Dropsy in a child
Issues of treatment of diseases of the genital organs in boys are always quite intimate for any parents. In some cases, fathers and mothers are so confused that they do not know who to ask for help.
What it is?
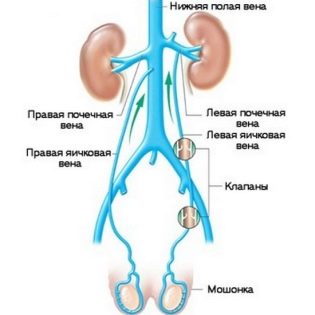
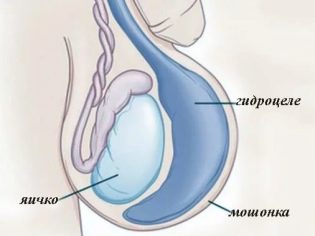
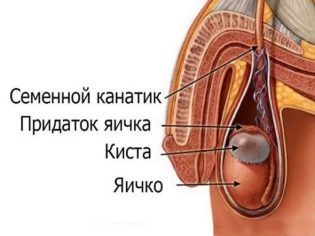
The testicles are paired genitals that are located in the scrotum. Under the influence of a number of factors, fluid accumulates in it. This leads to the development of dropsy of the testicular membranes. This swelling is also called hydrocele. In boys, this pathology occurs quite often.
In pediatric andrology, it is described as dropsy right testicle, and left. Often the process is two-way. Parents will be able to notice trouble even on their own. Usually, the baby's scrotum swells up or you can see its noticeable bulging.. These cases require immediate medical advice.
According to statistics, the disease occurs in every tenth child. In 9-10% of children, swelling of the testicular membranes occurs together with other diseases of the intimate organs at the same time. These include: inguinal hernia, dropsy of the spermatic cord gland, as well as the violation of the outflow of lymph from its membranes.
Causes and consequences
In boys, the disease is in most cases congenital. Usually the disease manifests itself in 1-2 years.
Some cases that occur with fairly erased symptoms can be identified in a child only at the age of 3 years. In complex clinical cases, an additional examination of the baby is required using modern instrumental diagnostic methods.
The following conditions lead to the development of this condition in boys:
- Weight is too low at birth. Babies born for some reason ahead of schedule are often more likely to develop dropsy. This is due to the presence of anatomical defects in the structure of the genital organs. Enough time is required to lower the testicles in the groin. When this period is shortened, the baby often has various defects in the structure of the genital organs.
- Birth injuries. Violation of childbirth can cause a variety of damage to the child. If the fetus is in pelvic presentation, as well as at birth of twins in a natural way - various injuries often occur, including the genitals. Also, a similar situation occurs in miniature moms who have given birth to a too large baby.
- Infectious diseases. Viruses and bacteria very easily penetrate the placental barrier. Getting into the body of the fetus at the stage of development of the genital organs, they cause in the baby various structural anomalies. Doctors consider the first and third trimesters to be the most dangerous period of pregnancy for the occurrence of these pathologies.
- Puffiness of adjacent organs. The fluid that forms in various diseases can easily flow from one anatomical zone to another and reach the scrotum. This feature is due to pediatric anatomy. Pathologies of the neighboring organs (often of the lower limbs) lead to the development of scrotal edema in the child, leading to hydrocele of the testicles.
- The development of cardiovascular failure. With this condition, the tendency to the formation of various edemas increases. Usually they are localized on the legs and in the pelvic organs. Swelling of the scrotum may even occur in a child with congenital heart disease. Typically, this combination indicates a strong distress in the children's body.
- Congenital defects of development. Often found in babies born before the prescribed period. Adverse symptoms parents celebrate in the first year of a child's life. In full-term babies, the duct connecting the peritoneum and scrotum grows.
Premature babies often face problems resulting from overgrowth disturbances.
- Consequences of viral infections. Children's andrologists note the development of acquired forms of the disease after suffering the flu. Viruses have a strong negative effect on many internal organs, including the intimate area. Pathology, occurring in a rather severe form and hydrocephalus, can cause the child to have severe edema in the scrotum.
- The consequences of injury. Damage to the external genital organs can cause the development of inflammation and swelling of the membranes of the testes. This condition is more often recorded in boys aged 12-14 years. Damage contributes to the rapid development of adverse symptoms. In some cases, surgical treatment is required.
- Diseases of the urinary tract. The organs of the genitourinary system are quite close to each other. This contributes to the rapid spread of infection. Often chronic pyelonephritis or cystitis leads to the development of inflammation in the intimate area of boys. In babies of the first year of life, this condition is recorded more often.
