What to do when a child burns?
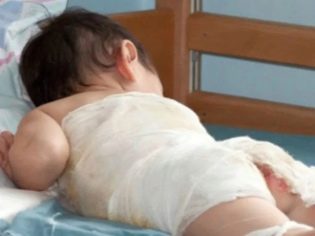
Inquisitive and ubiquitous children rarely miss the opportunity to learn something new and interesting. And because abrasions and hematomas, bruises and burns accompany childhood almost always. In this article we will tell what to do if the child has a burn, how to give him first aid.
What it is?
A burn is a violation of the integrity of the skin, damage to its structures by the aggressive effects of very high temperatures or certain hazardous chemicals and compounds. Most often, children get sunburn and radiation burns, which are caused by careless handling of electrical appliances. Often kids are burnt with boiling water, hot oil. Damage by chemicals - acids, alkaline compounds are also common. But frostbite or prolonged traumatic effect on the children's body by vibration (vibration injury) to burns traditionally have nothing to do.
Burn injuries are considered the most common injuries on the planet among children. According to medical statistics, burn injuries rank second in the number and probability of death. On the first - the damages received in road accidents and car accidents.
This type of injury is common in all age groups of children - babies, however, receive burns less often, each such case is associated exclusively with parental oversight and safety violations.
As soon as children learn to walk independently and begin to explore the world more actively, the risk of getting burned increases tenfold.
It is believed that burns are quite difficult to treat, and not always therapy is successful, despite the relatively high level of development of modern medicine.
Types and features
The main types of such traumatic lesions are names that are directly related to the cause of them. There are:
- thermal damage (caused by prolonged exposure to the sun, hot water, burns from iron, boiling oil, and so on);
- chemical burn (household chemicals, consumer and industrial acids and alkaline compounds act as a damaging factor, sometimes the injury is associated with contact with the juice of some plants, for example, burns from the Hogweed);
- radiation injuries (for example, electric current discharge, radiation traumatic injuries).
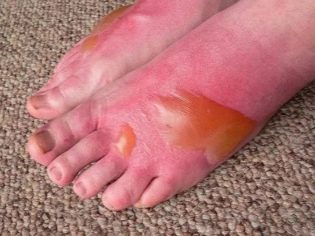
Burns are divided into different types and degrees, which depend on the extent of the lesion, the area affected and the depth of the traumatic effect. It is clear that a burn of the palm or finger will be more easily tolerated than the loss of the whole arm. The most painful are the skin lesions and foot burns.
Much depends on what it was and under what circumstances the injury was received. For children, the most common situations are:
- Open fire, flame. The area of the lesion of the skin is usually quite large, but the depth is relatively small - at the level of 1-2 degrees. When an injury is received by open fire, a child can often have associated burns of the respiratory tract, organs of vision, and this is the most dangerous factor. A common complication is infection of the affected tissues, because when the affected area is freed from particles of burnt tissue and clothing, it is not always possible to get all the fibers and threads.
- Burns liquids. Boiling water, milk, oil usually cause small burns in their area, but rather deep in their degree of manifestation (at the level of the second-third degree). Respiratory organs with such a thermal lesion does not suffer, burns are rather superficial.
- Steam. If the child is burnt by steam, then the tram area is mostly large. But such burns are not deep, for the most part they are superficial. Often, only the respiratory organs are injured (for example, when an inaccurate home inhalation is performed with hot steam).
Inhalation of vapor and respiratory tract burns are most dangerous. This complication in 99% of cases accompanies steam injuries.
- Hot hot items. Burns from an iron, a hot frying pan, and my mother's hair curling are the most common thermal injuries among children patients. The area of injury is always strictly limited to the size of the object to which the child is attached, if, of course, the touch was a one-time. Big it is extremely rare. But the depth of defeat is great - from 2 to 4 degrees. The most frequent complication is the violation of the integrity of the skin layers. This happens when rendering first emergency aid, when a hot object jerks sharply away from the skin. It is usually removed along with part of the epidermis and dermis.
