Dr. Komarovsky about pneumonia in children
The phrase "pneumonia" is very frightening to parents. It does not matter at all how many years or months the child is, this disease among moms and dads is considered one of the most dangerous. Is it really, how to recognize pneumonia and how to properly treat it, says Yevgeny Komarovsky, a well-known children's doctor, author of books and articles on children's health.
About the disease
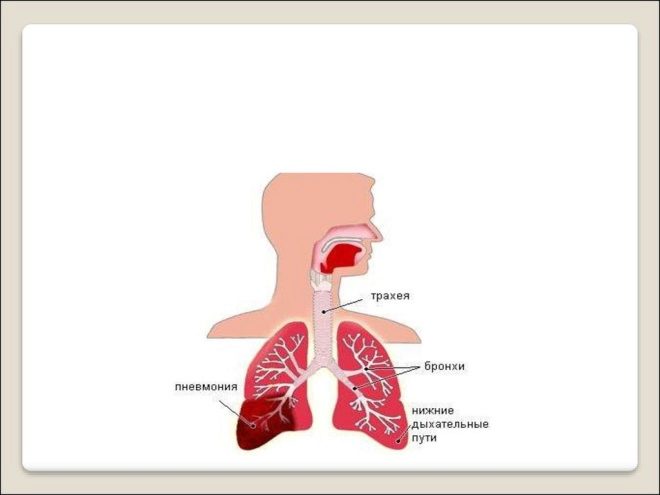
Pneumonia (that's what doctors call what people call pneumonia) is a very common disease, an inflammation of the lung tissue. Under the same concept doctors mean several ailments. If the inflammation is not contagious, the doctor will write pneumonitis on the card. If the alveoli are affected, the diagnosis will sound differently - "alveolitis", if the mucous membrane of the lungs is affected - "pleurisy."
The inflammatory process in the lung tissue is caused by fungi, viruses and bacteria. There are mixed inflammations - viral-bacterial, for example.
The illnesses included in the concept of "pneumonia" all medical reference books are classified as quite dangerous, because of the 450 million people from around the world who become ill with them a year, about 7 million die due to incorrect diagnosis, incorrect or delayed treatment, and also on the speed and severity of the course of the disease. Among the dead, about 30% are children under 3 years old.
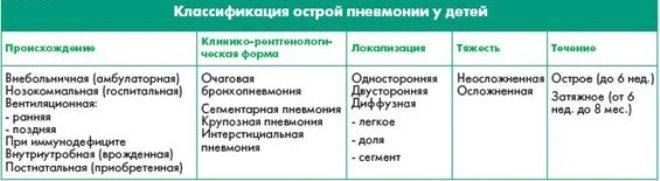
According to the location of the source of inflammation, all pneumonia is divided into:
- Focal;
- Segmental;
- Share;
- Drain;
- Total.
Also, inflammation can be bilateral or unilateral, if only one lung or part of it is affected. Rarely, pneumonia is an independent disease, more often it is a complication of another disease - viral or bacterial.
The most dangerous pneumonia is considered for children under 5 years old and the elderly, among such cases the consequences are unpredictable. According to statistics, they have the highest mortality rate.
Yevgeny Komarovsky claims that the respiratory organs are generally the most vulnerable to various infections. It is through the upper respiratory tract (nose, oropharynx, larynx) that most of the germs and viruses enter the body of a child.
If the baby’s immunity is weakened, if the environmental conditions in the area where he lives are unfavorable, if the microbe or the virus is very aggressive, the inflammation does not linger only in the nose or larynx, but falls below - in the bronchi. This disease is called bronchitis. If it cannot be stopped, the infection spreads even lower - to the lungs. There is pneumonia.
However, airborne infection is not the only way. If we consider that the lungs, in addition to gas exchange, perform several other important functions, it becomes clear why sometimes the disease appears in the absence of a viral infection. Nature placed on the human lungs the mission to moisten and warm the inhaled air, clean it from various harmful impurities (the lungs function as a filter), and also in a similar way filter circulating blood, extracting many harmful substances from it and neutralizing them.
If the baby has undergone an operation, has broken his leg, has not eaten something and has received severe food poisoning, has burned himself, has cut himself, this or that amount of toxins, blood clots, etc., gets into the blood in various concentrations. using a protective mechanism - cough.However, unlike household filters that can be cleaned, washed or thrown away, the lungs can neither be washed nor replaced. And if one day some part of this “filter” fails, becomes clogged, the very disease that parents call pneumonia begins.