Edema of the testicles is very dangerous. You can not neglect and ignore the first signs of this disease! This condition requires the appointment of mandatory treatment. If therapy for the disease was delayed for some reason, this may lead to serious complications in the boy in the future.
The most common effects include:
- Necrosis (death) of the scrotum and testicles. Prolonged squeezing leads to disruption of the blood supply and innervation of the intimate organs. Ultimately, this contributes to the development of persistent hypoxia (oxygen starvation). The chronic process is accompanied by the development of severe damage and cell death of the genital organs.
- Reproductive dysfunction. When the process is chronized, there is a violation of the formation of sperm. According to statistics, in 20% of men, with poorly treated edema of the testicles in childhood, infertility occurs. Treatment of this condition at an older age is quite problematic. In some cases, the male reproductive function is reduced almost completely.
- Compression of organs nearby. Most often in this condition, the intestine is damaged. This leads to various digestive problems. The most frequent manifestation is a violation of the chair. Babies with dropsy of the testicles also suffer from constipation or have an increased tendency towards them.
- The development of combined urogenital diseases. Severe swelling in the scrotum also leads to compression and disruption of other genital organs.
A prolonged condition contributes to the appearance of lymphocele in a baby. With this pathology, the outflow of lymph from the region of intimate organs is significantly disturbed.
Kinds
There are several options for dropsy testicles in boys. The impact of a variety of causal factors leads to their development. This classification has been used in pediatric andrology for many years. It is based on the anatomical defects that occur with different variants of the disease.
This pathology may be:
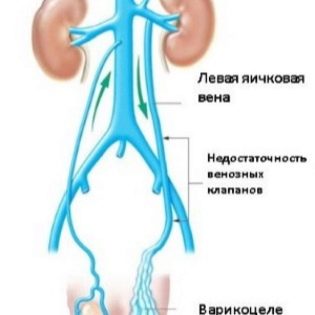
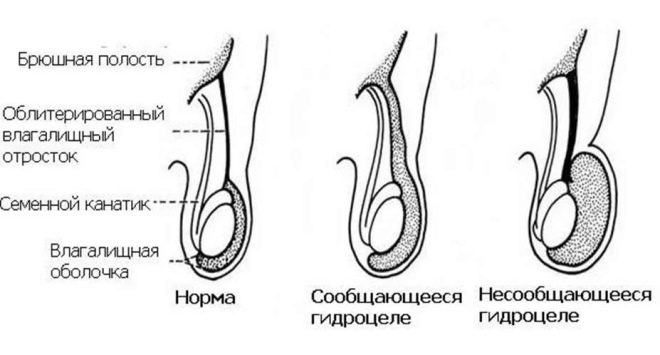
- Reported This form of the disease is congenital. The condition is characterized by the presence of a duct between the scrotum and the peritoneum. As a result, the free fluid can easily reach the intimate area. Its accumulation leads to the development of dropsy of the testes.
- Isolated In this case, the pathological fluid is formed in the scrotum itself, or between the sheets of the membranes of the testes, and not in the abdominal cavity. Most often, this condition contributes to the development of a one-way process.Adverse symptoms occur only on one side.
When establishing and formulating a diagnosis, it is very important to indicate when this pathology originated.
When anatomical defects appear immediately after birth, they speak of a congenital variant. If the scrotum edema is the result of various injuries and injuries, as well as a consequence of various infectious diseases, then they are talking about the acquired variant.
Signs of
The severity of the clinical manifestations of this condition may be different. It depends on many different aggravating causes. These include: the child's age, the presence of concomitant diseases, the level of immunity, and even social living conditions. Mild disease is difficult to diagnose at home. Often parents “miss” the first signs of illness in a baby.
The most characteristic symptoms include:
- Change in skin color in the scrotum. She becomes red. The skin to the touch - hot. Usually this symptom is well manifested in babies of the first years of life. With traumatic injuries on the scrotum, you can see various bruises or hematomas that have a dark blue color.
- Scrotal enlargement. She becomes tense. With a bilateral process, the scrotum is increased several times relative to the norm. If only one testicle is damaged, asymmetry is visible.
- Soreness or sensitivity to palpation. Inflammation leads to the fact that any contact with the scrotum causes an increase in pain. Usually, this manifestation is discovered by parents during hygiene procedures with a baby.
- Sensitivity during urination. In some cases, the combination of dropsy with diseases of the urinary system in a child also has various urinary disorders. The baby often asks to the toilet. Some urges are accompanied by increased pain.
