What to do if the skin of a child peels off?
Peeling on the skin of a child is an alarming symptom, but not always dangerous. If in time to find the cause that led to the violation of the skin, and eliminate it, the baby will please the parents with soft and delicate velvety skin. In this article we will talk about what to do if peeling began in children of different ages.
What it is
Peeling is a natural process. In this way, the outer layer of the skin - the epidermis is released from keratin cells. They mature and develop in the deep layers of the skin, during the day they travel from the depths to the surface, synthesizing keratin simultaneously, and then, when their life ends, die off and disappear. The peeling process in medicine has a very specific name - desquamation.
When pathological desquamations, keratin cells live for a shorter period, quickly come to the surface and die in large quantities - peeling becomes noticeable.
With physiologically caused desquamation, the process remains almost imperceptible to the human eye - scales that exfoliate are so small that you can only see from the microscope.
If the skin did not have the ability to peel off, the dead keratin cells of the epidermis would gradually create a thick and durable layer, keratinous, similar to the shell. To keep the skin elastic, nature created this unique mechanism in its own way - desquamation.
However, it is not always peeling that can be considered normal. Quite often, the lifespan of keratin cells is reduced due to a number of adverse factors, both external and internal.
Causes of peeling
Children's skin with enhanced desquamation can respond to both adverse living conditions and various diseases. In children of the first year of life, the peeling of the scalp and body is relatively harmless in nature - it indicates that the skin adapts to the new habitat, because during pregnancy the baby was surrounded by water, and after birth - by air.
Such natural desquamation usually does not have a catastrophic scale, but if a large area of skin is peeling off, then it is worth thinking about other, more serious reasons for this phenomenon. The most common causes of excessive desquamation are as follows.
Dry skin
Dryness of the skin is rarely congenital, because all children at birth have an adequate supply of lipid fatty grease, which protects the thin children's skin from the harsh realities of the surrounding world. This layer can be thinned under the influence of a variety of reasons, the most common is dry air and heat in the house where the baby grows.
The hotter the air is, the more dry peeling is more often observed in the winter when the apartments are heated, very dry air. Most often, due to the microclimate, the skin dries out in infants and children of preschool age.
In adolescents, the sebaceous glands work more actively under the influence of sex hormones. The disadvantage of this fact is the formation of acne, but the undoubted advantage lies in the fact that the peeling is almost not threatened.
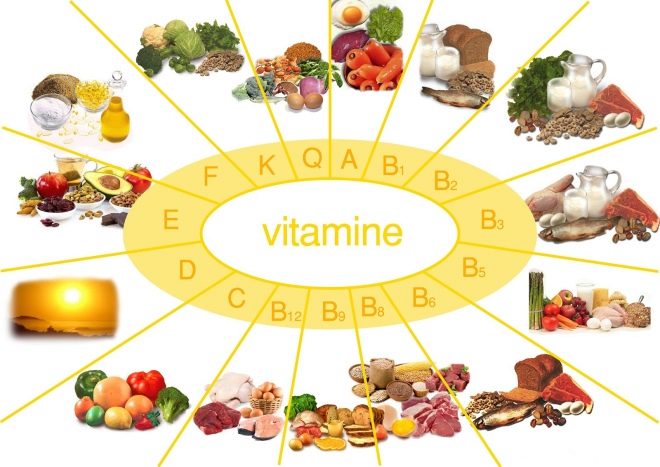
Vitamin deficiency
In children of any age, peeling may occur on the background of insufficient amounts of vitamins A and E in the body. It is these substances that make human skin elastic and elastic, regulate cellular metabolic processes in its layers. Such a vitamin deficiency occurs in infants, if breast milk contains little retinol (A) or tocopherol acetate (E).
Skin without these substances and in children of older age becomes fragile and vulnerable.
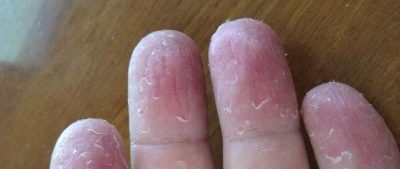
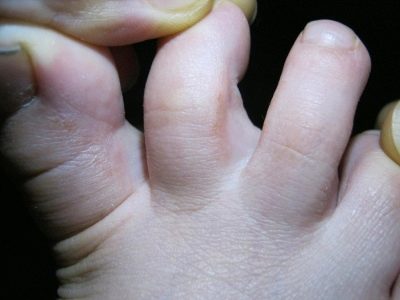
When flaking associated with a vitamin deficiency, flaking often occurs on the fingers, toes, on the nose, chin, and on the head.
Hygienic errors
Careless attitude to hygienic requirements, rare washing, skin contamination leads not only to flaking, but also to infection of cracks that have arisen. However, too diligent washing, daily use of soap, baby shampoos, bath foams also lead to drying of the skin and, as a result, to desquamation.
