How to remove swelling and itching in a child after an insect bite?
Small insects can do great harm to a child’s health. Bites flying and crawling creatures are able to deliver a child a lot of unpleasant sensations. In some cases, they represent a deadly danger to the baby. How to help the baby, if it was bitten by an insect, we will tell in this article.
How insects affect a child
Most often, children are bite by hymenoptera and diptera. If the aggressor has a sting, it usually has special glands that produce toxic substances. When they sting, they release these toxins, which cause local irritation, inflammation, and can cause an allergic reaction. In this case, the allergy can be both local and systemic, which is the most dangerous.
Diptera or fleas that are completely devoid of wings do not release any poison, but when they bite, the victim is anesthetized with special salivary enzymes, therefore such bites later on it itch and itch.
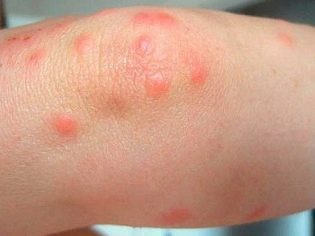
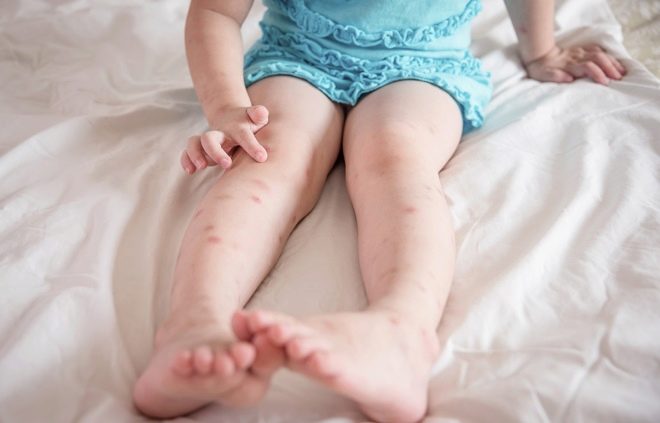
Multiple bites, such as lice, fleas, can cause a spilled allergic reaction, which manifests itself in extensive dermatitis.
Very dangerous for a child bug bite. It can cause severe swelling, even development anaphylactic shock.
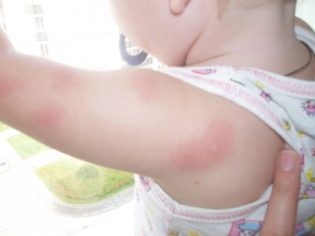
The bite of a midge or mosquito causes local redness, swelling, tenderness.
Blood-sucking insects are an additional danger - in addition to itching, which appears some time after the bite, there is a chance of infection with infectious diseasestransmitted by hematogenous route (through the blood).
It is almost impossible to protect a child from insects. If at home with the help of mosquito nets and fumigators it is still possible to somehow reduce the probability of a bite, then it is impossible to hide on the street in spring, summer and early autumn from flying and crawling aggressors. Therefore, it is important to be able to distinguish between dangerous bites and non-dangerous bites and to know how to help a child with itching, swelling, or pain syndrome.
Symptoms and signs
A child can react to an insect bite by one of three types:
- locally;
- extensively local;
- systemically.
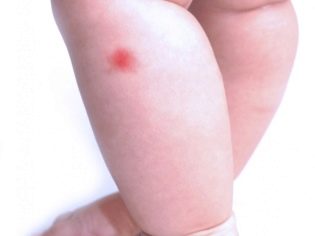
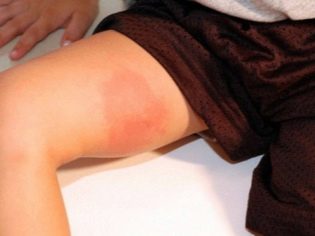
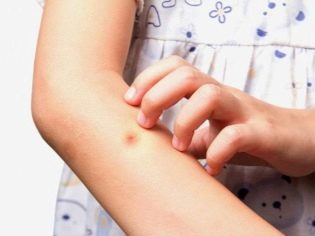
Redness, itching, pain only in the area of the bite - this is the most common common reaction. Such a bite, in which a puffiness or blister is more than 5 centimeters in diameter, is considered extensive.