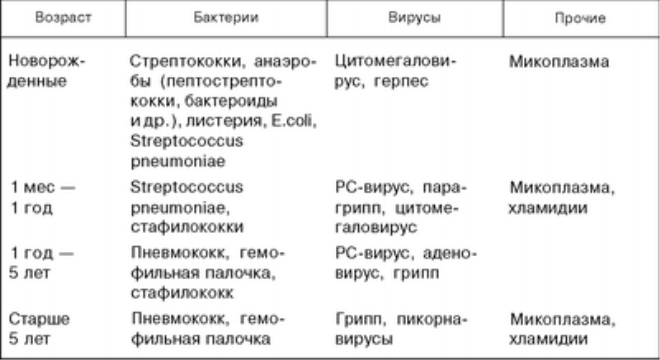
The causative agents of pneumonia can be a variety of bacteria and viruses.. If a child is sick while in hospital with another ailment, then he will most likely have bacterial pneumonia, which is also called hospital or hospital. This is the most difficult of pneumonia, as in the conditions of hospital sterility, the use of antiseptics and antibiotics, only the strongest and most aggressive microbes survive, which are not so easy to destroy.
The most common in children is pneumonia, which originated as a complication of a viral infection (ARVI, flu etc.). In such cases of inflammation of the lungs accounts for about 90% of the respective children's diagnoses. This is not even due to the fact that viral infections are “terrible”, but due to the fact that they are extremely widespread, and some children suffer from them up to 10 times a year or even more.
Symptoms
To understand how pneumonia begins to develop, you need to be well aware of how the respiratory system works in general. The bronchi constantly exude mucus, whose task is to block dust particles, microbes, viruses and other unwanted objects that enter the respiratory system. Bronchial mucus has certain characteristics, such as viscosity, for example. If it loses some of its properties, instead of fighting the invasion of alien particles, it itself begins to cause a lot of "trouble."
For example, too thick mucus, if the child breathes dry air, clogs the bronchi, interferes with normal ventilation. This, in turn, leads to stagnation in some parts of the lungs - pneumonia develops.
Often, pneumonia occurs when the child's body rapidly loses its fluid reserves, and bronchial mucus thickens. Dehydration of varying degrees can occur with prolonged diarrhea in a child, with multiple vomit, high heat, fever, with insufficient fluid intake, especially against the background of the previously mentioned problems.
Parents may be suspected of having pneumonia in a number of ways:
- Cough has become a major symptom of the disease.. The rest, present before, gradually pass, and the cough only intensifies.
- The child became worse after improvement. If the disease has already receded, and then suddenly the baby felt bad again, this may well speak about the development of complications.
- The baby cannot take a deep breath. Every attempt to do this leads to a strong coughing fit. Breathing is accompanied by wheezing.
- Pneumonia can manifest through the pallor of the skin. against the background of the above symptoms.
- The child had shortness of breath, and antipyretic drugs, which always always quickly helped, ceased to have an effect.
It is important not to engage in self-diagnostics, because the absolute way to determine the presence of inflammation is not even the doctor himself, but an X-ray of the lungs and bacterial sputum, which will give the doctor an exact idea of which causative agent caused the inflammatory process. A blood test will show the presence of antibodies to viruses, if the inflammation is viral, and Klebsiella found in the feces will come across the idea that pneumonia is caused precisely by this dangerous pathogen. At home, the doctor will definitely listen and tap the lung area of a small patient, listen to the nature of wheezing during breathing and during coughing.
Is pneumonia contagious?
Whatever is caused by pneumonia, it is in almost all cases contagious to others.If these are viruses, they are easily transmitted to other family members by air, if the bacteria are by contact and sometimes by airborne droplets. Therefore, a child with pneumonia should be allocated a separate dish, towel, bedding.
Treatment according to Komarovsky
After the diagnosis is established, the doctor will decide whether the child will be treated - at home or in a hospital. This choice will depend on how old the child is and how severe the pneumonia is. Pediatricians are trying to hospitalize all children under 2 years old, since their immunity is weak, and the treatment process should therefore be constantly monitored by medical personnel.
All cases of obstruction during pneumonia (pleurisy, bronchial obstruction) are the basis for the hospitalization of children of any age, since this is an additional risk factor, and recovery from such pneumonia will not be easy. If the doctor says that you have uncomplicated pneumonia, then with a high degree of probability he will allow her to be treated at home.
Most often, pneumonia is treated with antibiotics, and it is not at all necessary that you have to do a lot of sick and terrible injections.
The doctor will determine the antibiotics that can quickly and efficiently help, based on the results of the analysis of sputum for backwater.
Two thirds of cases of pneumonia, according to Evgeny Komarovsky, are perfectly treated with pills or syrups. In addition, expectorants are prescribed, which help the bronchi to clear the accumulated mucus as soon as possible. At the final stage of treatment of the child, physiotherapy and massage. Also, kids who are undergoing rehabilitation are shown walks and taking vitamin complexes.
If the treatment is carried out at home, then it is important that the child is not in a hot room, drink enough liquid, a vibrating massage is beneficial, contributing to the discharge of bronchial secretions.
Treatment of viral pneumonia will proceed in a similar way, with the exception of taking antibiotics.
Prevention
If the child is sick (ARVI, diarrhea, vomiting and other problems), you must make sure that he consumes a sufficient amount of fluid.. Drink should be warm so that the liquid can be absorbed faster.
