When does a newborn begin to hear and see?
The newly minted mom and dad begin to communicate with their baby from the first days of his life. And while the baby is sleeping, questions usually do not arise. Another situation - during wakefulness. The eyes of the baby are muddy, all the time mowing somewhere, the look does not focus. Parents often wonder if they see their children, whether they find out.
The ability of children after birth to sleep soundly, even if the room is noisy, also becomes a cause of doubt - and if the baby hears? In this article we will explain what and how your newborn sees and hears.
Formation of hearing and vision before birth
Children begin to hear in the period of pregnancy: in general - from the 17th week of pregnancy, and consciously and distinctly - at the 27th week.
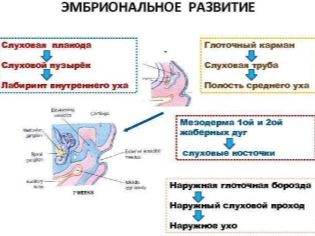
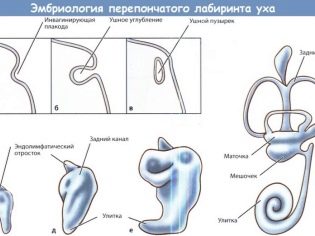
Hearing embryogenesis is very complex, long-lasting. The formation of the beginnings of the inner ear begins at about 5 weeks. At 8 weeks, the structures of the middle ear are formed, the outer ear (auricle) is formed in the last three months, and the cartilaginous tissue of the auricle hardens just shortly before birth.
Until the middle of the term of carrying a baby is the formation of a maze. It becomes hard by the 17-18 week, the hardening of the auditory ossicles continues and it lasts almost until birth.
The baby begins to pick up the first sounds in her mother's womb at 16-17 weeks, and so far these are not the sounds that we perceive with you. The crumb catches individual sounds from outside, listens to mom's heart, peristalsis of her intestines, blood flow, voice, but his brain does not analyze sounds yet, because the cerebral cortex is not yet formed. Thus, the fruit catches the vibrations created by the sound waves.
Fully capture sounds, that is, to hear and analyze the sound, the crumb begins only at the end of the second trimester. Already in the womb, he can turn the head on the sound. But the sounds for him are muffled, amniotic fluid, the dense abdominal wall of the mother contribute to this. After birth, auditory functions will have to be adapted to the new conditions of existence.
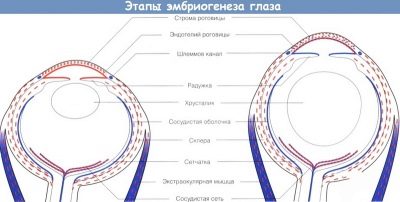
Vision is a little easier. Visual bumps (types of future eyes) begin to form in the second week of pregnancy. From 4 weeks begins the formation of the lens, and the eyelids and sclera are formed by the middle of pregnancy.
As with the sound recognition center, the center of vision in the brain appears by the beginning of the third trimester. From this moment on, the fetus begins to differentiate between light and darkness, night and day. By the time of birth, the eyes of the crumbs are formed, but differ in the immaturity of all its departments.
So see and hear the baby starts still in utero, before his birth. But this is a qualitatively different vision and hearing.
Hearing after birth
A child comes to this world to hear well. He has, if there are no pathologies or abnormalities in the development of the hearing organs, from the very first minutes he appears to assess into what a monstrously loud world he has appeared. Sounds collapse unexpectedly and plunge the kid into stress. Any loud sound can cause a reflex start.
The first month all your tales and songs, as well as grandmother and grandfather's lisping, for the baby is an empty sound. He is in the process of adaptation and is not yet able to recognize familiar and unfamiliar sounds. But already in 1 month, the baby begins to listen to the voices.
The first thing he catches is intonation. Already from the first weeks of life, the baby will feel precisely the intonation. What exactly this mother will say - a fairy tale or formulas from the field of nuclear physics in a sincere voice - does not matter.
By three months, the child’s hearing center is synchronized with the speech, and in response to the familiar sound, the crumb can already respond with a welcoming surge of pens, intonation gooks. By six months, children are perfectly aware of where the sound is coming from, turn their heads to the sound, react to their own name.
If you really want to please your baby with delicate songs and poems, memorize them by the age of six months. In 5-6 months, baby will be able to appreciate them.
What does the child see?
A newborn child perceives the world visually as clusters of dull spots of various sizes without pronounced boundaries. Clearness of view in the first weeks of life is absent. And so to place above the crib of a newborn bright toys and a mobile at least does not make sense, at least up to the age of 1 month.
Already in a month a baby can distinguish some large objects, separated from his face at a distance of about 40 centimeters. But to keep the gaze on it the baby is not yet able. The eye muscles are too weak for the child to focus his gaze in a static position.
The sight of a baby up to a month is not black and white, as some people think, and also is not upside down. Children see everything in a normal position in space, but blurry (due to physiological long-sightedness). Because of the small eyeballs, the formation of the image occurs outside the retina, and not on it.
A newborn child has a developed visual reflex - if you shine a flashlight in the face of a child, he will jerk, blink, and may even cry. When he is full three weeks old, the baby will begin to see blurry spots almost in color - the formation of color vision begins. This means that the baby can not yet see the mother and distinguish her from other people visually, but this does not mean that he knows her, just perceives the closest person crumbs using tactile sensations and the familiar smell.
