Doctor Komarovsky about Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is found in the child in the analyzes. A microbe with this beautiful name can be extremely dangerous - all parents know about it. But what is the main danger, and how to avoid it, most moms and dads do not know. The famous pediatrician Yevgeny Komarovsky knows exactly what this “terrible beast” is and what confused parents should do with it.
What it is?
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most dangerous representatives of the family of staphylococcal microbes. It got its name because of the color - under a microscope the bacterium looks like an orange-golden oval grain. It belongs to the category of opportunistic microbes that can cause severe damage under certain conditions. It is quite resistant to antibiotics, for a long time can exist even in an aggressive environment.
Scientists have tried to dry it under the scorching rays of the sun - the germ remained alive for 12 hours. And when they tried to boil it in an oily substance, then for almost 10 minutes it stood firmly at a temperature of 150 degrees.
Staphylococcus aureus - the only one in its family in the process of vital activity, secretes a particularly dangerous substance (enzyme) - coagulase, which violates the composition of the blood. The microbe penetrates into microthrombi, to which the effect of immunity does not extend. This can cause a life-threatening sepsis. When exposed to the bloodstream in different organs, the bacterium of golden color causes severe lesions.
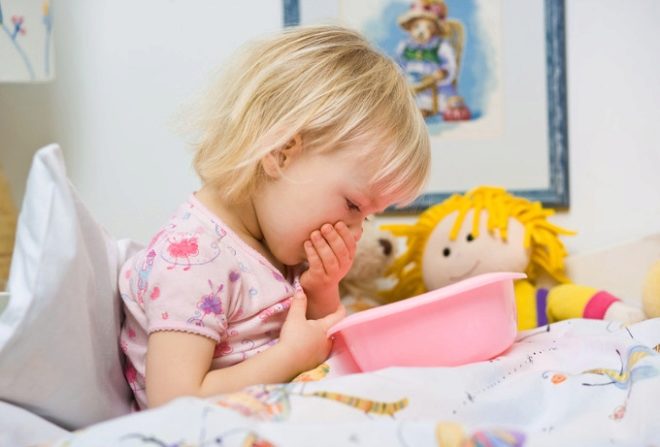
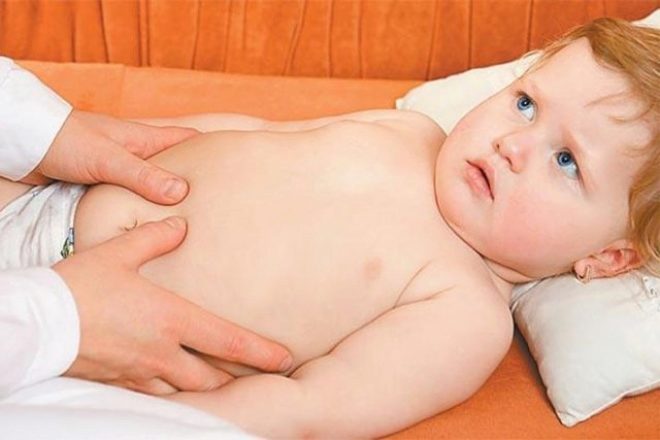
If the microbe got into the lungs - it will be staph pneumonia, difficult to treat form of the disease. If the bacterium has "subsided" in the heart, the valves are affected and the heart activity is disturbed. A bacterium with a systemic infection can be detected in the liver, in the kidneys, in the brain, and in any other internal organ. The most "innocuous" of its existence - life on the surface of the skin, in this case, it causes the occurrence of ulcers, boils. By the way, this microbe is the only one able to survive in a salty environment, which is human sweat. Therefore, if sweat glands are affected, purulent pimples or boils have appeared, then there is no doubt that Staphylococcus aureus is to blame.
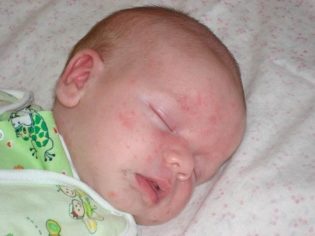
Often with a bacterial cutaneous lesion in infants, parents do not attach rashes Of particular importance, confusing infection with diaper dermatitis, with diaper rash and even diathesis.
Staphylococcal lesion differs from all these “childhood” troubles by the presence of pus and increased body temperature.
The toxins that Staphylococcus aureus secrete during the breeding process are themselves quite dangerous, especially for newborns, which is why an analysis of the presence of this bacillus in a child is required in the hospital.
Every inhabitant of the planet faces this microbe every day. The most frequent "date" with her occurs in food poisoning, After all, the pathogenic microorganism feels great in butter cream, in meat and vegetable salad, especially flavored with mayonnaise, in canned foods. Symptoms of poisoning (vomiting, diarrhea) is caused not by the microbe itself, but again by the toxins that it begins to emit when ingested with an infected food.
