Hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns
With the diagnosis of "hydrocephalus", the parents of the infant may face in the maternity hospital. Often, pathology is also found later, after discharge. The confusion and fright of the newly minted parents are quite understandable, because the pathology is considered quite serious. But hydroencephalopathy is not a sentence at all, and modern medicine has many ways to help a child. From this material you will learn how to relate to such a diagnosis and how to treat a baby.
About the disease
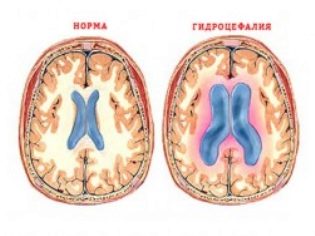
The brain of the child is washed by the cerebrospinal fluid, which is called CSF. This fluid is incredibly important - it cleans and washes the brain, delivers to it the white blood cells necessary for protection. Liquor production is continuous. In a healthy child, it does not stagnate - washing the brain, the cerebrospinal fluid again enters the spinal canal. In violation of the outflow of cerebral fluid begins to accumulate in the ventricles of the brain and under its shells. This condition is called dropsy, or hydrocephalus of the brain.
Increasing the level of fluid leads to an inevitable and obvious increase in pressure inside the skull. Under pressure, some structures can partially or completely suffer, “leach out”. Severe atrophic hydrocephalus can be quite devastating to the brain.
The earlier this condition is found in infants, the better. The initial stages of the anomaly are quite easily removable without significant consequences for the health of the child in the future. Hydrocephalus of a moderate degree may well lead to disruption of the functioning of certain parts of the brain, which may manifest as impaired speech, psyche, neurological pathologies, problems with hearing and vision, coordination of movements and movements in general. If you do not help the child with dropsy of the brain, it can die.
This condition occurs on average in one newborn by four thousand.
Classification and causes
In newborns, there are two types of dropsy - congenital and acquired. Congenital forms develop against the background of damaging factors even during the prenatal stay of the baby. This may be an infection in the mother, especially dangerous diseases in the first trimester. Certain malformations of the central nervous system can also cause the accumulation of cerebral fluid in the brain.
Acquired forms of the disease are most often found in premature babies, as well as in children who have suffered a birth trauma. Inflammation of the drainage abilities of the cerebrospinal fluid can cause an infection that the baby has contracted after birth, as well as the development of a tumor in one or another part of the brain.
Classification of hydrocephalus implies a clear separation of the types of ailment at the site of fluid accumulation. It can be external, internal or combined. The outer form implies the stagnation of fluid in the outer shell, the body of the brain is not affected. Most often, the external form is recorded in children as a consequence of birth trauma.
With the internal form, the cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the ventricles of the brain, and when combined and mixed, under the membranes and in the body of the brain. This is the most severe form of pathology.
During the examination, they try to immediately identify not only in which area the accumulation of fluid occurs, but also in which place the barrier to outflow has arisen. On this basis, hydrocephalus can be open and closed. In the first case, there are no obstacles to the movement of the cerebrospinal fluid, but its number raises significant questions. In the closed form, the cause of a violation of drainage usually lies in abnormalities of the structure of the ventricles or liquor ducts. The accumulation of cerebral fluid in this case almost all affects the internal parts of the brain.
If an anomaly is found within two days after development, the word “acute” appears in the diagnosis. Subacute dropsy develops over several months, very slowly and almost imperceptibly. Chronic hydrocephalus is present in a child for more than six months and can “hide” for quite a long time, because the accumulation of liquor occurs gradually. The closer to the chronic stage, the less favorable will be the projections for the future.
Hydrocephalus is called compensated, and its symptoms are not determined externally - the baby looks healthy and behaves normally. With the deterioration of the condition and the manifestation of external signs speak of decompensated form of the disease.
The degree of anomaly is assessed separately - it can be moderate or severe. In terms of development, the dropsy is divided into progressive, stable, and regressive, at which the symptoms diminish, go down.
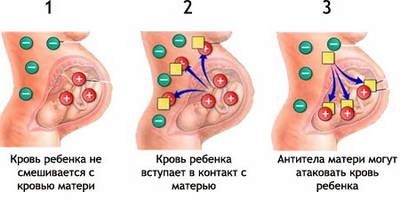
Dropsy of the brain in a newborn can develop on the basis of Rh-conflict with the mother, on the basis of existing genetic diseases, and against the background of rapid birth. Often it develops after birth due to infection with meningitis.
