Swelling of the brain in the newborn
Pathological conditions in newborn babies always cause great concern on the part of parents. Of particular importance - the presence of pathology in the brain. Cerebral edema is a fairly common situation that occurs in the smallest patients.
The reasons
Brain edema is a clinical situation that is accompanied by fluid accumulation between various brain structural formations. This pathology is usually not an independent disease, and occurs in a variety of pathological conditions.
The development of cerebral edema in infants leads to the effects of a variety of reasons:
- Birth injuries. Traumatic brain damage caused to the child during childbirth can contribute to the development of various intracerebral pathologies. One of these manifestations may be swelling of the brain tissue. Postnatal clinical options are found mainly in complicated course of labor, as well as in the wrong obstetric manual.
- Fetal pathological conditions, leading to oxygen starvation of tissues (hypoxia). Violation of oxygen entering the blood leads to various cellular metabolic disorders. Brain cells or neurons are very sensitive to oxygen saturation (blood filling). The decrease in its entry into the children's body during fetal development contributes to the development of tissue hypoxia, which provokes further signs of cerebral edema in the child. Most often, such clinical forms occur in premature babies.
- The development of postpartum asphyxia. This pathological condition occurs in the baby immediately after birth. It is characterized by the appearance of a marked impairment of respiratory function, and in severe cases, even complete cessation of breathing.
- Too long and difficult delivery. Violations of labor contribute to the progression of oxygen starvation of brain cells in a child. Obstetrician-gynecologists conducting natural childbirth, always monitor the condition of the baby during the entire period of expulsion of the fetus from the uterus. Prolonged standing of the child in the mother's birth canal can increase the signs of hypoxia and lead to the development of signs of edema of the brain tissue after birth.
- Intrauterine infections. Many pathogenic viruses and bacteria easily penetrate the hemato-placental barrier. Getting into the children's body through the nutrient blood vessels of the placenta, they are rapidly absorbed into the systemic children's blood flow and spread to all internal organs. Such infection leads to the fact that microbes can reach the brain and cause severe inflammation in it.
- Congenital anomalies development of the nervous system. They are found in babies in the first months after birth. Pronounced anatomical and functional defects of the nervous system affect the work of the brain. The presence of such pathologies often leads to the development of cerebral tissue edema in babies.
- Hypernatremia. This pathological situation is associated with an increase in the level of sodium in the blood. Disturbances of metabolic processes lead to increased puffiness, which can also appear in the brain tissue.
- Inflammatory brain diseases - Meningitis and meningoencephalitis.In this case, edema of the brain tissue occurs as a result of a pronounced inflammatory process and is a complication of the main diseases. To eliminate excess fluid accumulation in the meninges, treatment of the disease that caused this clinical condition is required initially.
- Purulent brain abscesses. They are encountered quite rarely in babies. Basically there are complications of various infectious diseases of the brain. Occur with the appearance of the most adverse symptoms. Surgical treatment is used to eliminate them.
For information on what is cerebral edema and a more detailed description of all its possible causes, see the following video.
Symptoms
It is often difficult to suspect swelling of the brain in a newborn baby at the initial stage. Clinical signs of this condition appear only with a pronounced course of the disease.
Many attentive parents will be able to suspect this pathology on their own, because many of the symptoms that appear in a child lead to a significant change in his usual behavior.
In the advanced stage of the disease a child has a headache. It can manifest itself in different ways: from mild ailment to significant pain syndrome, which brings expressed concern to the baby. From the side noticeable change in the behavior of the baby. He becomes more lethargic, restless, in some cases, on the contrary, the child is growing apathy and indifference to everything that happens.
In infants, the appetite is disturbed, which is manifested, as a rule, by refusals from breastfeeding. The child is poorly attached to the breast or sucks very slowly. Against the background of severe headache, the baby grows nausea. With severe pain even vomiting occurs. Usually it is single, not abundant in the amount of discharge. After vomiting, the child feels much better.
Suffer and mood baby. He becomes more whiny, capricious. Some kids often ask for hands. During the rise of symptoms, a child has serious problems falling asleep. It is usually difficult to lay him down, but he may wake up several times in the middle of the night and cry. The duration of daytime sleep is also shortened.
Severe swelling of the brain contributes to the appearance of systemic disorders of other internal organs. The pulse of the baby decreases, blood pressure can decrease in some cases even to critical values.
Developed intracranial hypertension leads to compression of the nipples of the optic nerves, which is clinically manifested by impaired of view, frequent blinking and squinting.
Diagnostics
To establish the correct diagnosis, it is not always sufficient to conduct only a clinical examination. Cerebral edema, occurring in a rather mild form, can only be diagnosed using additional instrumental methods. The indications for the purpose of the research are established by children's neurologists. These specialists, after examining the child, constitute the tactics of diagnosis and treatment in each particular case.