- Chemical Acid Burns. Despite the fact that chemical burns are considered to be among the most dangerous for children, they are rarely deep. This is due to the chemical properties of acids. After contact with the skin, such substances cause fairly extensive lesions, but the affected tissues quickly turn into a scab, and this becomes an obstacle to the penetration of acid into the deeper layers of the skin. A curious fact - the more concentrated the acid, the burn will be less deep, because a scab will form from burned tissue more quickly.
- Alkaline chemical burns. Alkalis are more insidious substances, since neither the scab nor other biological protein barriers for penetration of an aggressive compound into the skin layers under their influence are created by the body. Alkaline lesions are quite deep and dangerous.
- Electric burns. If a child has been defeated by a discharge arc, then burn marks will necessarily appear in two places on the body - at the point of entry of the discharge arc and at the point of its exit. This type of burn has a small area, but it has significant depth. The most dangerous condition occurs when the electric current from the entry point has passed to the exit point through the heart region.
If the defeat came from a short circuit, and the current did not travel through the body of the victim, then the burns will have all the characteristics of burns by open fire or flame.
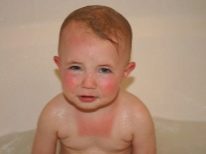
- Sunburn A widespread thermal injury, especially in the summer. The area of damage with excessive exposure to UV rays is large, sometimes it captures the whole body. The degree is rarely higher than the second. The greatest danger is the concomitant possible thermal damage to the retina, as well as dehydration and heat stroke (sun sickness). The burns themselves can be easily treated, if they do not exceed the second degree.
- Radiation and ionizing burns. These are the most severe forms of burns, because tissue regeneration is hampered by the disruption of the vessels and the increased bleeding caused by this. It is clear that the main danger in case of skin damage by radiation or light radiation during an atomic explosion does not cause a burn, but a rapid radiation sickness.
- Combined and combined burns. Combined are those skin lesions that are accompanied by an additional injury - a fracture or dislocation, for example.And combined are those thermal or chemical injuries that are caused by exposure to several harmful substances and factors.
Degrees
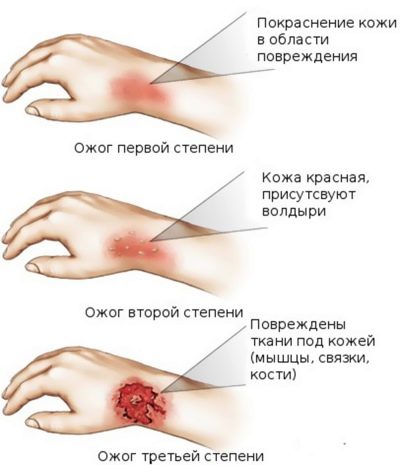
Foreign doctors use a three-stage classification of all burn injuries, regardless of the cause. Their classification is pretty simple. In the first degree, only the outer skin is affected; in the second, the middle layer, the dermis, is affected. And at the third stage, both the superficial epidermis, the midline dermis and the subcutaneous tissue are affected. Russia uses a four-stage classification, which prescribes to divide four degrees.
Our standards, approved in the middle of the last century, look like this:
- Burns 1 degree. These are the lightest burns, in which only the outer layer of the skin-epidermis is affected. They appear reddening the skin of different intensity. The site of exposure is slightly swollen and quite sore. As a rule, such injuries do not require qualified medical care; they disappear after a few days; scars and scars do not remain after recovery.