Symptoms and signs
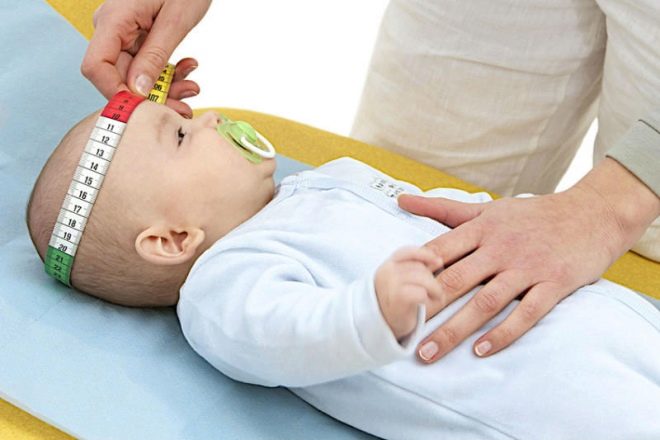
The main feature of hydrocephalus in a newborn is an enlarged head size. If a healthy toddler has a girth of the head 2 centimeters more than a chest girth, then by half a year the situation is changing and the proportions are reversed. In a child with dropsy, the head continues to be larger than the chest.
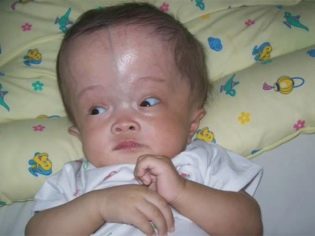
A rather specific type of skull is peculiar to hydrocephalus - the frontal lobes bulge, the head looks somewhat unnatural. But in a newborn, such a sign only makes itself felt in the case of a severe disease of congenital origin. External changes in the skull with compensated dropsy develop gradually.
The norm for a newborn is considered to be the girth of the head within 33-35 centimeters. But deviations from the base sizes cannot yet speak about the presence of dropsy, because a big head can only be an inherited feature of the appearance of a small person. The disturbing symptom is not the initial size of the head, but the rate of its growth. If the girth for the first month of life was not 0.5-1 cm, but 4 or more, the doctor may well suspect hydrocephalus from the toddler.
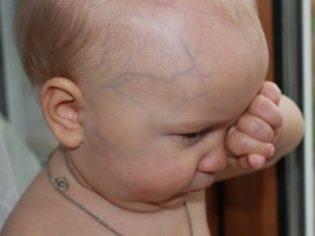
If by the end of the neonatal period the head girth is growing rapidly, additional signs may appear, for example, blue vein veins on the forehead and the back of the baby’s head. By the 28-day age, the crumb will not even try to hold the head, will not try to follow the eyes of the mother and smile.
The skin over a large "fontanelle" will be convex and pulsating. A child may show poor appetite, restless sleep, constant crying and very slow weight gain. By two months, nystagmus of the pupils of the eyes and bulging of the frontal lobes may appear. By the same age, divergent squint may occur.
Severe dropsy, requiring urgent medical intervention, is manifested by vomiting and monotonous weeping.
Establishing diagnosis
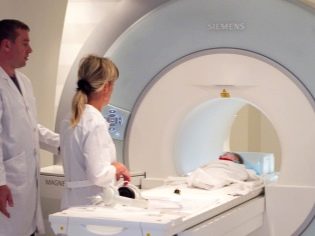
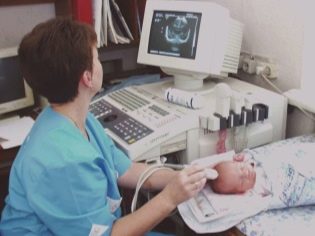
The main way to check for concerns in newborns is to conduct neurosonography - an ultrasound of the brain through an unclosed spring. For questionable results, MRI or CT may be recommended.Neurosonography is now ordered by the Ministry of Health to all babies at the age of 1 month without exception.
With hydrocephalus as a diagnosis, doctors are often reinsured, setting the excess of fluid from a study of 30–40% of toddlers. In this case, the wording may be different, indicating the detection of the enlarged ventricles of the brain. Parents from neurologists hear about increased pressure inside the skull more often. At the same time, most moms and dads do not have any reason to worry - the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in newborns can be increased for quite normal, physiological reasons. Therefore, it is important to monitor the state of the baby in dynamics.
