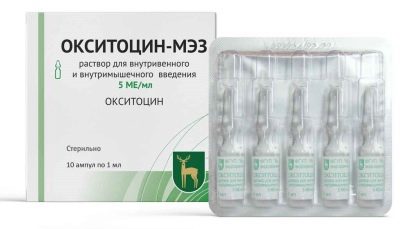
"Oxytocin" is a hormonal drug, which is produced by many Russian and foreign pharmaceutical companies only in an injection form. Its main component is a synthetic hormone, which is a complete analogue of oxytocin, which is produced in the human body. Its synthesis occurs in a section of the brain called the hypothalamus, after which the hormonal substance is transferred and accumulates in the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, from which it is released into the bloodstream.
The main objective of this hormone, actively forming by the end of pregnancy, is increasing the tone of the uterus and the activity of its smooth muscles, due to which the labor activity begins. Oxytocin affects specific receptors located in the muscular layer of the uterus, and increases the content of calcium ions in its cells. This leads to the stimulation of rhythmic contractions, strengthening and frequent contractions. In addition, under the action of such a hormone, the cervix of the uterus is reduced and opens more actively.
Oxytocin is equally important for normal lactation. This hormone acts on the mammary glands, stimulating smooth muscles in the alveoli, making milk easier to enter the sinuses and is released from the breast. In addition, studies have shown that oxytocin is important for reducing fear and anxiety, as well as for partner relationships (this hormone brings a sense of calm and increases confidence).
The "Oxytocin", produced in ampoules, also has all these properties. The uterus reacts to the drug almost immediately if the drug is injected intravenously, and after about 3–7 minutes if the solution is injected intramuscularly. The effect of the drug lasts from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the method of application and the sensitivity of the receptors in a particular woman.
The medicine itself is a clear liquid poured into 1 ml glass ampoules. Usually it is colorless, but a slight yellow tint is also the norm. The patient receives 5 IU of the hormone from the contents of one ampoule, and sterile water is an auxiliary inactive component of the medication, but some manufacturers also have acetic acid and chlorobutanol hemihydrate in the solution. One pack of "Oxytocin" includes 5 or 10 ampoules.
Why use during childbirth?
First of all, “Oxytocin” is administered if the amount of naturally-produced hormone in the woman's mother’s body is too low and the delivery process is delayed, which becomes dangerous for the expectant mother and baby. In this situation, the injection is performed when the contractions suddenly began to weaken or completely stopped. In this case, the cervix must be ripe and softened.
In addition, "Oxytocin" is used in such cases:
- if there is a danger to the life of the mother due to preeclampsia;
- if the amniotic fluid is poured out and the labor does not begin;
- if the child has a Rh-conflict and you want to cause birth faster;
- if there are signs of post-term pregnancy;
- if the fetus died in utero.
Why is introduced after childbirth?
Injections of "Oxytocin" after birth are necessary at the risk of bleeding and poor uterine contraction. With these indications, the drug is the prevention of serious complications, for example, if the postpartum uterus does not return its natural size, it threatens to penetrate the infection and severe blood loss. It is also administered to women undergoing cesarean section, so that the uterus is normally reduced in the postoperative period. Due to the effect of oxytocin on lactation, injections can also be given if there is insufficient milk release.
Instructions for use
During childbirth
"Oxytocin" can be injected either intramuscularly or into a vein. In addition, the doctor may prick this medicine directly into the tissue of the uterus, for example, in its wall or in the neck. During the use of the medication, both the uterine contractions in the woman and the heart activity in the infant must be monitored in order to have time to react to any negative changes.
The dosage of the drug is determined individually, as it affects both the route of administration and the clinical situation. If the drug is decided to be introduced into muscle tissue, then a single dose will be from 2 to 10 IU. The drug may be administered intravenously in a jet (this injection is performed very slowly) or with the help of a dropper.
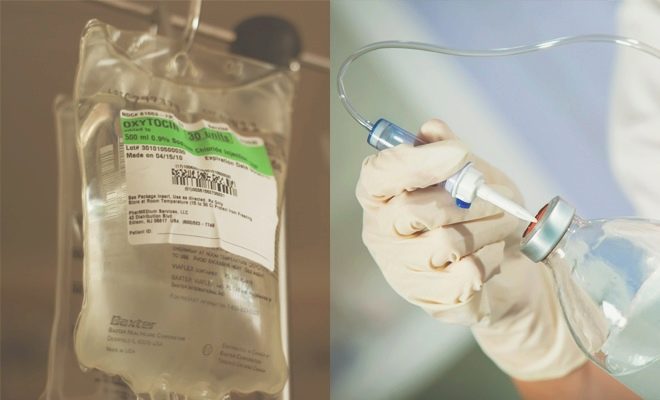
With intravenous injections, a single dosage is usually 5 IU. If drip infusion is prescribed, this amount of hormone is added to 500 ml of saline or glucose solution. Drug administration starts at a low speed, and then gradually increase the number of drops per minute until the uterus begins to contract normally, after which the rate of hormone intake is gradually reduced.