A systemic reaction can be said when the signs of an allergic reaction begin to appear far enough away from the bite site itself.
Discomfort caused by a bite can last only a few hours (such as when a wasp bite), and it can hurt and itch for several days (so bites mosquito, bee, bedbugs).
Traces of some bites can be noticeable even a year later, and if the puffiness does not subside, such traces are often mistaken for benign tumor processes.
Stinging insects can be very insidious - their bites most often cause systemic allergies.
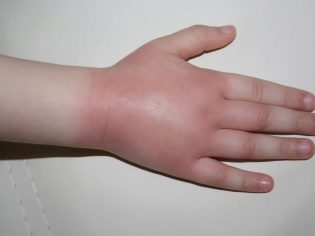
For example, a bee sting in the arm can be expressed both as local redness with swelling, and as a giant swelling of the entire limb, and as anaphylactic shock, which can be fatal.
The consequences of a bite depends only on the personal characteristics of the child’s body.
If he is allergic to bee products, then bee stings are very dangerous for him. A significant role is played by the place of injury. - Bites on the face, in the eyelid, in the ear are always more dangerous than bites in the leg.The closer to the brain and respiratory organs, the more dangerous the possible swelling.
Light bites are accompanied by pain in the area of the bite, itching, and sometimes a feeling of fear (toxins of some insects have an interesting panic effect on the human psyche).
If a child has shortness of breath, pain (headaches, abdominal or any other), in addition to the obvious bite mark, we are talking about an allergic reaction of the first type that is more dangerous for the baby’s health, but not fatal.
When a severe bite (the second type of reaction), the child begins to experience nausea, respiratory failure, severe fear, his voice becomes hoarse, delusions can appear. Shock is accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, cyanosis of the skin, spontaneous urination, loss of consciousness.
The reaction to the bite can be not only allergic, but also toxic. This becomes possible if a child is immediately bitten by a large number of unfriendly-minded individuals.
A few hours later begins vomiting, diarrhea, redness of the skin, swelling.
First aid
Before you begin to treat a child, you should carefully examine him, find out where and what is swollen, whether he has fever, nausea, headache, shortness of breath.
If this is observed, you should immediately call an ambulance. Similar should be done in the event that there were several bites at once.
Immediately after the bite:
- The lesion is washed with cool running water., and then treated with hydrogen peroxide or one of the aniline dyes (Zelenka, "Fukortsin»).
- The child is given an age dose of an antihistamine drug., which should be in every home first aid kit - "Suprastin", "Tavegil», «Loratadine"," Erius "," Zyrtec ","Tsetrin" and so on.
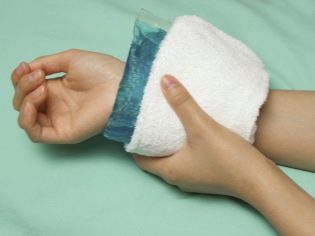
- A small piece of ice is applied to the site of the insect bite.. Effectively remove the tumor will help liquid ammonia, if they previously moisten the ice.
If you quickly provide first aid in the manner described above, then the edema will subside in about half an hour. If the moment of the bite went unnoticed, and the symptoms showed up much later, then the first aid is too late, you will have to think about how and what to treat the effects of the bite.
Treatment
Means for the treatment of bites should be purchased in advance and kept on a “rainy day” in the home medicine cabinet, so that they are always at hand. Rules of therapy do not imply the use of several local drugs, since this can only contribute to the strengthening of the local allergic reaction.
With a light bite, only ointments that are used topically are sufficient; with a common one, parallel administration of antihistamines may be necessary.
If with allergy medications everything is more or less clear, they are usually in the first-aid kit, then with topical medications there are many questions concerning, in particular, whether children can use this or that medicine.
Here is a list of topical medications that are approved for use in children to relieve itching and swelling from insect bites.
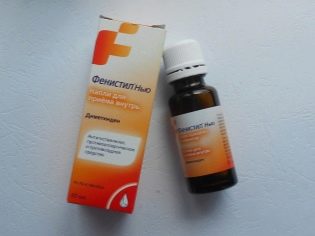
Phenystyle
Quickly and effectively relieves allergies, especially at the local level, and is good for bites caused by severe itching.