Neurosonography itself can not be a reason for establishing a diagnosis of "dropsy of the brain." If there are serious visual abnormalities, computed tomography or MRI will be shown. Newborns such diagnostic methods carried out in a state of deep sleep sleep medication (anesthesia).
If the doctor recommends to undergo echoencephalography or electroencephalography, mother and father of the infant may well refuse with a clear conscience. These methods are not considered informative in the case of hydrocephalus, but by old standards continue to be prescribed.
Forecasts and consequences
If the diagnosis is confirmed, any sensible parent has a quite reasonable question about predictions - what will happen to the baby next? No doctor will be able to answer this question, since predicting hydrocephalus is considered ungrateful.
Light open dropsy usually has no consequences, however, provided that it was discovered in time and properly treated. With a closed occlusive type dropsy, the consequences for the baby’s health and development are almost inevitable.
Congenital forms of dropsy are treated faster than acquired ones. Severe deep-seated forms of the disease often lead to moronity, mental disorders, and developmental delays. Against the background of severe hydrocephalus, cerebral palsy and epilepsy can develop.
The disease itself is considered curable in medicine. Its consequences can be incurable. If you take care of the child at home and follow the doctor’s recommendations, the forecasts are more positive than the forecasts with the same form and stage, but the child is abandoned at the maternity hospital and who went to the baby house.
Treatment
The main official method of treatment is surgery. But quite often, with mild forms of dropsy, doctors prescribe and conservative treatment. It is based on diuretics, which contribute to the removal of fluid from the body. In addition to medicines, some folk remedies can be recommended, for example, lingonberry leaf.
Most often in the treatment regimens there are drugs such as "Diacarb"And" Asparkam "," Mannitol "and potassium preparations. Baby gymnastics, massage, sometimes physiotherapy. If there are no positive changes in 3-4 months, re-examination shows the absence of any significant effect, it is recommended to have an operation.
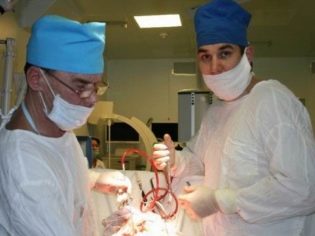
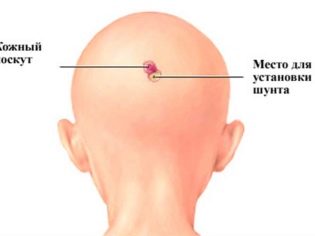
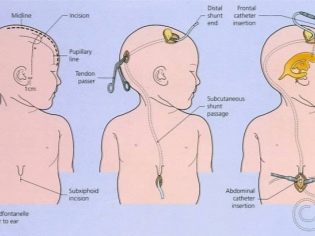
Most often bypass. As part of the intervention, trepanning of the skull is made and extra fluid is expelled through a silicone shunt inserted into the brain ventricle. The second end is brought into the abdominal cavity, laying a tube under the skin of the child.
Shunting is quite dangerous, complications occur in 50-60% of cases. The shunt has to be changed, the child has to undergo serious surgical intervention again. Alternative drainage operations do not solve the problem, since the fluid after a single pumping can accumulate again and again.
Endoscopic operations are very popular. In modern clinics and medical centers, the shunt is being installed on a baby in this way.
After the operation, the child is in the dispensary for a neurologist for life.
Opinion of Dr. Komarovsky
When the diagnosis is proven and justified, it is important for parents to keep themselves in their hands, the well-known children's doctor Yevgeny Komarovsky believes. Reasonable and calm attitude to the prescribed therapy is the key to success. In practice, things may not be at all the way we would like. Alarmed and desperate parents often begin to look for osteopaths, who guarantee that they will be able to correct the bones of the neck and skull without a surgery, so that the outflow of fluid will return to normal.
Yevgeny Komarovsky emphasizes that appeals to such specialists may end up for the child and his mom and dad pretty badly. According to the doctor, there is no official benefit from osteopaths. And there are no doctors of such specialization. And the consequences are, and they are very sad.
About hydrocephalic syndrome in children under one year old, its signs, diagnosis and prognosis, see the next video.