Newborn asphyxia: from cause to effect
A child in the womb is in dire need of a steady supply of oxygen. It is important for the work of all organs, tissues, systems.
No less high is the need for oxygen both during and after childbirth. The state of acute shortage - hypoxia can lead to asphyxiation of the newborn - asphyxiation. This condition is very dangerous in and of itself, and its long-term consequences.
What it is?
The one who suggested calling the state of oxygen starvation in newborns just asphyxia was not quite accurate: until now, not all neonatologists accept and accept this term. "Asphyxia" - asphyxiation, impulse, this is how the term can be translated from Greek. Therefore, many doctors believe that talking about asphyxia is reasonable and fair only in the case of stillbirth.
In pediatrics, another interpretation of the term has been adopted: asphyxiation means the absence of gas exchange processes in the lungs of a newborn, and the child may be alive (there is a pulse, there are signs of life). therefore speaking of asphyxia, usually imply hypoxia - oxygen starvation. But the term "hypoxia" is more applicable to the fetus during its prenatal development, and "asphyxia" - to born children. In the ICD, each of these two states has its own description.
In any case, a condition is described in which the child's body undergoes certain changes due to an acute or chronic lack of oxygen.
Changes occur at the level of biochemical processes, hemodynamic, clinical. This is a very dangerous condition in which the baby’s brain is primarily affected.
Neonatal asphyxia occurs in about 4-6% of newborns, but the data are average. If we talk about premature babies born before 36 weeks of gestation, then asphyxia is registered in 9-11% of babies, and in term infants, the frequency of the spread of pathology does not exceed 0.7%.
To objectively imagine the danger of this pathological condition, it is enough just to get acquainted with the dry facts of medical statistics:
20-50% of children with intrauterine hypoxia die in the womb;
59% of babies with severe uncompensated intrauterine oxygen deficiency are born dead;
in 72.5% of cases, asphyxiation of the newborn becomes the main cause for the death of the baby in the first few days after birth or its disability.
The consequences of asphyxia in newborns are difficult to predict, because everything depends on how irreversible will be the changes caused by the lack of oxygen in the children's body.
Causes
Newborn asphyxia is not a separate disease, but a syndrome that most often develops due to pregnancy complications, pathologies in the fetus and his mother. Oxygen could not be enough even in the womb, for a more or less long time. In this case, they speak of primary asphyxia.
Its root causes are very numerous and it is extremely difficult or impossible to establish the exact one in principle:
intrauterine infections (mom had been ill with the first trimester or later rubella, cytomegalovirus infection, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, herpes infections);
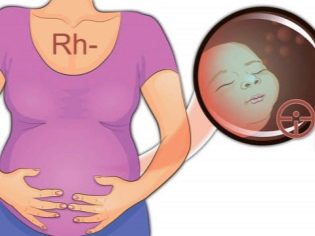
rhesus conflict (the Rh-negative mother develops an immunological incompatibility with the fetus, if the child borrows a positive Rh factor from the father);
congenital anomalies child development;
absolute or partial lung obstruction fetal amniotic fluid or mucus.
The risk factors for the development of primary asphyxia are any acute and chronic diseases in the expectant mother, especially when it comes to pathologies of the cardiovascular system, lungs, thyroid, diabetes mellitus.
The risk of asphyxia increases with preeclampsia, the presence of bad habits in women, from which she did not want to give up even during the period of carrying her child.
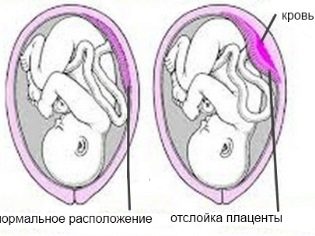
Risk factors include a postponed pregnancy (42 weeks or more) due to the exhaustion of the placenta, in which it cannot fully provide the baby with oxygen. Acute hypoxia develops with early detachment of the "children's place", as well as in complicated childbirth (protracted, rapid, amid weakness of labor forces).
Secondary asphyxia in the fetus develops in violation of the blood circulation of the brain, as well as in any pneumopathy - a condition in which the lung tissue is not fully expanded, and the lungs can not function after the baby is born in full force.
The etiology may be different, but the clinical picture is almost always similar.
What's happening?
