Impetigo in children
The unpleasant and contagious skin disease of impetigo can make life difficult not only for one specific child, but also for the whole children's group. You will learn about this disease, how it is transmitted and how it can be cured.
What it is
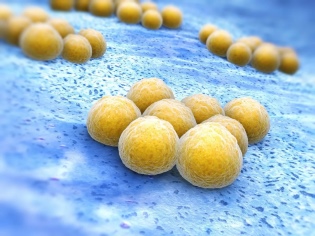
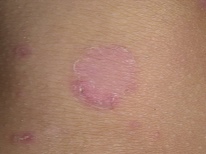
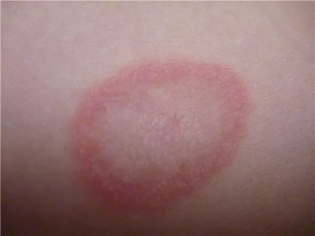
Impetigo - pustular infection of the skin. It is always caused by bacterial infection. The main "culprits" of pustules on the body and face are Staphylococcus aureus, acute streptococcus. Sometimes they act together.
The illness is rapidly spreading in closed children's communities - in kindergartens, schools, sanatoriums and holiday camps.
The disease causes not only cosmetic inconvenience due to the presence of ulcers on the skin, but it can also have quite serious complications - damage to the renal glomeruli (glomerulonephritis), damage to the heart muscle and membranes (myocarditis), it is possible the appearance of abscesses.
The disease occurs in adults, but in children it is diagnosed much more often. In addition, of all the bacterial external lesions of the skin, it is impetigo that is considered the leader in prevalence in pediatric practice.
Varieties of ailment
Depending on the type of microbe and the degree of damage, the disease is divided into:
- contagious impetigo;
- impetigo vulgaris;
- bullous impetigo;
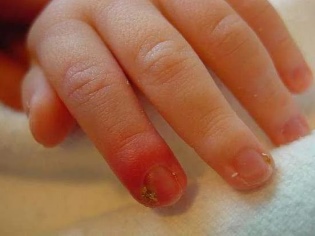
- impetigo bockhart;
- slit impetigo.
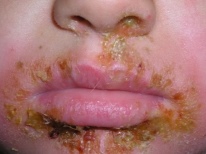
Contagious disease cause streptococci. This is the most common type of illness in children. Bullosa impetigo is a staphylococcal subspecies and is quite difficult to proceed. Vulgar (or ordinary) is called the mixed form of the disease, which is caused by both staphylococci and streptococci. Slit-like impetigo - streptococcal lesion of the corners of the mouth, folds in the area of the wings of the nose. Bockhart disease is always caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
There are several other subtypes of the disease, but they are almost never diagnosed, because they exist only on the pages of scientific works, encyclopedias and completely repeat the clinical picture of the main types of the disease. Their treatment is no different from basic therapy, and therefore doctors do not bother to set such rare diagnoses.
Diagnosis, by the way, is quite simple - it consists in a general blood test and analysis of the contents of a purulent blister on the skin. This allows you to accurately determine which of the germs caused the disease and prescribe treatment.
The reasons
Staphylococcus and streptococci surround the child almost everywhere. But this does not mean that every baby is at risk of developing impetigo.
Infection contributes to:
- wounds and abrasions on the skin;
- heat, high humidity conditions;
- hygiene violations;
- the post-illness period, when immunity is weakened;
- elevated blood sugar, diabetes.
Mostly at-risk groups include children under 6–7 years old, children frequently visiting a common pool, and public baths. Impetigo often develops in children who suffer chronically or have recently had other skin diseases.
Symptoms and signs
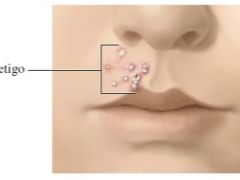
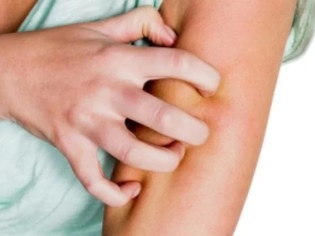
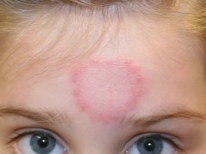
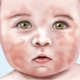
The incubation period of the disease lasts on average 7-10 days. That is exactly the time it takes for microbes to adapt, suppress local immunity and begin to multiply. Impetigo is manifested by rash and scabbing. The affected places give the child a lot of discomfort - itching, burning, pain.
When the baby cannot cope with the itching, he begins to comb the rash, and the microbes are able to spread to neighboring areas of the skin. So is self-infection.
