Polyoxidonium for children: instructions for use
Every mother of an often sick baby thinks about strengthening the immunity of a child. Pharmacies offer many drugs that belong to the group of immunomodulators.
Among them there is a domestic medicine called Polyoxidonium. Is it prescribed to children, and how does it act on the children's body?
Release form
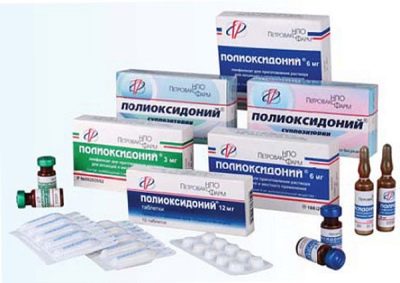
Polyoxidonium is manufactured by the Russian company NPO Petrovax Farm in three versions:
- Pills. They are sold in cellular packages of 10 pieces, and in one box there are 1-2 packages (10 or 20 tablets). Such Polyoxidonium is characterized by a round shape, the presence of risks on one side, and the letters “ON” on the other. The color of the tablets is usually white, but may be tinged with yellow.
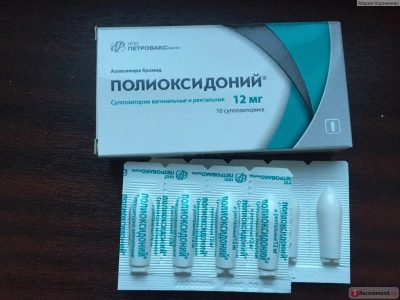
- Suppositories. This form of the drug has a homogeneous structure, a light yellow tint, a specific aroma (cocoa butter gives it) and a torpedo shape. The medicine is sold for 10 candles in one pack, packed in 5 pieces in a PVC film sheath.
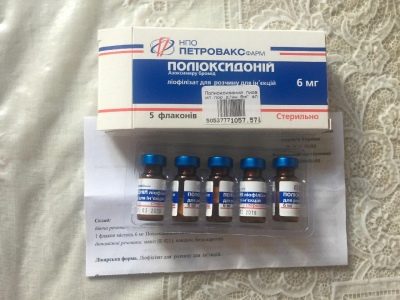
- Lyophilisate. Such Polyoxidonium is a porous mass of white-yellow color placed in glass ampoules. The vials are sealed with a rubber stopper and aluminum cap. Depending on the dosage, there is 4.5 or 9 grams of the drug inside one bottle. In one box 5 bottles are sold, which can be located between cardboard inserts and in film packaging. Especially for hospitals, boxes with cardboard partitions are produced, inside which 50 bottles of lyophilisate are placed.
Composition
The main ingredient of any form of polyoxidonium is called azoxymere bromide. Its quantity in different preparations differs:
- in one tablet this substance is contained in a dose of 12 mg and supplemented with mannitol, potato starch, povidone K17, stearic acid, lactose monohydrate;
- one candle may contain both 6 mg and 12 mg of azoxymere, as well as cocoa butter, povidone K17 and mannitol;
- in one bottle Azoxymere lyophilisate is represented by a dosage of 3 mg or 6 mg and is combined with povidone K17 and mannitol.
Operating principle
Polyoxidonium has a complex effect on the human body:
- Such a drug has an immunomodulatory effect associated with a direct effect on phagocytic cells and natural killers. In addition, azoxymere bromide stimulates the production of antibodies and interferons of the alpha and gamma types.
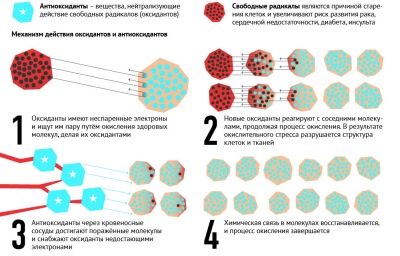
- The drug has antioxidant properties due to the high molecular nature of its main component and the characteristics of its structure. It is able to intercept free radicals and prevent lipid peroxidation due to the destruction of active iron ions.
- Reception Polyoxidonium has a detoxification effect. It consists in blocking toxins and salts of heavy metals, as well as in stimulating their elimination.
- The drug also has a moderate anti-inflammatory effect, as it normalizes the ratio of anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory cytokines.
The use of Polyoxidonium increases the resistance of the organism to both local and generalized infections. In this case, the drug improves protection against bacteria and against a viral or fungal infection.
Through the use of Polyoxidonium, it is possible to restore the normal state of immunity if the immunodeficiency is secondary (if various infections, postoperative complications or injuries have led to it).
If the drug is used under the tongue, it activates the early immune defense against infectious agents by stimulating the bactericidal properties of immune cells and saliva.
If Polyoxidonium is swallowed, then the drug stimulates the cells of the lymph nodes in the intestine. At the same time, the drug has no carcinogenic, teratogenic and allergenic effects.
In addition, the drug does not provoke irritation of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nasopharynx when applied topically.
A rectal suppository or an ingested tablet is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and has a bioavailability of approximately 70%. After swallowing, the maximum of azoxymere bromide in plasma is noted after 3 hours, with the administration in the rectum of the drug in suppositories - after 1 hour.