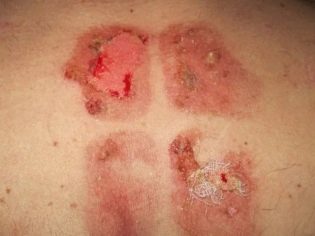
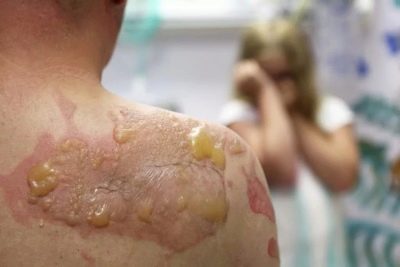
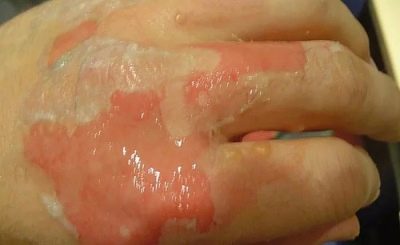
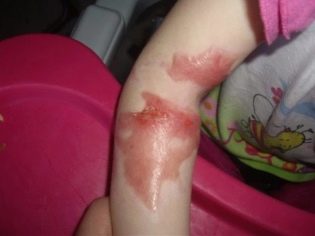
- Burns 2 degrees. With such an injury, not only the superficial parts of the epidermis are affected, but also part of the germ layer of the epidermis. It is not difficult to recognize this degree - the affected area of the skin not only turns red and swells, but also becomes covered with blisters and blisters filled with serous fluid. The temperature of the 2nd degree burn is elevated to subfebrile values (37.0 -37.8 degrees). In some cases, medical help is needed to avoid the possibility of infection of wounds that have arisen at the site of bursting blisters. A newborn and a baby with such a burn must be examined by a doctor; older children can be content with home treatment.
- 3 degree burns. When they are affected, both the outer and middle layers of the skin (epidermis and dermis) are affected. There are two subspecies of such injuries - burns of 3 A degrees and 3 B degrees. Letter A refers to injuries.in which the dermis is partially affected. The sebaceous and sweat glands remain intact, as well as some of the hair follicles. Such burns look like a dark scab. The bubbles that appeared in the shortest time after receiving the burn are large, they are filled with serous fluid and blood impurities. Despite the terrible appearance, the child almost does not feel pain. The doctor should deal with the treatment, the therapy takes place in the hospital if the child is small and at home with a visit to the doctor if it is a teenager. The skin can recover on its own, provided that there is no secondary bacterial infection. Under the letter B mean such severe burns, in which not a single layer component of the dermis (middle layer) has survived. Burned out all the layers to the fiber. Treatment always requires compulsory medical supervision in the hospital of specialized burn centers or relevant departments of hospitals.
- 4 degree burns. This is the most extreme degree in which all skin structures, including fatty tissue, completely die. There is blackening and charring of bones and muscles. Pain is absent completely, because the nerve endings have died. A large area of such burns leads to shock and often death. A small area gives doctors the opportunity to compete for the life and health of a small patient. The situation is almost always complicated by the development of a burn disease. (reaction of the whole body to the injury), sometimes - the development of sepsis.
The predictions are ambiguous. The outcome is affected by the age of the child, the state of his immunity, the presence of additional diseases.
Effects
In order to evaluate possible further “echoes” of a burn injury, you need to know exactly the extent, depth and area of the lesion, assess the severity of this lesion and which structures and tissues of the body are affected.The formation of the consequences is influenced by the fact how urgently and correctly the first aid was provided, and subsequently - what treatment was prescribed. Unfortunately, quite often doctors make mistakes in assessing the extent and depth of the lesion, underestimating them, which leads to serious consequences.
When burns 1-2 degrees of traces on the skin may not remain. But with a 2–3 degree, even with correct and timely medical assistance, scars and scars remain on the skin, the place of injury is overgrown with coarse scar tissue. Many of these effects are partially reversible - specialists in the field of plastic surgery come to the aid of young patients.
With severe or extensive burns, burn disease develops. It can accompany and superficial forms of injury, but on condition that more than 30-35% of the body is affected.
If a fourth degree burn, then 10% of the body for an adult is enough for the development of the disease and only 5% of the body for children.
When it develops a shock that can last from days to three days. Then begins the stage of the strongest intoxication, in which decay products enter the blood. With the progression of the wounds begin to fester, and it can last up to several months. Quite often, for a burn disease, the child requires surgical assistance aimed at forcibly cleaning wounds.
After the disease, complications often develop - lymphadenitis, the appearance of abscesses. The hardest consequence of a burn is gangrene.