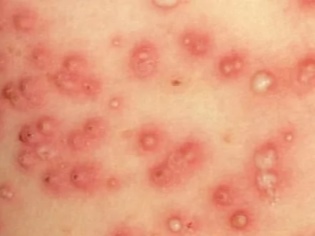
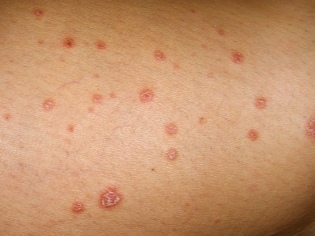
Most often, the first elements of a rash appear at the base of the hair follicles. Rash with watery heads can appear on any part of the body.
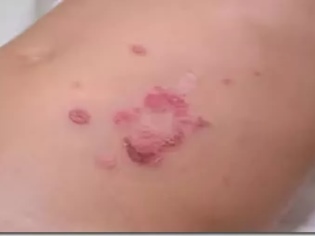
Sometimes in the liquid that fills the bubbles, there may be an admixture of blood. Pretty quickly, the rash burst and the affected area becomes covered with a yellowish crust.
From this point on, the unbearable itching stops, the crusts dry up and gradually disappear. In their place remains a small pink spot, which eventually passes without a trace, leaving no scars or spots.
Often a rash in children begins from above and spreads down. First of all, the nasolabial triangle, the corners of the lips, the chin are affected. In response to inflammation, nearby lymph nodes may increase slightly.
More discomfort delivers illness caused by streptococcus. A staph infection does not cause severe itching, after the bubbles burst, they turn into ulcers, a slight burning sensation can be observed during this period. The most painful is mixed (vulgar) infection.
The disease is very contagious, it is transmitted by contact. In the children's team, the ailment spreads very quickly, since children share toys, dishes, bedding.
In young children, the disease causes changes in the general condition - they may experience discomfort, loss of appetite, sleep disturbances.
Treatment
Germs for breeding prefer a warm moist environment. Therefore, it is important at an early stage after the discovery of the first rash to completely limit contact with the baby water. The affected skin cannot be wetted.
At home, the treatment will include several important actions: treatment with an antiseptic, the use of drugs that the doctor deems necessary to prescribe. For local treatments, the bubbles should be opened and carefully lubricated with a cotton swab what is left of them.
Although the infection is bacterial in nature, antibiotics are not always prescribed to the child. In case of a mild and limited ailment disease, antimicrobials are usually not needed, antiseptic treatment is sufficient.
How and what to treat if the infection is quite spilled and serious, the doctor decides. He does this in view of the age of the small patient and the sensitivity of the bacteria detected by the tests to various antibiotics. Sometimes an antibiotic ointment is quite sufficient; in the more severe forms of impetigo, systemic antibiotics are prescribed, which your baby will need to take in pills or suspensions.
The most commonly prescribed are:
- Antiseptics - a solution of brilliant green (brilliant green), iodine, hydrogen peroxide.
- Ointments - tetracycline (eye), erythromycin.
- Antibiotics - "Ampicillin», «Amoxicillin"," Erythromycin ","Clarithromycin», «Cefazolin».
It is strictly forbidden to smear the rash with anything until the doctor sees the child. Since under a layer of green stuff it will then be rather difficult to establish what the rashes actually appeared.
When impetigo is detected, it is necessary to report this not only to the polyclinic, but also to the children's institution, which is attended by the child - kindergarten or school. Staphylococcal and streptococcal infections, even for one pupil - this is the reason for large-scale testing and finding the source of infection.
Folk remedies are not worth treating impetigo. In any case, experts warn of such actions of parents. The complications of a neglected infection can be too serious if the string or chamomile with which the sores were moistened will not work.
And she is not likely to take action.If everything is done correctly, the treatment will not be long and difficult, after 7-10 days the problem will be completely resolved.
Prevention
Impetigo prevention is quite simple and fits into the basic concepts of hygienic principles. The child must learn to wash their hands more often. A small child should timely trim the nails on the handles.
In children, especially in the first year of life, they are very sharp, and if the mother misses the moment, the child can be scratched with the grown nails. And the wound is a potential breeding place for microbes.
Scratches and abrasions to the child must be treated with hydrogen peroxide and alcohol-containing antiseptic. It is important that the child is not in contact with people who have or have recently had streptoderma.
It is important to monitor the cleanliness of the skin, to bathe the child in a timely manner, to avoid contamination of the injured skin areas - abrasions or cuts. On the scale of the whole organism, it is very important to strengthen the child’s immunity so that he learns how to "repel" the pathogenic microbes. To do this, it is recommended to harden, take vitamins, according to age, a balanced diet, adherence to the daily regimen and the absence of strong stress.
See the following video for what streptococcus is and how to deal with it.