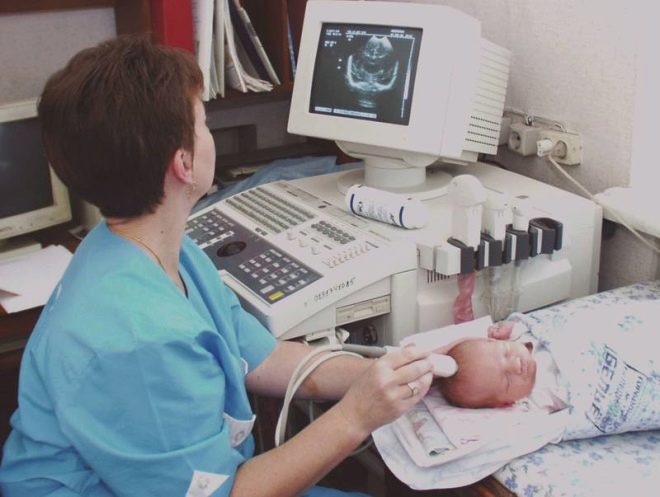
Ultrasound examination of the brain using the Doppler scan mode helps to identify various pathologies of the brain in children, including the presence of stagnant fluid inside the brain structures. Using special echo signs, the doctor determines the severity of functional disorders. This study is completely safe, has no radiation exposure and can be used even in the smallest patients.
Using ultrasound, you can also determine the localization of maximum fluid accumulation, identify periventricular edema, as well as measure the blood flow in the blood vessels supplying the brain.
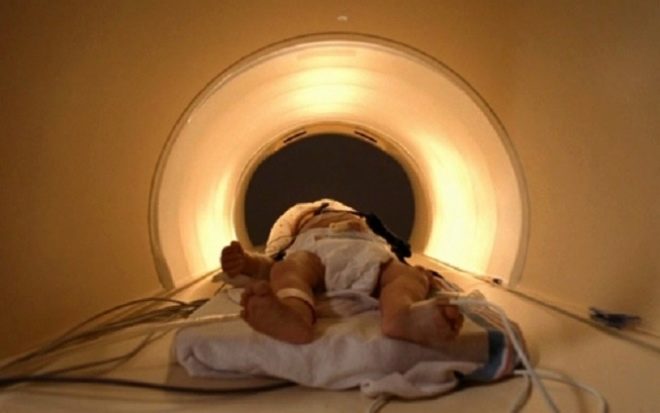
High-precision brain tests today also include magnetic resonance and computed tomography. These methods allow doctors to obtain an accurate description of the existing structural abnormalities and various pathological processes in the brain tissue. Additional methods of diagnosis also include examination of the fundus to detect indirect signs of intracranial hypertension, which is a frequent consequence of pronounced cerebral edema.
Effects
The prognosis of the disease is usually favorable. However, it is determined individually based on the overall well-being of the baby. Children with persistent disorders in the nervous system and suffering from infectious diseases of the brain in severe form are at risk for the development of adverse complications. The effects of severe cerebral tissue edema transferred include:
- the occurrence of epileptic seizures;
- impaired memorization and concentration in more adulthood;
- various speech and behavioral disorders;
- difficulties with socialization;
- vegetative-visceral syndrome.
Treatment
Therapy of cerebral edema includes the appointment of several groups of drugs. The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the cause that caused the accumulation of excess fluid in the brain structures. Symptomatic treatment is auxiliary and necessary to eliminate all adverse symptoms that have arisen during the course of the disease.
The following medications are used to eliminate excess fluid from the brain:
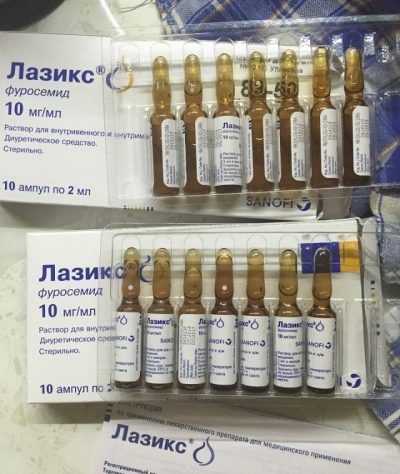
- Diuretics or diuretics. They are the basic drugs for the treatment of any pathological conditions associated with the formation of edema. Diuretic therapy has a significant therapeutic effect and leads to a fairly rapid improvement in health. To eliminate adverse symptoms in children's practice are used: “Lasix”, “Fonurit”, “Novurit”, 30% urea solution.
Treatment with these drugs is carried out strictly in the hospital.
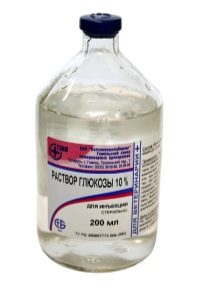
- Dehydration therapy. Includes intravenous administration of various solutions. This type of treatment improves cellular metabolic processes, which contributes to a better work of the brain and a decrease in fluid between brain formations. Hypertensives are administered to babies. solutions of 10% calcium chloride, 10% sodium chloride, 10% glucose solution other.
- Anti-edema therapy. For drugs that reduce puffiness, is glycerin. Usually, he is assigned to the children orally, along with various drinks: juices, fruit drinks, compotes. The average daily dosage is 0.5-2 g / kg body weight of the child.
- Protein solutions. They help to improve metabolic processes in tissues, and also have a beneficial effect on the protein balance in the children's body. As such agents, a 20% albumin solution is usually used, or plasma is introduced.
- Glucocorticosteroid drugs. Necessary to eliminate signs of swelling of the brain and improve well-being. Usually, up to 10 mg of hydrocortisone is used in children. The dosage is selected individually, taking into account the child's body weight.