First aid
If the child has been burned, the parents should urgently give him first aid, on how correctly it will be done, depends on the final prediction and severity of the consequences of injury:
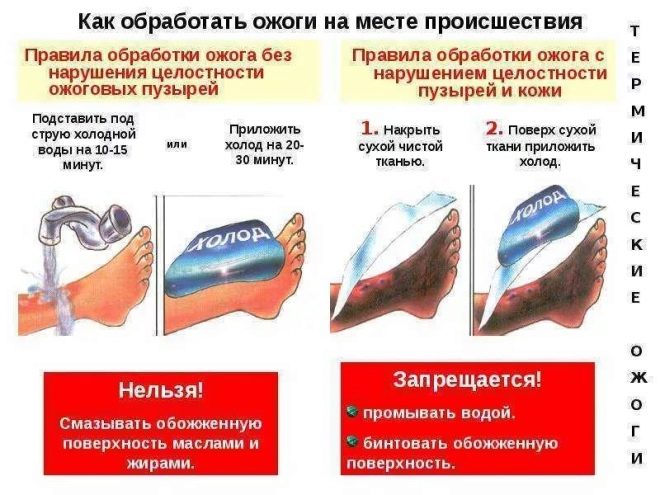
- It is important to interrupt baby’s skin contact with what caused the damage as soon as possible.. If it is the sun's rays, you need to put the child in the shade, if the object is hot, you need to quickly, but very carefully and carefully remove the object from the skin, if it is a chemical burn, it is important to quickly wash out the lesion with running cool water in large quantities.
- When an electric injury does not need to grab the child and try to drag him to the side, because the current will hit the one who is trying to help. It is necessary to stop the supply of electricity by turning off the device or de-energizing the entire room.
- Thermal burns need to cool the skin, if, of course, they are not broken. In case of sunburn, it is recommended to put a sheet or diaper dipped in cool water, and when boiling with a burn, make several washes with cool running water. The duration of each wash should not exceed 10-15 minutes. Such measures have a beneficial effect on the further development of the situation only under the condition that a cool effect was made on the burned areas of the skin no later than two hours after the injury.
- In the event of a burn with an open fire, it is not worth trying to independently extract from the affected area the melted remnants of clothing, fabrics, and individual threads. It’s still impossible to do this completely at home, and the risks of bleeding, infection of wounds and the occurrence of pain shock increase many times. It is best to cover the affected area with a sheet moistened in cool water and call an ambulance or take the child to the nearest hospital if the burn is small. In case of extensive burns, transportation in an ambulance car is required, as some technical capabilities of such a car may be needed to maintain a stable condition of the baby.
- Chemical burns after thorough washing of the injured areas of the skin, the affected area should be left uncovered, free of oxygen and call an ambulance or take the child to the emergency room or hospital on their own.
Sometimes parents themselves exacerbate the condition of their child and complicate the task of the doctors who have to treat the baby, when it is only out of good intentions that they try to be first aid with serious errors. Here is a list of things that should never be done if a child has suffered a burn injury:
- Lubrication of burns with products containing fats is strictly prohibited. Children's cream, butter, sour cream on the burn - this is additional work for doctors who will have to remove the greasy film, and additional torment for the child who will have to endure this removal. Fatty substances do not provide any practical and therapeutic help, they do not reduce burn, they do not relieve pain, they do not contribute to healing.
Sour cream on your back in case of sunburn or iron burned palms is a common misconception that has already harmed more than one thousand little patients with burns higher than 1 degree.
- It is not possible to cool the skin exposed to heat or radiation by applying ice to the affected area. Only natural fabrics, moistened with cool water.
- With a combined injury or a combined burn, there is no burn in the first place, and other injuries, and therefore the severity of fractures, dislocations, concussions cannot be underestimated. Not every burn and collateral damage makes sense to transport a child for hospitalization. If there is a suspicion of a fracture of something, it is better to provide first aid that is relevant for a burn injury and call an ambulance, ensuring that the child is in a horizontal position with his head elevated at rest.
- Make any injections, including painkillers, do not smear the area of burn with ointments. This can make diagnostics difficult and lead to incorrect medical actions. For example, at 3-4 degrees of thermal or chemical damage, the victim does not feel pain due to the death of pain receptors and nerve endings. This is an important diagnostic feature. If, however, pre-administer drugs and relieve pain, then the child temporarily stops feeling pain even with lighter burn injuries. This will increase the risk of medical error.