With injection, the bioavailability of the drug is higher (about 90%), and the maximum concentration in the blood is reached faster (after 40 minutes). The drug does not accumulate, and turns into low molecular weight compounds and is excreted mainly by the kidneys.
Indications
Monotherapy with Polyoxidonium (receiving only this drug) is prescribed with the preventive purpose:
- to prevent recurrence of herpes on the lips or in the area of the nose (prescribed pills), as well as in urogenital organs with herpes lesion (use candles);
- to reduce the frequency of exacerbations in chronic inflammatory processes in the region of the oropharynx, middle or inner ear, the delivery sinuses or the upper respiratory tract (use suppositories and tablets);
- to reduce the risk of secondary immunodeficiency (used tablet form and candles);
- for the prevention of SARS and influenza during an epidemic or in the period before the seasonal outbreak of such diseases (prescribed suppositories or lyophilisate);
- to reduce the risk of infection after surgery (using lyophilisate).
For the purpose of treatment, Polyoxidonium in any form is used in children in combination with other drugs for infection or acute inflammation in the mouth, nose, bronchi, ears, pharynx, and paranasal sinuses.
Besides, medication prescribed for allergic diseasesif they are complicated by infection (including those with atopic dermatitis and bronchial asthma). Lyophilisate is additionally used in children with intestinal dysbiosis.
Polyoxidonium in candles also written out:
- with tuberculosis;
- with cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis and other inflammatory diseases in the pelvic area;
- for rheumatoid arthritis;
- for trophic ulcers, burns, or fractures (to activate tissue regeneration);
- in cancer pathologies to reduce the negative effects of other drugs, radiation and chemotherapy.
From what age is appointed?
Children of the first years of life are allowed to give only a lyophilisate, since in this form Polyoxidonium is allowed from 6 months of age.. If the child is already 3 years old, tablets can be used in his treatment.
As for the candles, in childhood only the drug is shown with a dosage of 6 mg. Such suppositories are used in patients older than 6 years.
Contraindications
Polyoxidonium can not be used in such cases:
- if hypersensitivity to azoxymere bromide or another component of the selected form of the drug is detected in a small patient;
- if the child has developed acute renal failure.
Tablets are not prescribed for children with glucose and galactose malabsorption syndrome, as well as with a deficiency of lactase and intolerance to milk sugar.
If a child has been diagnosed with chronic renal failure, the treatment is carried out carefully and the medication is used no more than twice a week.
Side effects
Any negative effects while taking Polyoxidonium tablets are not observed.Medication in candles in children with hypersensitivity provokes itching, swelling or redness of the area around the anus.
When using a lyophilisate in rare cases, body temperature rises, an allergic reaction develops or the child’s behavior becomes restless. In addition, chills, induration, redness, or soreness at the injection site may occur with the injection.
If the child in the treatment or prophylactic use of such a drug felt unwell, you should inform your doctor.
Instructions for use
Pills
Polyoxidonium in solid form can be taken in two ways:
Absorb under the tongue. Such use is prescribed to children older than 3 years.
Ingested when drinking water. This method is recommended for patients older than 10 years only with respiratory diseases.
The drug is given before meals in about 20-30 minutes. If such Polyoxidonium is used for treatment, then the drug should be absorbed or swallowed twice a day. A single dose for small patients 3-10 years is half a tablet, for children over 10 years old - the whole tablet.
For prophylactic purposes, a solid form of Polyoxidonium is given in the same doses - half a tablet for a child under 10 years of age and a whole tablet for a patient who is already 10 years old.
In order to prevent SARS, flu or complications of a chronic infection, the medicine is taken once a day. If the drug is prescribed for the prevention of recurrence of herpes, it should be given twice a day to the child, as in the treatment.
The duration of the course in childhood in most cases is 7 days.
For the prevention of exacerbations of any chronic infections, tablets dissolve within 10 days.
A 10-day course is also needed in the treatment of pathologies of the respiratory tract, if the pills are administered orally. Re-admission after the course is possible after 3-4 months.
Candles
This form of polyoxidonium in children is used exclusively rectally. A candle is inserted into the rectum after cleaning it with an enema or after a bowel movement.
A single dose for patients 6–18 years old is one suppository containing 6 mg of active compound. Depending on the reason for the use of such schemes:
- Three days for 1 candle daily, and then another 7 suppositories every other day (a total of 10 candles per course). Such an intake of Polyoxidonium is prescribed in the treatment of exacerbations of chronic pathologies of an infectious nature.
- 1 candle every day for 10 days. This scheme is used for acute infections, allergic diseases with infection, exacerbation of urological diseases or with the aim of activating the regeneration processes. In addition, since the drug is taken for the prevention of SARS and influenza.
- Three days on 1 suppository every day, and then 17 candles every other day (total 20 candles per course). This mode is used for lesions of the lung tuberculosis bacillus. After completing the course, supportive treatment may be prescribed for 2-3 months, during which suppositories are placed twice a week.
- 1 suppository every other day for 20 days (10 candles in total). This scheme is prescribed for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for the prevention of acute herpes or other chronic infections.
