Edema of the testicles in newborns and infants
Quite often, after the birth of a little boy, his parents show signs of genital diseases. Such congenital pathologies cause moms and dads a lot of different issues that require a mandatory and correct solution.
What it is?
Edema of the testicles in newborns is a fairly common pathology. Every tenth born baby has this disease. Usually the first adverse symptoms of the disease are recorded in infants. Specific markers of the disease begin to be detected in babies in the first days after birth.
The boys may experience swelling of both the left and right testicle. Also, the process is often bilateral. The development of this condition leads to the impact of various factors and causes. Dr. Komarovsky believes that congenital variants of the disease are most characteristic of newborns.
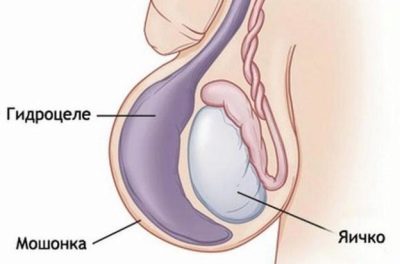
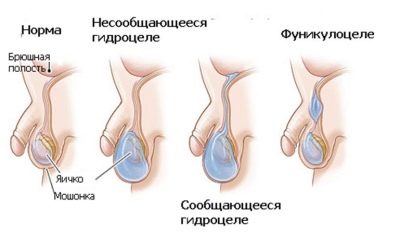
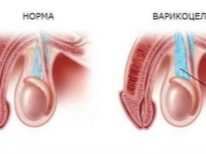
When dropsy or hydrocele, a cluster of excessive secretion levels forms between all the sheets that cover the testicles. Usually in the norm between the membranes covering the internal genitals of the baby, there is a small amount of lubricant. It provides normal sliding and gonadal function. In various pathological conditions, this process is disturbed and the liquid forms excessively much. This pathology is called dropsy.
According to statistics, in three out of four babies, the disease is mild. After an illness, children usually recover completely. However, in 25% of cases, hydrocele of the testicles leads to the development of long-term adverse effects. In adulthood, they contribute to the appearance of reproductive problems or even cause infertility in men.
The reasons
All causative factors causing dropsy in newborns and infants can be divided into several categories. This division allows doctors to accurately determine the cause of the disease, and therefore choose the optimal tactics for keeping the baby in the future. This disease can be both congenital and acquired condition. According to statistics, congenital forms account for more than 80% of cases.
The development of this state in the smallest children lead:
- Infections suffered by mom during the carrying of the future baby. Pathogens, as a rule, very easily penetrate the placental barrier. Getting through the feeding vessels of the placenta to the baby, they cause severe infectious inflammation. Such microorganisms contribute to the development of anomalies and defects in the structure.
- The birth of the baby before the date of birth. Numerous combined pathologies in the structure and functioning of the male glands are found in premature babies. In the period of the third trimester of pregnancy, the final completion of the organogenesis of the male genital glands occurs. Thus, the testicles should descend from the abdominal cavity to the groin. The birth of the baby in earlier periods leads to the fact that the male sex glands are still not completely complete.
- Various effects and damage during childbirth. Such injuries are recorded during natural childbirth. Pregnancy with a large fetus in a narrow pelvis of the mother increases the likelihood of various injuries during childbirth.Pelvic presentation of the fetus and overly active labor can cause birth defects.
- Heredity. Scientists have found that in families where the congenital forms of dropsy of the testicles are recorded, more babies with this disease are born. Currently, the exact genes that encode a hereditary relationship have not yet been established. However, there are a large number of different scientific theories that support the fact.
- Anatomical defects. Diseases leading to increased intra-abdominal pressure, lead to the accumulation of excess fluid between the membranes of the testes. Usually these pathologies occur during fetal development. Abdominal wall defects also contribute to the development of dropsy of the testicles in newborn babies.
- Traumatic injuries. Most often occur in violation of the proper treatment of the child. The fall of the baby on the floor can cause injury to the external genital organs and even the appearance of signs of internal bleeding. These forms of the disease are called acquired, since they arise after the birth of the child.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system. Congenital torsion of the testicles, defects in the structure of the external genital organs, cleft of the duct between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum area lead to the appearance of signs of hydrocele in the child. The protracted course of urological diseases also contributes to the disruption of the formation and outflow of fluid between the membranes.
- Tumor and malignant neoplasms. Rapidly growing tumors disrupt the development and functioning of the organs of the genitourinary system in the baby. Most often, oncological processes occurring in the intestines and lymph nodes lead to this condition. Usually dropsy of the testicles in this condition is bilateral.
