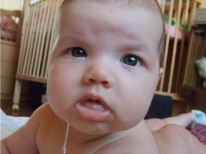
Abundant salivation in a child
Young babies often have increased drooling. Abundant salivation in a child does not always indicate the presence of pathology.
The reasons
In children, there is a more abundant salivation - compared with adults. This feature is quite physiological, in most cases it does not require treatment. All the causes that cause increased saliva or hypersalivation in babies can be divided into physiological and pathological.
During the first year of life, excessive salivation is a normal process. Symptoms of hypersalivation will pass on their own, treatment is not required. Elevated saliva from the first month of life and during the first year is the norm for all babies. The occurrence of a strong drooling at an older age speaks more about the possible presence of pathology, which led to the development of this symptom.
When is it safe?
In babies at 2 months, increased saliva is often observed. This is due to the lack of teeth. This feature allows the baby to eat mother's milk. This feature is manifested in every healthy infant at this age.
Newborns who were born before the prescribed period often have increased hypersalivation. This is due to the underdevelopment of the salivary glands during the period of intrauterine development. After birth, premature babies usually have a stronger salivation than their peers who were born in time.
At 3 months in infants, there is a strong salivation as a result of the first teething.
This process is accompanied by the appearance of pain and itching in the area of the tooth holes, which leads to the active work of the salivary glands and increases salivation. Usually, the final eruption of all teeth takes a lot of time. Most often it ends by 3-4 years.
During breastfeeding, the baby receives protective antibodies from the mother. Increased drooling is a manifestation of local immunity. This condition helps the child to cope with various infections. The secretory immunoglobulins in saliva help to prevent pathogens from entering the human body.
If the child is on artificial feeding, then he also often has hypersalivation. In the composition of saliva there are many different enzymes that allow you to break down proteins and carbohydrates that are part of the adapted nutrient mixtures. Often transfer to artificial feeding occurs in 4 months. At this time, the baby and the first signs of increased drooling appear.
When should you start worrying?
Not always the development of excessive salivation is safe for the baby. Often, the appearance of this symptom contribute to various diseases.
Among the most common pathological causes that lead to the development of increased salivation, can be identified:
- Inflammation of the oral mucosa. Ulcerative defects lead to increased salivation. With the development of stomatitis in the mouth, numerous erosions and ulcers are formed. This condition contributes to the formation of large amounts of saliva.
- Gum disease. Inflamed mucous membranes in the area of the dental wells also contribute to the spread of inflammation to the salivary glands, which begin to produce large amounts of saliva.
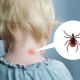
- Worm invasions. Helminths, which are parasitic in the body, begin to secrete numerous toxic products of their vital activity. These substances can enhance the formation of saliva. Most often helminth infection occurs at the age of 8-12 years.
- Various diseases of the central nervous system. Hypersalivation often develops in babies with congenital injuries and brain damage. For some forms of cerebral palsy, increased saliva formation is also characteristic.
- Inflammatory diseases of ENT organs. Otitis and sinusitis are often causes of excessive saliva production.
- Medication. Some products have side effects, causing hypersalivation.
- Toxic poisoning. The ingestion of mercury, lead, and various chemical pesticides contributes to the abundant formation of saliva.
- Fungal infection. Excessive growth of candida on the mucous membranes may contribute to the appearance of oral candidiasis in the child. This condition is accompanied by excessive formation and saliva secretion.
- Cold and infectious diseases. With these pathologies, copious salivation is auxiliary. The body thus wants to get rid of pathogenic microorganisms. Usually with colds, there is a combination of hypersalivation with high fever. Catarrhal symptoms appear: runny nose, redness in the throat, cough.
- Allergies. With the development of allergic rhinitis or conjunctivitis, increased salivation is also observed. Most often it occurs after inhalation of plant pollen or in contact with domestic animals. Many children do not tolerate flowering meadow grass and wild flowers.
- Traumatic injuries. As a result of falls, the salivary glands become inflamed. This leads to increased secretion of saliva. Most often this problem occurs in children from 6 years.
How does it manifest itself?
Increased drooling is characterized by excessive formation and salivation. In infants food often gets on the clothes, if you do not use special apron or aprons during the feeding. Kids in the first months of life often pull various objects into their mouths. Nipples and rubber toys as a result of excessive salivation are constantly wet.
Excessive saliva can cause irritation or redness near the corners of the mouth. In case of infection, inflammation may develop. If severe salivation caused gingivitis or stomatitis, then bleeding sores appear in the mouth.
Food can easily traumatize them, which leads to the appearance of pain during feeding.
What to do and how to treat?
If you are going to treat increased drooling in a baby, you should find out the reason that led to the development of this symptom. If the child has worms or chronic diseases that cause hypersalivation, the baby should be shown to the pediatrician. The doctor will prescribe additional tests that will help establish an accurate diagnosis. After that, he will be able to recommend medications that will contribute to the normal separation of saliva.
If the salivation is insignificant, there are no other symptoms, you can use drugs prepared at home.. For the normalization of the salivary glands and the rehabilitation of the oral cavity decoctions of chamomile, sage, calendula are perfect.
To prepare a useful home remedy, take 1 tablespoon of chopped vegetable raw materials and pour a glass of boiling water over it. Insist for half an hour. After that, the resulting infusion filter with a sieve or through cheesecloth.Rinses with herbs should be done 3 times a day.
Using herbal remedies to eliminate excessive drooling is a very safe method.
However, some babies may develop an allergic reaction to herbal ingredients. In this case, you need to stop rinsing and discuss the situation with your doctor.
If a baby has constantly drooling, it is possible to use a special bib that is on the neck and prevents saliva from entering the clothes. To prevent the development of redness and irritation on the face of the baby, you should regularly monitor the child and remove the saliva on the skin. You can also use special creams and ointments that help to cope with irritations.
For these purposes, the following tools are suitable: "Bepanten Cream", preparations of the series "Weleda", "Pantestin" and many others. Before applying the cream, the skin should be wiped with a clean gauze cloth dipped in boiled water, cooled to room temperature. With strong drooling, the child’s clothes and underwear should be changed as often as possible.
Physiological causes that contribute to the appearance of strong salivation in the baby do not require treatment and pass on their own - after a while. If pathological conditions are the cause of hypersalivation, then treatment of adverse symptoms will require treatment of primary diseases that have caused excessive salivation.
You will learn more about salivation in babies from the following video.