- 1 candle daily for 2–3 days, and then 1 suppository twice a week (up to 10 candles in total). According to this scheme, Polyoxidonium is prescribed to patients with oncopathology, starting treatment 2-3 days before radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Lyophilisate
This form of polyoxidonium can be used in three ways:
- Parenteral - the drug is injected into muscle tissue or drip into a vein.
- Intranasal - medication drip into the nose (in one of the nasal passages).
- Sublingual - the drug is dripped into the mouth under the tongue.
The method of application, the desired dose and duration of therapy are determined by the doctor taking into account the severity of the disease and the age of the child.Before parenteral administration, the contents of the vial are mixed with a solvent, which is usually served by sterile saline.
For intramuscular injections, special sterile water can also be used, and if the child is difficult to tolerate injections, the lyophilisate can be diluted with a 0.5% novocaine solution (if there is no allergy to such anesthetic).
The bay is filled with liquid by a porous mass, it is left for 2-3 minutes, and when the medicine swells, gently mix, making rotational movements. If a drip is administered to a vein, then the diluted drug is then injected into a bag or vial of saline.
To use the lyophilisate sublingually or in the nose, it must also be made liquid. To do this, in one bottle with a dosage of 3 mg add 1 ml of non-heated boiled water, saline or distilled water. With this dilution, 20 drops of the drug, 0.15 mg of the active ingredient in each drop, are obtained. If a vial with a dosage of 6 mg is used, 2 ml of solvent is added to it, thereby obtaining 40 drops of 0.15 mg.
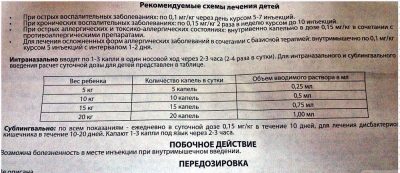
The daily dose of lyophilisate in childhood is determined by weight and is 0.1 mg / kg for parenteral treatment and 0.15 mg / kg (1 drop) when used in the nose or under the tongue. The maximum daily dosage of the medication is considered to be 40 drops, that is, children weighing more than 40 kg are given no more than 40 drops per day.
The dose calculated per day for intranasal use is divided into 3 doses, and for sublingual - by 2. The interval between the use of drops should be at least 1-2 hours. The duration of the course is usually up to 10 days, but for the prevention of SARS and flu, the medication can be dripped up to 1 month.
Overdose
There have been no cases of adverse effects of Polyoxidonium in the overdose until this time. If, after accidentally taking any form of medication in too high a dose, any negative symptoms appear, you should show the patient to the doctor.
Interaction with other drugs
According to the manufacturer’s information, Polyoxidonium can be combined with antihistamines, antibiotics, antiviral drugs and many other medicines.
Terms of sale
Lyophilisate is the only form of Polyoxidonium for which you need a prescription from a doctor. Other types of medication can be freely purchased at any pharmacy without a prescription, but consultation with a physician is desirable. The average price of 10 tablets is 700-750 rubles, one pack of 10 suppositories of 6 mg costs approximately 850-900 rubles, and for 5 bottles of lyophilisate of 3 mg you need to pay from 700 to 800 rubles.
Storage features
The shelf life of all types of Polyoxidonium is 2 years and is marked on the package. If it has expired, the use of this drug in children is unacceptable. To store any of the medicines you need to find a place in which it will be inaccessible to children.
The temperature regime for each form of polyoxidonium will differ:
- tablets can be kept at a temperature of +2 to +25 degrees;
- storage of suppositories requires a cool place with a temperature of +2 to +15 degrees;
- sealed lyophilisate should be kept in the refrigerator, since the storage temperature recommended for manufacturers for this form is from +2 to +8 degrees;
- diluted lyophilisate, which is going to drip under the tongue or in the nose, it is permissible to store at room temperature for 48 hours after opening and breeding. If the drug is diluted for injection, it can not be stored.
Reviews
On the use of Polyoxidonium in children, parents in most cases respond positively. The main advantages of the drug are its quick therapeutic effect, safety in childhood, a wide range of applications and many dosage forms.
Among the disadvantages usually mention the high cost of this drug.. Also, sometimes you can see negative reviews, which indicate the lack of improvement after a course of treatment.
The opinion of immunologists and pediatricians about Polyoxidonium is different. Some doctors note its positive effect and use in their practice, prescribing children with tonsillitis, adenoiditis, influenza, dysbiosis, rotavirus infection and other diseases.
Other doctors, among whom Dr. Komarovsky, doubt the effectiveness of this medication and do not advise using any immunomodulators in children without indications and an immunogram.
Analogs
Instead of polyoxidonium, the doctor may prescribe another medicine with a similar effect on the immune system, for example:
- Anaferon;
- Groprinosin;
- Wobenzym;
- Tsitovir-3;
- IRS-19;
- Lycopid;
- Derinat;
- Imunorix;
- Arbidol.
Such medicines are presented in different forms, contain different active ingredients and have their own age limits, so the choice of analogue should be entrusted to a doctor.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you how to choose high-quality immunomodulators in the next video.