Lipid protective layer, which protects the skin from external aggressive factors with frequent use of cosmetics and alkaline detergents, such as soap, is quickly erased, the skin ceases to retain moisture.
Because of the violation of hygiene requirements, peeling usually occurs behind the ears, on the scalp, on the legs and arms, inside the ear.
Hormonal changes
The most deep-seated causes may be hormonal status. Usually peeling skin reacts to a change in the balance of certain hormones. Such desquamation often occurs during adolescence, when hormonal status changes on the face of a child, on heels and palms.
External environment
The skin of a child is especially susceptible to peeling, which walks long and long in the sun, in strong winds, during frost. Searing of the epithelium and premature death of keratin cells in this case have only external reasons. Such desquamation manifests itself in all open parts of the body that are exposed to wind, sun, and low temperatures. Usually the skin flakes in places, there is a slight discoloration of the skin on the affected areas.
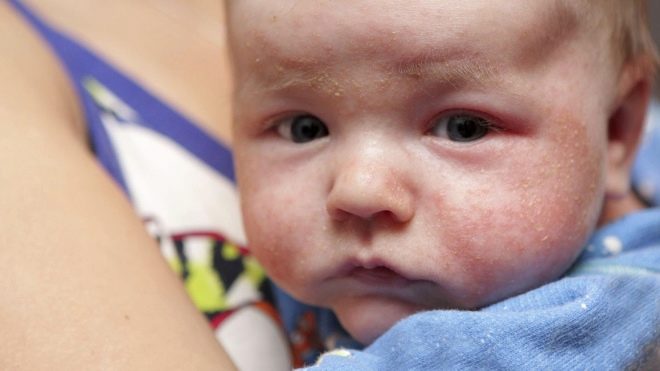
Allergic reaction
When food, drug, seasonal and other types of allergies, which are accompanied by dermatological symptoms, peeling, as a rule, does not begin immediately, but several days after the appearance of a rash and redness. Red scaly stains prone to fusion may appear on the body, on the face on the chest and back. In babies under one year old, such spots with fragments of desquamation often appear on the back of the head and on the forehead, between the eyebrows.
Peeling in this case is caused by the pathological drying of areas of skin that have previously undergone an inflammatory process under the influence of an immune response to protein antigens or under the direct action of an allergen without the participation of the immune system.
Fungal diseases
The cause of severe peeling can be a fungal skin disease. There is a great variety of fungi that can cause mycoses. Desquamation in this case accompanies the skin lesion. in locations of colonies of fungi.
In children, such peeling usually has a whitish, almost colorless shade. Most often localized on the scalp, on the foot, on the palms and on the back of the palms, on the eyebrows and even on the upper or lower eyelids, if the mycosis has spread to the ciliary zone.
Other diseases
Peeling of the skin is accompanied by diseases such as psoriasis, ringworm, seborrhea, some forms of diabetes, problems with the thyroid gland, as well as problems with the kidneys and extensive worm infestations.
What does this look like?
Peeling, which should not cause great concern, does not look inflammable, without redness, swelling, but without the formation of deep bleeding cracks in the skin.With physiological desquamation, a rash never appears, the skin does not exfoliate with large “patches”, there is no grayish or silver discoloration of exfoliating scales. Infected cracks are dangerous.
If the skin is dry, then its integrity is easily broken even with a light touch. Under such conditions, the accession of a bacterial or viral infection may occur, the “entrance gate” for which will be a crack or microtrauma that has appeared on the skin. In this case, inflammation, suppuration, soreness.
If you find such signs, you should definitely consult with your doctor, since the causes of desquamation may be far from harmless.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is that the doctor collects a complete history - when and with what state of health the child was born, whether there are dermatological problems in his immediate relatives, what he eats, what he has been ill with lately. In appearance of the skin, the presence or absence of itching, pain sensations doctor can put forward presumptive diagnoses.
Putting everything in its place will help laboratory diagnostics. A blood test, urine and feces - this is the necessary minimum, which will have to pass. Sometimes they can send a blood test for hormone levels, as well as an allergy test, if the child suspects an allergic reaction.
Treatment
General recommendations:
- Treatment of dry skin, regardless of the cause, always begins with a change in the child’s living conditions.