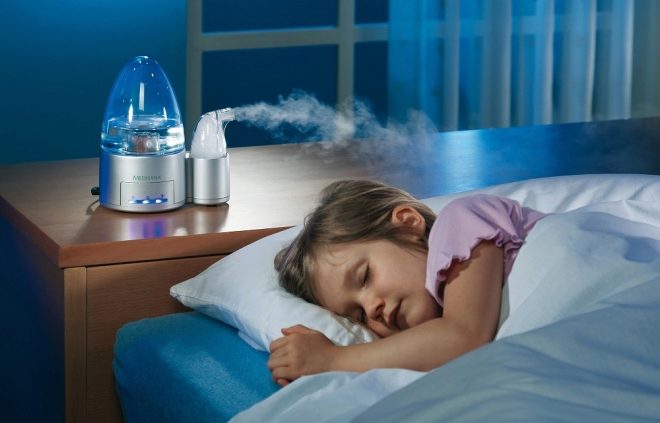
A sick baby must breathe clean, moist air. To do this, you need to ventilate the room, humidify the air with a special device-humidifier or with the help of wet towels hung around the apartment. We can not allow the room was hot.
The best parameters for maintaining the normal level of viscosity of mucus are as follows: air temperature is 18-20 degrees, relative humidity - 50-70%.
If the child is sick, you should try to free his room as much as possible from everything that can accumulate dust - carpets, soft toys, upholstered furniture. A large number of inhaled dust particles only accelerates the thickening of sputum and increases the risk of developing pneumonia. Wet cleaning should be carried out 1-2 times a day, chlorine-based detergents should not be added!
If the child coughs, you do not need to give him all sorts of cough remedies at home.
Cough is needed to get rid of excess sputum. If the cough reflex is stopped at the very peak of the disease with antitussive drugs, then there will be no sputum output, and the risk that pneumonia starts will increase significantly. Mucolytic (expectorant) products (plant-based), the task of which is to dilute the sputum, are welcome, but, according to Komarovsky, with strict observance of all the above points.
With ARVI in any case can not take antibiotics. Even if your doctor advises you to start doing this to prevent pneumonia. Even the newest antibiotic is not able to destroy all the microbes that exist in the human body, while antimicrobial agents do not act on viruses at all.But it has been proven that taking them with influenza or ARVI increases the probability of developing pneumonia by 9 times!
When a cold caused by a viral infection, you should not immediately begin to drip vasoconstrictor drops in the nose to the child. So the higher the likelihood that viruses, bypassing the nose, go straight to the lungs right away and cause an inflammatory process there.
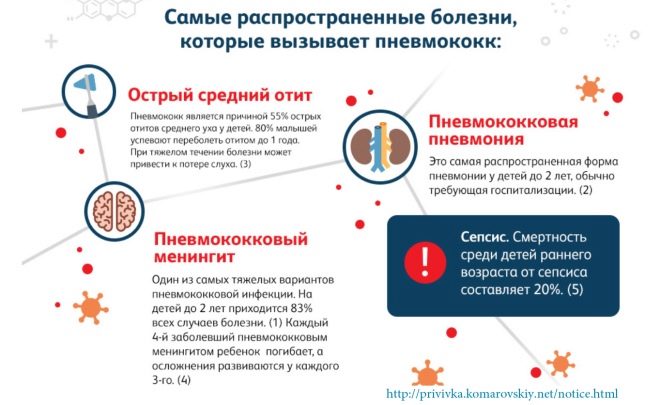
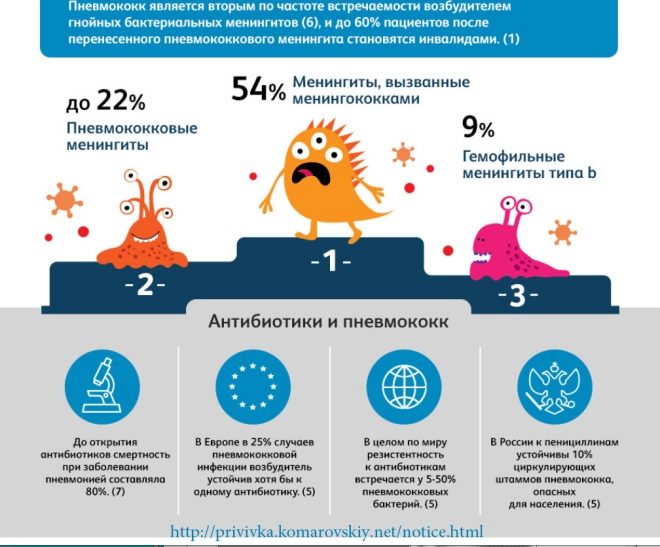
A great way of prevention is vaccination against pneumococcal infection. It is pneumococcus that causes the most severe forms of pneumonia. A child of the first year of life as part of the immunization schedule is given a vaccine that helps the body produce antibodies to pneumococcus. Even if the infection happens, the disease will be easier. The vaccine is administered several times. In the first months of life, 2 years, 4 years, 6 years and 12 years. In any case, it is not worth refusing vaccinations, says Yevgeny Komarovsky.
For details, see the transfer of the doma Komarovsky.