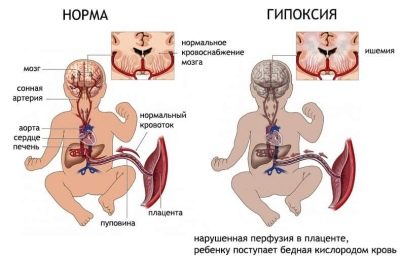
Regardless of what causes oxygen deprivation, pathological changes in the children's body develop in a similar scenario. Disturbed metabolism, blood circulation. The more prolonged the oxygen starvation, the more severe the consequences it may entail.
The lack of oxygen in the blood of a child entails a sharp increase in the number of nitrogenous compounds and a decrease in the amount of glucose. The content of potassium increases dramatically, and then the content of potassium drops sharply. With this electrolyte instability, the cells are overfilled with fluid.
If the hypoxia is acute (has arisen recently), then the amount of circulating blood increases, and if the lack of oxygen is chronic, then the amount of blood in the body, on the contrary, decreases. The blood becomes more dense, viscous, in it the number of platelets is increased. The brain, kidneys, heart, and liver suffer from this. Edema usually develops in these organs. Violation of hemostasis, an increase in blood viscosity leads to ischemic brain damage, hemorrhage (like a stroke). All tissues of internal organs are experiencing oxygen hunger. The heart reduces the volume of the release, the blood pressure drops.
Further, it all depends on how severe the changes and lesions caused hypoxia in the tissues of the organ.
Classification
Asphyxia is primary and secondary. Primary - this is a congenital form, when the baby was experiencing oxygen deficiency in the womb. The pathogenesis can be different, as in the case of secondary asphyxia, which has already arisen at birth or in the very first hours of the child’s existence outside the womb. Primary, in turn, can be both acute and chronic. The severity of asphyxia solves a lot - from the nature of resuscitation to predictions for the future.
The degree is determined by the state of the child in the evaluation on the Apgar scale:
heart rate: 0 points - absent, 1 point - less than 100 beats per minute, 2 points - more than 100 beats per minute;
breath - 0 points - absent, 1 point - irregular inhalations and exhalations; 2 points - even and rhythmic, loud cry;
muscle tone - 0 points - limb sagging, 1 point - flexion of arms, legs, 2 points - active movements;
reflexes (tickles the soles, the nasal passages irritate the catheter) - 0 points - no reaction, 1 point - the child makes a face with a grimace; 2 points - sneezes, screams;
color of the skin - 0 points - bluish or pale skin (white asphyxia), 1 point - normal skin, but bluish arms and legs, 2 points - the same pink color of the skin on the body and limbs.
The first time a child is given an assessment in the first minute of life, then in the fifth. If in the fifth minute a newborn gains 7 or less points, it is additionally estimated at 10, 15 and 20 minutes of life. But it is the “five-minute” score that is considered the most accurate.
The higher the number of points scored by the baby, the more favorable the forecasts. Easy degree - 6-7 points on Apgar. The average degree of asphyxiation at 1 minute is 4-7 points according to Apgar, and severe oxygen starvation - from 0 to 3 points at the first minute of life.
Additional laboratory and instrumental studies help to more accurately classify oxygen starvation.
Symptoms and signs
If you carefully review again the criteria of Apgar scale, you can understand how a child with asphyxia looks.
- If asphyxia is mildthen the baby has the first breath in the first minute of life, but the breathing is somewhat relaxed, the legs and arms can have a bluish tinge, the nasolabial triangle turns blue, there is muscular activity, but it is reduced.
- With moderate asphyxiation The first breath of the baby also occurs in the first minute, but breathing is usually noticeably weakened, irregular, a weak cry, more like a squeak, slowed heart rhythm, cyanosis of the face, arms and legs are clearly visible even for non-professionals.
- With severe hypoxia inhalation may be later than the first minute, irregular breathing, apnea may occur, irregular heartbeat, rare, child is pale or bluish, no cry, no reflexes. There is a higher probability that post-hypoxic brain damage starts in the first days after birth - the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disturbed, and hemorrhage can develop in the brain.