The World Health Organization has calculated that of all cases of infection with staphylococci, about a third is accounted for by Staphylococcus aureus. It is this pathogen that is often able to survive in the hospital (with constant treatment with antiseptics), such a "modified" pathogen is the most dangerous because it causes so-called hospital or hospital infections.
All the "horrors" that Staphylococcus aureus is capable of doing, fade slightly before a normal, healthy immunity, the microbe cannot provide anything from its arsenal to it, and therefore for every toxin a healthy person's body finds its antidote, but it takes time.
Symptoms
By itself, staphylococcus does not manifest itself until under the influence of certain circumstances (reduced immunity, associated infections) begins to actively develop and multiply. This will be the beginning of a staph infection that can be easily recognized by the obligatory presence of pus, high fever, an acute inflammatory process.. The symptoms directly depend on the type of lesion - where the staphylococcus hit, what hit it, what is the severity of the lesion:
- On the skin. With such a dislocation of the microbe in the child will appear pustules, boils, "barley" and other purulent formations.
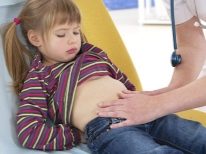
- In the intestine. There will be fever, vomiting, diarrhea, general intoxication of the body.
- In blood. High fever, fever, general serious condition, altered blood count, purulent inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- In the internal organs. When purulent inflammation of certain organs will be different symptoms, depending on the specific organ. For all types of lesions - high fever and severe pain.
Norms and pathology
The norm is the absolute absence of this microbe in bacterial culture. However, such a pure analysis is very rare, in practice it is very rare, remaining only a theoretical probability.
Since staphylococci are present almost everywhere, they surround the child constantly, some microbes can be found in the analyzes that do not pose a danger to his health and life.
So, if, when analyzing a smear in the throat of a child older than a year, 10 to 4 degrees of Staphylococcus aureus were found - this is a variant of the norm, but if the same amount is detected in the infant's smear, this will be considered a threatening pathology. It is also important to monitor the growth of Staphylococcus aureus colonies - for this, bacterial seeding, blood and feces are repeated several times to see how fast the bacteria multiply, how quickly the infection begins to grow.
Treatment according to Komarovsky
The detection of staphylococcus in the analysis of the child is not yet a reason for treatment if there are no pronounced symptoms of infection.
The question of prescribing treatment arises when there are such symptoms, and it is not just a matter of Staphylococcus aureus in the feces or a throat smear, but of a staphylococcal infection.
With all the aggressiveness of staphylococcus golden brown, he has a weak spot, which is used by doctors. The bacterium, which is difficult to kill with antibiotics and antiseptics, can easily be neutralized using the most common brilliant green that is in every home medicine chest. Doctors have not yet found the answer to the question of why this is happening, but this is truly so.
If a staph infection is found in a child who was at home, then the prognosis is more favorable than if the child contracted a golden pathogen in the hospital where he was treated. With a severe course of infection, the child is hospitalized. In the hospital with a probability of 100% put an infant with such a diagnosis.
Home treatment is possible only for children after 3 years, provided that their condition is not serious, does not constitute a danger to life.
Most often, the standard treatment regimen includes:
- Staphylococcal bacteriophage. It is prescribed even for infants.
- Antibiotics. Appointed at the discretion of the attending physician, most often use antibiotics - nitrofurans. The treatment is long - about 14 days.
- With intestinal manifestations (vomiting and diarrhea) prescribe means for oral rehydration, designed to restore the balance of mineral salts and fluids in the body, promptly prevent the state of dehydration.
- Adsorbents. If a child has a staph infection with diarrhea, the doctor may prescribe such medications (“Smecta», «Enterosgel") To reduce the harmful effects of toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus.
- Infection caused by this pathogen is not treated with the help of folk remedies. Dr. Komarovsky warns that self-treatment with "grandmother's" recipes can significantly complicate the condition of the child, since the time required for qualified medical treatment of the ailment is passing.
Tips
If Staphylococcus aureus is found in milk in a nursing mother, this is not a reason to refuse breastfeeding. Komarovsky explains that it is quite difficult to take mother’s milk for analysis, while ensuring its complete sterility. Staphylococcus, which is on the skin of 80% of the population, is very likely to fall into the expressed milk. It will be presented in a small amount and its detection does not mean at all that the child will be seriously infected and will get sick with a staph infection.
Prevention is unlikely to wash hands and other parts of the body, said Komarovsky. Although hygiene is certainly very important. However, there is no guarantee that new microbes will not get into freshly washed hands from the environment. Ways of transmission of the microbe are varied - from airborne to domestic and food. Therefore, the main principles of prevention of staphylococcal infection should be as follows: strengthening the child’s immunity so that no staph is safe for him, hardening, active lifestyle, balanced, healthy diet.
How to treat Staphylococcus aureus, see the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.