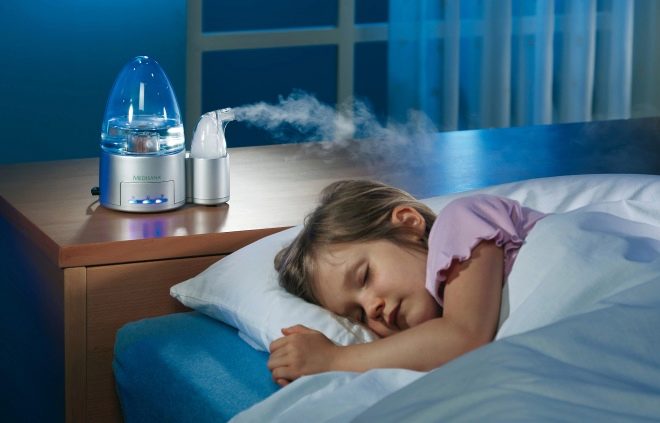
- Maximum moisturize the air in his room, begin to monitor the temperature of the air. The best from the point of view of the beneficial effects on the skin are such parameters: the temperature is not higher than 21 degrees of heat and the humidity of the air - 50-70%.
- The humidifier will help to create such conditions, the benefit of the device is inexpensive, as well as special taps - limiters that allow you to adjust the temperature in the radiators.
- To reduce sweating, which also contributes to the drying of the skin, help properly selected clothing and, most importantly, its quantity. You can not wear a child too warm, muffle him. You should also avoid prolonged contact with the skin of synthetic fabrics, in which perspiration and evaporation is disturbed.
- At the time of treatment should limit the use of soaps and shampoos, even if they are children, special hypoallergenic. Washing with soap should be done no more than once a week; you should also wash your head with shampoo no more than once every 7 days.
- Foams, gels and other cosmetics for the skin should be discarded altogether.
- Dry skin can not be treated with alcohol and solutions containing alcohol, lotions.
- Do not wash the child with too hot water, soar with a broom in the bath. But the door to the bathroom at the time of the water procedures should be kept closed to create additional moisture in the air.
- After bathing, the places with peeling should be lubricated with any greasy oil-based agent, for example, baby cream. The use of powders with the propensity of the skin to dryness is prohibited.
- It is important to ensure that the child drank more liquid, is not long in the sun or in the wind. Usually these measures are more than enough to solve the problem of peeling the skin once and for all.
- If the cause of desquamation is related to the disease, then appropriate treatment is added to the indicated recommendations.
With allergies
To rid the child of allergic spots with a scaly surface, doctors recommend antihistamines - Suprastin, Erius, "Tavegil" other. But first of all they try to protect the child from contact with the allergen. They reconsider its nutrition, exclude products that are dangerous from the point of view of the likelihood of developing allergy. Special attention is paid to detergents and laundry detergents, so that they also do not contain allergens.
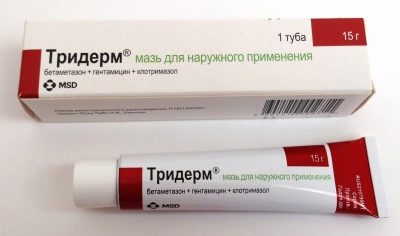
Declare a house dust war. If peeling during the week does not pass, the doctor may prescribe hormone-based ointment - "Advantan, "Triderm". In severe cases, antihistamines are given to the child along with calcium supplements, and treatment with glucocorticosteroid hormones, in particular, “Prednisolone».
With a fungal or bacterial infection
If laboratory tests reveal a fungal or bacterial skin lesion, the doctor prescribes an appropriate therapy. In case of mycoses, the child undergoes a rather long antifungal treatment, both with external preparations and preparations for oral administration. After the prescribed course, a short break is taken and then the treatment is repeated to prevent relapse.
Bacterial infections often require antibiotic use - most often in ointments, as well as antiseptics (aniline dyes, hydrogen peroxide).
With vitamin-deficient desquamation
It is often possible to restore the balance of vitamins A and E after the appointment for topical application of oil solutions of these vitamins. They are applied and easily rubbed into flaky places after bathing, when the skin is steamed and saturated with moisture. Care should be taken to lubricate the peeling areas on the face and behind the ears.
Then the child is discharged vitamin complexes by age, and give advice to parents on the organization of food baby - buckwheat porridge, red and orange vegetables, butter, fatty dairy products, fresh greens and fruits, cod liver - this is exactly what should be on the child's table with a deficiency of vitamins A and E.
Usually, after the elimination of the disease or condition that caused the deterioration of the appearance of the skin, desquamation stops.
Prevention
In order to keep the skin of a son or daughter always elastic and not peeling, it should be observed preventive measures for skin dryness:
- Do not overheat or supercool the child.
- Do not experiment with cosmetics and various detergents.
- Frequently aerate and do wet cleaning at home.
- Ensure that the child drank enough liquid.
- Do not wipe baby skin with vodka and alcohol.
- Do not give a child without a prescription any medication.
- To harden the baby from birth (the skin produces local immunity up to 5-6 years, the first five years are very important for the tempering procedures).
- Follow the diet - do not give allergenic foods, as well as to control that the diet has enough of the necessary microelements and vitamins for normal growth and development.
For how to care for dry atopic skin, see the following video.