Kinds
Varian dropsy of the testicles can be different. It depends on the mechanism of damage and the presence of an anatomical defect. Violation of the correct and physiological structure of the genital organs contributes to the appearance of excessive fluid accumulation between the membranes of the testes.
Currently, children's urologists distinguish several types of dropsy of the testicles in babies:
- Communicating. Normally there should be no communication between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum. When the duct that connects these anatomical zones is not overgrown, fluid flows out and flows into the external genital area. This condition is congenital. Quite often, this option is recorded in newborns.
- Isolated In this case, the process is one-sided. Only one testicle is affected. The second with this form remains intact. All clinical signs will occur only on the injured side. This form is found in infants and infants rather rare.
When making a diagnosis, doctors also make a note about when the disease occurred. If the disease has already formed during the prenatal development of the baby, then this form of the disease is called congenital. In case of traumatic injuries, cancer tumors, as well as other conditions that have arisen later, they already speak about the acquired variant.
Doctors also distinguish the following clinical forms of dropsy of the testicles:
- Sharp They are registered in babies for the first time in their lives. With adequate treatment, they usually do not become chronic. For recovery requires timely diagnosis and selection of the optimal treatment tactics.
- Chronic. Characterized by the gradual appearance of adverse symptoms. Require regular monitoring by medical professionals. Toddlers with chronic forms of dropsy of the testicles are observed regularly by urologists. With a protracted course of the disease, surgical methods of treatment are often required.
Symptoms
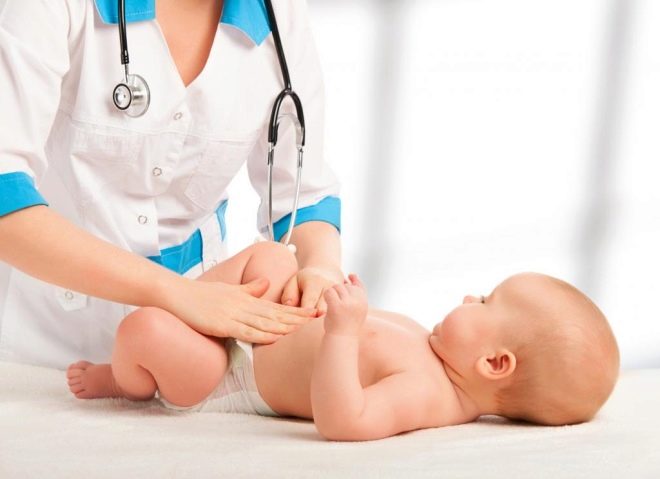
Suspect the disease can any parent.To do this, it is enough just to closely monitor the external condition of the external genital organs in a newborn child. It is easiest to notice any changes during daily hygiene procedures. Any abnormalities should push the parents to contact the specialist with the baby.
For dropsy of the testicles in newborns, the most common symptoms are:
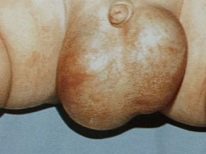
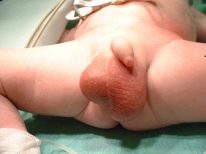
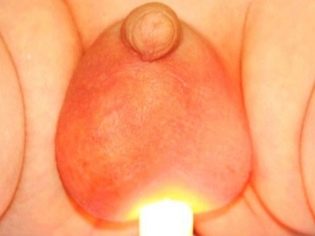
- Scrotal enlargement. Usually it increases in size several times. With a unilateral process, the scrotum becomes highly asymmetrical. It's pretty easy to notice, even at home.
- Redness of the skin. Normally, the skin in the scrotum has a dark brown color. With dropsy, it turns red. To the touch you can feel that the skin above it becomes somewhat hot to the touch.
- Soreness Pain syndrome is most often manifested during active movements, after a hot bath, and in some cases - after urination. Tracking this symptom in babies of the first year of life is quite difficult. Pay attention to how the baby behaves after and during urination.
- Excessive mobility of the skin of the scrotum. Excessive accumulation of fluid contributes to a better sliding of the testicular membranes relative to each other. This contributes to the occurrence of this symptom. In severe cases, increased mobility also joins pain in the intimate area.
- Change in appearance. When fluid enters the cavity of the inguinal canal, the scrotum becomes a characteristic “hourglass” shape. Usually, this symptom is detected by urologists during the clinical examination of the baby. With the development of a one-sided process, the change from the affected side becomes noticeable relatively healthy.
- Violation of general well-being. Kids are becoming more capricious. In some cases, with a mild course of the disease, the child’s behavior remains almost unchanged. Severe forms of the disease are accompanied by a rise in temperature to subfebrile and even febrile numbers, impaired appetite and sleep. Children can abandon the usual activities and active games.