The preparation is produced in the form of a gel, drops and capsules. Capsules can be given to children - adolescents from 12 years. All other forms can be used from any age.
Children from 1 month to 1 year are allowed to give no more than 3-10 drops per day, babies up to 3 years old - up to 15 drops at a time, children older than 3 years old - up to 20 drops at a time.
Before giving the child drops, they should never be heated, otherwise the medicine will lose its effect and there will be no effect.
The cream (gel) is used only locally, has no age limit, it can be applied to the bite site up to 5 times a day, easily rubbing it into the surface. Putting a bandage on top is not necessary.
Nezulin
This cream has not only anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects, but also helps the bite wound heal faster without a trace. It acts fairly quickly, which is important for children's use, it has no age limit.
The tool has a delicate texture, easily absorbed, does not leave greasy stains and marks on clothes.
It contains a wide range of herbal remedies (lavender, mint, chamomile, and others), as well as dexpanthenol, which helps the healing of the skin.
Apply it in place of the bite can be up to 4 times a day, easily rubbing the cream into the surface of the skin.
Psilo balm
This drug in the form of a gel is approved for use for children who have already turned 1 year old. This is an antiallergic antihistamine topical.
Place the bite, pre-cleaned and dry, smeared with a thin layer of gel 3-4 times a day.
In addition to blocking histamine receptors, the agent has a cooling effect that helps reduce itching and reduce swelling.
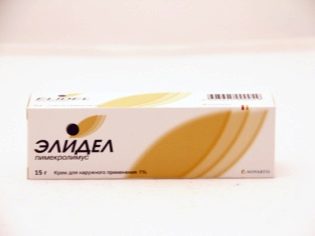
Elidel
This is a non-hormonal anti-inflammatory agent. It does not act immediately, but only some time after rubbing in, when the inflammatory process begins to decrease.
Apply this cream can be used to treat bites in children who have already turned 3 months.
The tool can not be used long and constantly, but in the case of insect bites, this, fortunately, is not required. It can be applied twice a day with a break of 12 hours.
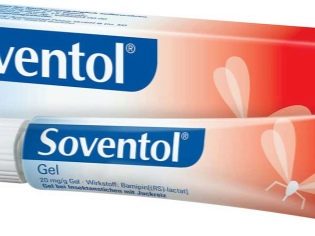
Soventol
This cream is used in the treatment of children older than 3 years.
Active ingredients allow you to quickly block histamine receptors, which reduces the appearance of allergies.
After the first application, it is recommended to wait half an hour and apply the cream again. After that, the tool is applied no more than 3-4 times a day.
Rescuer
It is a balm based on herbal ingredients and ingredients of animal origin. It not only anesthetizes and relieves inflammation, but also contributes to a more rapid healing of damaged skin.
There is no age limit for the balm, it can equally be used for infants and for children of school age.
Most of these funds are also effective for burns, cuts, abrasions, sunburn, which makes them versatile and necessary for a first-aid kit in a family where children grow up.
Going into nature, it is useful to have in the first-aid kit not only one of these means, but also an ampoule "Prednisolone».
An injection of this hormonal drug can save a child's life in the field if an extensive swelling and anaphylactic shock develops after an insect bite.
What not to do
If a child has a bite, presumably left by an insect, you should not try to find out for yourself what kind of "beast" bit the beloved child. This is a waste of time.
First aid is universal for any bite, and severe forms that require the intervention of a doctor are “investigated” in the laboratory. The type of toxin and the alleged appearance of the insect will become clear after analyzing the infiltration from under the skin.
Do not smear the bite with iodine or alcohol. This will only increase the redness and burning sensation. There is also no need to apply antibiotics and ointments with antibiotics.
It is impossible without the recommendation of the doctor to smear the place of bites with hormonal ointments for the child. The use of hormones is appointed as a last resort. Unbeknownst to the doctor, these drugs can only be used in an emergency situation when life threatens.
For more on helping a child with insect bites, see the next video.