- Self-clean the wound from scabs or other foreign particles With the help of tweezers, as it is sometimes advised to do some "experts" from the Internet, it is absolutely impossible. Without a full-fledged anesthesia (the tablet “Analgin” is not considered such anesthesia), the procedure will torture the baby, and the lack of a full-fledged lighting (as in the operating room) will not allow you to see and remove foreign objects without exception. In addition, there is the possibility of bleeding.
- Nothing to never bandage. Incorrectly applied dressing will only increase the swelling and lead to necrotic changes. In addition, doctors still have to remove such a bandage, and this will cause great pain to the child.
- Sometimes well-meaning parents in case of severe burns and concomitant injury, bleeding try to put a child harness. You can not do this. Impaired blood supply in the affected limb can lead to necrosis. A child who could be provided with normal medical care may end up losing a limb altogether.
- It is very important to remember that if there are several burn victims, first of all, it is necessary to provide emergency assistance to those who are silent. With high probability, this child is in shock, he develops a burn disease that threatens his life. A child screaming and begging for help is always a patient with smaller lesions, because at stage 4 he will neither scream nor ask. This child is assisted secondarily.
When providing first aid, some parents often forget that all actions should be phased and coordinated, without too much fuss and panic. There is only one algorithm: to eliminate the impact - to request medical assistance - to cool down the burn site if the skin is intact.
If the burns have violated the integrity of the skin, deep charred wounds, bones, muscle fragments are visible, nothing can be cooled and touched.
You just need to call the resuscitation team and monitor the condition of the child. If you lose consciousness, you can bring it to life by bringing a cotton wool dipped in namutyr to your nose, while cardiac arrest - you should definitely massage the heart with hands over and mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration. In an extremely serious condition associated with respiratory tract burns, loss of consciousness and the development of respiratory failure, the child should be quickly and decisively intubated with improvised means — using a kitchen knife or any sharp object to dissect the trachea and spout of the kettle or any tube for insertion into the trachea, so that Provide your baby with oxygen.
Treatment
Light burn therapy
Grade 1-2 burns usually do not require inpatient conditions, although a baby with a lesion area of more than 5% of the body can also be sent to the hospital. At home, at the first stage (on the first day or two) it is forbidden to apply ointments and creams on burns, and also to bandage the child. In case of severe pain, lidocaine spray can be used for anesthesia; when the temperature rises, paracetamol-based antipyretic agents can be given.
In the second stage, when the blisters and blisters begin to open, you need to treat the surface with antiseptics. It is best to use disinfectants in the form of sprays, for example, "Miramistin", Or liquid antiseptics that do not contain alcohol, such as classical hydrogen peroxide. At the final stage, when the burn becomes covered with a crust or dries out if there were no blisters, it is acceptable to use for the child such external means as “Baneocin», «Panthenol"And"Bepanten».
It is impossible to remove the crusts, dressing burns at the final stage is impractical if the child is large enough, and understands that it is not necessary to touch the sore spot. If the toddler is at a less conscious age, it is better to apply a light, recent bandage.
Severe Burn Therapy
In case of serious burn injuries, when there is a need for hospitalization, in addition to treating the skin and using antibiotics locally and systemically, doctors will conduct active infusion therapy for the child. The fact is that large or deep burns result in the loss of protein and a large amount of fluid in the children's body. This deficiency will be filled by making the child droppers with saline, glucose, calloid and crystalloid solutions.
If burns are caused by electric current, heart drugs may be added to the infusion. In almost all cases, intravenous nutrients are prescribed.
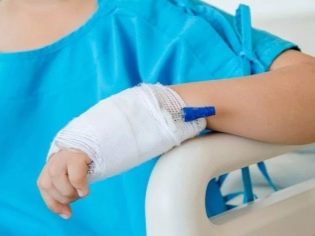
Skin treatments can be done in two ways - open and closed. When an open wound is not tied up, because the natural dry scab prevents the growth of pathogenic bacteria in the affected area. The wound can be irradiated with infrared rays, use fans for drying. With the closed method using dressings, antimicrobials are simultaneously prescribed. The specific means and method of bandaging depends on how quickly the burn heals.