Diagnostics
The mild course of the disease for a long time may remain undetected. Precinct pediatricians often do not establish the first clinical signs of the disease in a timely manner, since the baby’s well-being hardly changes. Only attentive and sensitive attitude on the part of parents to their child contributes to the timely diagnosis of these diseases.
If you suspect that the child has signs and symptoms of dropsy of the testicles, be sure to show the baby to a pediatric urologist or andrologist. Doctors will conduct the necessary clinical examination and examination, as a result of which they will be able to establish a preliminary diagnosis.
In difficult cases, the appointment of special instrumental methods of research confirming the presence of dropsy testicles in a child.
The following methods are used for additional diagnostics:
- Ultrasound of the scrotum and testicles. This method allows not only to establish the presence of free fluid, but also to determine its quantity. This study is safe and does not bring any pain to the child. To establish the correct diagnosis is quite a quarter of an hour. The method is informative and successfully used in pediatric urological practice throughout the world for many years.
- Diaphanoscopy. The study allows to describe the outer surface of the testicles. With the help of a special lamp, doctors detect the presence of pathological fluid. The method is quite informative and safe. It also does not cause pain even in the smallest patients.
Effects
The prognosis of the disease is usually favorable. In 80% of cases after treatment, full recovery occurs. For the cure is very important timely diagnosis and the appointment of the correct treatment.Optimally selected therapy leads to the complete elimination of adverse symptoms. Even in adulthood, boys do not have any significant abnormalities in reproductive function.
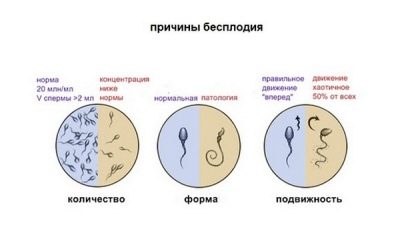
In about 20–25% of cases, long-term adverse effects may occur. Most often it is a violation of reproductive function and the development of male infertility. Prolonged squeezing of the testes with fluid leads to persistent hypoxia. Such oxygen starvation of organs contributes to the formation of abnormalities in spermatogenesis. This disturbed process causes the formation of non-viable sperm.
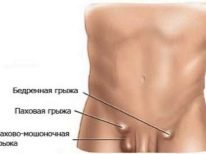
Also, chronic hydrocele of the testicles contributes to the development of the boy's associated urinary tract diseases. Violation of the outflow of fluid from the scrotum can lead to conditions accompanied by increased intra-abdominal pressure. The protracted course of the disease leads to child inguinal hernia. This condition requires surgical treatment.
Treatment
Disease therapy should be prescribed in a timely manner. The faster the pathology is established, the higher the chances for a complete cure. Usually, with properly selected tactics, recovery takes place at the onset of three years of age. The choice of treatment remains for the pediatric urologist. In order to draw up tactics, the doctor must take into account several factors: the age of the baby, the presence of associated diseases, the state of immunity, as well as the individual anatomical features of the child.
Currently, the following methods are used to eliminate signs of dropsy of the testes in babies:
- Expectant tactic. Up to one and a half years, surgical treatment is usually not carried out. Often this time is enough for the final formation of the male genital organs in small boys. In this case, the duct between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum is completely closed, which contributes to the normal formation of fluid between the membranes of the testes in the future.
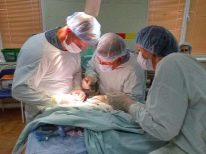
- Surgery. Performed in boys older than two years. Currently, various operations are used in urological practice. They are aimed at eliminating the pathological fluid in the scrotum, as well as to normalize the functioning of the male genital organs. In the presence of inguinal hernia an operation is also carried out to eliminate it.
- If symptoms of dropsy of the testes occur, then various medications are used. Such drugs reduce swelling and inflammation in the affected intimate area. Usually, urologists prescribe them only for coursework. Constant use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs for dropsy of the testicles in newborns is not required.
Medical monitoring of a newborn baby or infant with this pathology should be regular. Any deviations should be promptly identified and eliminated. Surgical treatments are used only with the ineffectiveness of all previous therapeutic methods.
The treatment of dropsy of the testicles at home is not strongly recommended by doctors. This can only contribute to the transition of the disease to the chronic form. Some babies after such home-based treatments only develop persistent allergic reactions. Treat dropsy testicles in a child follows only with the obligatory participation of the urologist.
About in what cases it is necessary surgery with dropsy of the testicles, see the following video.