After a month, the crumb begins to hold his gaze on a static object, however, he is capable of it only very briefly. At 2 months, focusing on the subject becomes longer and, with a bang, the baby begins to see the mother's face and distinguish it from other faces. At the same age comes the ability to recognize red.
At three months, the baby begins to follow the object with the eyes; he is good at it if the object of interest moves smoothly. Yellow is added to the colors that the baby sees and distinguishes.
By the end of the fifth month of life, the child can distinguish the colors of the spectrum, including green and blue, he recognizes loved ones and can view objects at a distance of a meter from himself. At 6 months, the child looks reasonably and fixedly, the vision becomes stereoscopic, three-dimensional. Starting at 7 months, the child consciously evaluates objects, the distance between them, switches his attention from nearby objects to distant objects and vice versa.
How to help your baby develop the senses?
Thus, after the birth, the baby every day will improve its perception of the world - auditory and visual. The task of loving parents at this stage is to help the child to make the adaptation processes more comfortable.
For the development of hearing, you need to talk more often with your baby, letting him listen to various sounds - high-frequency, mid-frequency and low-frequency. Include your baby music, better - classical. Try to exclude too loud and harsh sounds, but in the quietness of the child also should not be left.
All developmental activities, bathing, massage, daily gymnastics, accompany with conversations with the crumbs, songs and rhymes, jokes, sing him lullabies.At first, the crumb will only perceive the intonation nuances, but gradually learn to listen to the words.
It should be noted that the development of the ability to listen and hear develops speech skills, because the majority of babies are trying to hum, to repeat, heard the combination of sounds by 3-4 months.
For the development of vision it is necessary that the baby’s room is sufficiently well lit by natural sunlight. Twilight slows down the development of organs of vision.
Toys and rattles should be hung at a distance of 40 to 60 centimeters from the level of the face. The bed in the room should be placed so that the mother could approach her on the right and on the left. Then the baby will perceive the world around on both sides.
Rattles and other toys need to choose the color that the baby can already see, from 2 months - red, from three - red and yellow, from six months - all colors. Next to the bed in the nursery should not be mirrors and sources of artificial lighting.
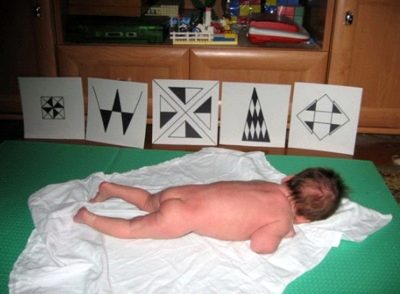
From one and a half months, it is possible to show the child contrasting black and white geometric figures drawn by mom on a sheet of paper or printed from the Internet. With a three-month crumbs classes should be conducted using bright and colorful objects and drawings.
Walking in the fresh air, you need to pay attention to the baby birds, animals, cars and people. So the baby will quickly learn to confidently follow moving objects.
The main thing that parents can do for the development of children's sense organs is to closely observe the child’s behavior. When detecting anxiety symptoms, it is necessary to show the child to the appropriate specialist.
Signs of pathologies
Suspected hearing problems can be due to the lack of response to a sharp sound. The newborn must react to it with fear, shuddering, closing eyes.
If the baby does not react to the voice addressed to him, to the sound of rattles in 2-3 months, this is a good reason for a visit to a specialist - audiologist. Sometimes babies can only hear low and medium frequencies, but not high ones. This will indicate a certain degree of hearing loss. You can check this by pouring some semolina into a glass or metal jar. Shake the jar over your baby's head. If he demonstrates a reaction to the sound, everything is all right with hearing.
Vision problems are less amenable to self-diagnosis at home. But parents should contact an ophthalmologist if a child at the age of 1 month does not have a pupil's reaction to a bright light (the pupil does not narrow), if at three months of age he does not fix his gaze and does not try to look at silent objects.
Problems may indicate a lack of ability to keep track of the mother moving around the apartment and behind the moving toys above the crib. And in six months, a child with visual perception problems may not recognize the mother and not distinguish her from strangers.
In order to notice existing or developed deviations in time, parents should not neglect the mandatory medical examinations of the child.
- First inspection held in 1 month. As part of this examination, the child is tested for auditory and visual reflexes.
- Second inspection need to go in half a year. Premature babies are advised to do this earlier - at three months.
- Third Mandatory Medical Exam child is held at the age of 1 year. During this event, the child is examined by an ENT and an oculist. If there are problems, then the otolaryngologist gives a referral for consultation to the deafening road, and the oculist prescribes additional hardware diagnostic examinations.
It should be noted that premature babies, babies who survived the state of acute hypoxia in childbirth and have ischemic brain lesions are more susceptible to vision and hearing problems from birth.
Quite often, problems with hearing and visual function are manifested in children born of pregnancy, accompanied by Rh-conflict.Also, diseases of the organs of hearing and vision are very often inherited, if the parents or in the third generation have relatives with hearing loss, glaucoma, cataracts, congenital blindness, or dystrophy of the retina or optic nerve.
For information on when newborns begin to hear and see, see the next video.