When dressings will be used drugs that have activity against microbes - hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate solution. To maintain the physiological balance, a solution of furatsilin and dioxidin, anti-bacterial preparations Levomycetin Ointment and Erythromycin Ointment, as well as antibiotics sulfonamides, are used. Antibiotics will not always be applied directly to the wound. Sometimes they just soak bandages.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is not always necessary, but sometimes the child can not do without it. This applies to situations involving the need to clean deep burn wounds, as well as to remove burned tissue fragments or necrotic consequences. For cleaning wounds, an operation is performed - necrotomy. It takes place with local anesthesia. The surgeon cuts through the affected area, gets to the living layer, and cleans all layers that are not recoverable.
Necroctomy is prescribed when you need to completely remove large areas affected by the burn, or amputate the burned limbs or parts thereof.
Dermatoplasty is a cosmetic surgery, it is done to its children in order to reduce external defects and minimize the visual harm done to the baby’s skin. Plastic surgery is done for injuries up to grade 3 inclusive. In a child with a 4 degree, such an operation does not make sense. Often enough, a child with severe burns alternately performs all three operations.
Rehabilitation
The child can easily cure light burns that the mother can cure at home. The same can not be argued if the baby had to endure serious burns. This is primarily a major psychological trauma and rehabilitation includes not only the measures of the physiological plan, but also psychological assistance to the child in a continuous mode.
Post-traumatic stress disorder in children after burns is so severe that they need the help of qualified psychotherapists and even psychiatrists.
According to statistics, in varying degrees, such a disorder develops in 8 out of 10 children. After a severe burn, the child will gradually increase motor activity. The doctor will write out the exercises and the time of classes in the individual rehabilitation plan. Parents should strictly follow the points of these recommendations at home.
After the first stage, which is based on the restoration of movements and psychological adaptation, a decision will be made on the possibility and necessity of cosmetic plastic surgery.
Prevention
Most often burns are children under 5-6 years old and teenagers. The first is almost always (in 95% of cases) injured at home. The second - out of the house. To protect the child from burn injury, it is necessary to strictly follow simple safety rules:
- A child should not be left alone where the risk of getting burned is high. - in the kitchen, in the bathroom, in the outbuildings, where boilers or gas boilers are located.
- Pans with cooked soup only and pans with meatballs should be placed on the farthest from the edge of the burner, and if they are left on the edge, the handles should be turned to the side so that the child cannot reach them and overturn the container with boiling water.
- All hot liquids (kettle, cup with tea) should be removed as high as possible and as far as possible from the edge of the table. If a child is sitting at the same table with adults, then he should not reach for dishes with hot foods.
- Do not keep the baby in your arms or wear it on yourself in a “kangaroo” while cooking. Anything can happen.
- All electrical wires in the house, where children grow up, they must be put away in special electrical boxes so that the child cannot reach them even with a very strong desire and desire.
- If possible, then you should limit the temperature of the water in the faucet in the bathroom and in the kitchen so that the child cannot get burned if the faucet is accidentally opened. Special electronic limiters will help limit the temperature.
- If the child is playing on the floordo not carry a cup of hot tea or a tray of hot soup over him. In this way, many babies and get severe burns.
- Electric tiles and heaters with an open type of helix, it is advisable not to use at all in a house where children grow up, and if there is no opportunity to abandon their operation, the devices should be placed where children never penetrate under any circumstances.
- Particular attention should be paid safety of the child when resting in the country or on a picnic. The kid should not come close to the brazier or bonfire, do not need to teach him to make a fire and use a cigarette lighter, pick up flammable liquids.
- Household chemicals and any caustic and dangerous substances (solvents, acids, alkalis) should not be freely available. It is not enough just to put them in a specific “secret” place, you should definitely make sure that this place is well locked, for example, on a lock, in order to exclude accidental detection of chemicals by children.
How to give first aid to children with burns, see the next video.