After childbirth
If “Oxytocin” is prescribed to prevent uterine bleeding, the drug is administered intramuscularly within two to three days after birth, 1-3 times a day. If the bleeding has already begun, usually an infusion is used, adding up to 40 IU of oxytocin per 1000 ml of saline. During cesarean section, 5 IU medications are injected directly into the muscle tissue of the uterus immediately after the last place has separated.
Can it hurt?
Despite the many positive functions and benefits of oxytocin, such a hormone can cause negative consequences. Sometimes this is due to the fact that it is not used according to indications, namely: if a woman wants to give birth faster or an unscrupulous doctor seeks to complete the birth process as soon as possible, thereby reducing the duration of this period of risk to the body of the patient and the fetus. The causes of the harmful effects of "Oxytocin" on the mother and baby are also non-compliance with contraindications and erroneous dosage.
It should be understood that Oxytocin, like many other medicines, has its side effects.
But, since it acts immediately on the parturient and on the fetus, the negative effect of the drug can also spread immediately to the woman’s body and to the baby. In the future mother, the medication can provoke vomiting, bradycardia, increased blood pressure, nausea, arrhythmia, water retention, bronchospasm and other side effects.
In an infant, Oxytocin can cause neonatal jaundice, a decrease in the amount of fibrinogen, an impaired heart rate, and other negative symptoms. Crumbs, which were born after the stimulation of the genera with Oxytocin, often behave restlessly, sleep poorly, and are easily excitable. They show increased muscle tone, frequent regurgitation, hyperactivity and other disorders. This is due to the fact that the hormone spasms blood vessels in the uterus, because of which the baby loses oxygen.
As already mentioned, it is very important to determine before administration of the drug whether there are any contraindications for “Oxytocin”. This medicine is prohibited to prick to stimulate childbirth if:
- the fruit is located incorrectly, for example, transversely or obliquely;
- the pelvis of a pregnant woman is narrow;
- the fruit is too large;
- a woman has hypersensitivity to any component of the medication;
- The presentation of the infant is abnormal, for example, facial;
- childbirth began prematurely;
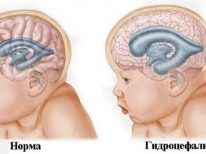
- baby hydrocephalus;
- there is a risk of uterine rupture, for example, a woman has had a fibroid or a cesarean section;
- the woman previously had multiple births;
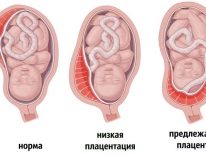
- An ultrasound scan revealed placenta previa;
- on the cervix there is a tumor or cicatricial changes, due to which its full disclosure is impossible;
- the cervix is not yet ripe;
- a woman has serious diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- future mom suffers from bronchial asthma.
If the pregnancy is multiple, there is hypoma in the uterus or the fetus has revealed hypoxia, the question of the use of Oxytocin is decided individually, as these contraindications are relative.
Another condition for minimizing the damage from stimulation with “Oxytocin” is to observe the correct dosage of the solution, because if it is exceeded, too much stimulation of the uterus will occur, which can lead to rupture of its walls and premature separation of the placenta. Too much of a hormone dose can also cause bleeding in the postpartum period, and in an infant, overdose of Oxytocin will cause hypoxia or even asphyxia.
Do I need to prick?
Although "Oxytocin" and has some side effects, and the process of childbirth after stimulation with such a hormone may not go quite smoothly, but in some cases, the injection can not do. Competent doctors prescribe it only in situations where all the disadvantages of the medication turn dark before a real threat to the life of the mother or baby. In their opinion, the use of this medication is less harmful than an unscheduled cesarean section (in situations where there was no indication for surgery).
So that the minuses of "Oxytocin" do not affect the health of the mother and karapuz, a good specialist will take into account all the important factors, including the rate of neck opening, the length of the dry period, and the size of the woman's pelvis, and history. And only if the use of the hormone is justified, it will appoint a future mother.
It is also necessary to clarify that it is permissible to prick "Oxytocin" during childbirth or in the postpartum period only within the walls of a medical institution.
See the following video for oxytocin and its role.