Necessary actions and surveys
Clinical recommendations for doctors imply rendering first emergency aid to a child with asphyxia, to his services all the possibilities of resuscitation of the obstetric institution. It all depends on the severity of the pathological condition. Some children have enough oxygen masks, others need to connect to a ventilator.
In any case, the Apgar assessment is not limited to. The lack of oxygen and metabolic disturbances are also indicated by laboratory testing of the blood of a newborn. A child born with oxygen starvation syndrome, or a baby who has developed such a condition after birth, is observed around the clock by neonatologists and children's neurologists. Ultrasonography, an ultrasound of the brain, is performed on the second day in order to understand how large-scale changes in brain structures and membranes are.
Treatment
If the baby has asphyxia of mild and moderate degree, then first of all, crumbs, according to the protocol of the Ministry of Health, in which the procedure is indicated, clean the nasopharynx, mouth, stomach from the contents - water and mucus. Oxygen mask improves the ventilation process, in the umbilical cord injected 20% glucose solution and cocarboxylase - this is necessary for metabolic and energy processes in the body.
To feed the baby's mother will bring when his breathing is fully stabilized, when the condition of the newborn will not cause concern to the medical staff.
If the asphyxia is moderate, but the above measures did not help, the child may be intubated with trachea and provided with mechanical ventilation. Intravenous electrolytes are injected into the child, because the imbalance of their balance, as we remember, leads to impaired hemodynamics.
In severe hypoxia, the child is on the ventilator; a heart massage can be performed if the heart rhythms are greatly reduced. Glucose, calcium supplements, adrenaline, prednisone are introduced. The child is fed through the probe, the mother does not bring for feeding.
Often after as the baby’s condition improves, it becomes necessary to additionally observe the work of his central nervous system, and therefore mommy and her newborn are not discharged home, but transported to a specialized children's hospital, where the treatment continues, the baby receives qualified nursing care, his mother learns the features of caring for the baby.
After the baby is at home, no matter what degree of severity he had asphyxia, he was put on record with a child neurologist at a clinic in the community.
Forecasts
Parents who are faced with such a pathology are interested in predictions - what is the danger of this condition for the development of a child at an older age? Even the best doctor will not answer this question, because projections depend on the severity and duration of oxygen starvation, and on the timeliness and correctness of medical care, and from higher powers, the influence of which physicians recognize, although they cannot explain.
Since the brain and the nervous system suffer most often as a result of asphyxiation, the consequences are often associated with disruption of the central nervous system. The harder the violation, the higher the probability of death of the baby or his life-long disability.
Usually, during the first three years, babies who have experienced moderate or severe asphyxia may experience behavioral abnormalities - increased activity or lethargy, high nervous excitability.
The immunity of these guys is somewhat weakened compared with the immunity of healthy peers. There may be more or less serious developmental delay.
Projections are relatively favorable only with a mild degree of a pathological condition. In other cases, everything is very individual.
Much depends on how correctly the mother will take care of the baby after being discharged home. She will need to follow all the recommendations of the doctor., regularly visit with a child neurologist. Many show therapeutic massage, vitamin therapy. At any temperature increase, you will need to call a doctor - hyperthermia can significantly worsen the condition of a child with impaired functions of the central nervous system.
Reducing the temperature to 35.6 degrees is also a reason for going to a doctor, hypothermia is no less dangerous after suffering asphyxiation.
Prevention
Prevention of asphyxia should be given attention during the period of pregnancy, and from its first days. In pediatrics, obstetrics, there is a list of the main examinations that the expectant mother should undergo in the process of waiting for the baby. Important is considered family planning - if a woman pre-treats her diseases and infections before conceiving a child, the chances of having a healthy heir are significantly increased.
To prevent a dangerous condition it is recommended to get registered early in female consultation. Doctors will assess risk factors and will regularly conduct examinations that will help to identify the state of the umbilical cord, placenta, fetus (ultrasound, CTG, USDG). In case of detection of the critical state of the baby, it is often made the decision about emergency early delivery in the interests of the fetus.
A woman who is preparing to become a mother needs to trust her doctors, but you should not forget about your participation in prevention: you should give up bad habits even before the child is conceived, food should be balanced, the day regimen should be reasonable, gentle. The doctor should be visited without a permit, on dates appointed by the midwife.
For the causes of fetal asphyxia and its consequences, see the following video.