- Symptoms of intoxication. Some variants of the disease are accompanied by an increase in body temperature up to 37-38 degrees. At the height of hyperthermia, fever may occur or chills appear. Chronic inflammatory process in the field of intimate organs leads to the appearance of signs of a persistent temperature increase in the baby.
- Behavior change. Kids become more capricious, they can whimper. With severe pain syndrome - even cry. Children of the first years of life often ask for their hands. A child's sleep is often disturbed. Difficulties with falling asleep or repeated waking up during the night are usually noted.
- Delayed urine excretion. This symptom develops with a rather severe and neglected course of the disease. This disrupts the excretion of urine from the bladder. Portions are small in size. In this case, the parameters of the general analysis of urine, as a rule, do not change.
- The increase in pain in the scrotum. The first stages of the disease are usually not accompanied by the appearance of adverse symptoms. Subsequently, if treatment fails, the pain syndrome becomes more noticeable. The baby may complain of discomfort or even pain. Most often it appears after a hot bath, a quick walk or a trip to the toilet.
Diagnostics
Suspected disease can be in the early stages. To do this, it is very important to monitor the state of the intimate organs in a child. It is best to do this during daily hygiene procedures. Parents should pay attention to any abnormalities arising in the external genital area of the baby. If there is a change in the color of the skin of the scrotum or its increase - you should always consult with your doctor.
For additional diagnostics, it is better to contact a pediatric andrologist or urologist.These doctors have sufficient knowledge in the treatment of diseases of the intimate organs in boys.
You can contact a medical professional from the very first days of birth. Such consultations will help identify the disease in its early stages and help prevent the development of long-term adverse effects.
Usually, to establish the diagnosis, doctors conduct several additional studies. To pre-establish the disease is enough even a simple clinical examination. During this, the doctor examines the external genitals of the baby and carries out all the palpation tests that allow to establish the correct diagnosis. In complex clinical cases, additional tests are required.
According to the purpose of the pediatric urologist for the diagnosis of dropsy of the testicles are used:
- Ultrasound examination of the scrotum and testicles. This method is absolutely safe and painless. During the procedure, the baby does not feel any pain at all. For the diagnosis is enough just 15-20 minutes. The method is fairly accurate and highly informative.
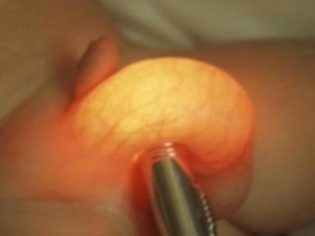
- Diaphanoscopy. This method isthat intimate organs are translucent with the help of light. The study reveals the presence of free fluid between the membranes of the testes. The method is widely used in pediatric urological practice throughout the world.
Laboratory tests, including a complete blood count and urine test, are auxiliary. Usually they are appointed only to establish the cause of the disease, as well as to establish the degree of functional impairment. For example, a complete blood count can accurately determine the presence of a viral or bacterial infection in a child’s body, which often causes the disease. Increased leukocyte levels indicate the severity of the process. Changes in the parameters of the general analysis of urine are found only in cases of neglected cases of the disease and are practically absent in the initial period of the disease.
Treatment
Therapy for edema of the testicles should be carried out as quickly as possible. Early treatment helps to cope with adverse symptoms and reduce the likelihood of delayed effects of the disease.
Disease therapy involves the sequential administration of several groups of drugs.
For the treatment of this condition are used:
- Symptomatic painkillers. They allow you to eliminate the pain syndrome that occurs in the scrotum with a strong squeezing fluid testicles. As anesthetics can be used: Ketorol, Ibuprofen, Analgin, Nimesulide other. Drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets or injections. Appointed strictly by a doctor.
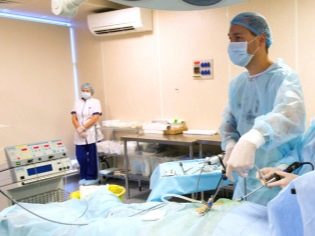
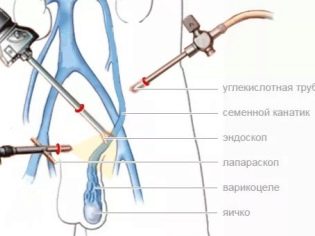
- Surgery. Indications for them are individual. The decision of the surgical removal of fluid from the scrotum is made by the treating pediatric urologist. Usually they are appointed in cases where there are anatomical defects. Ross's surgery is a fairly common method of eliminating the adverse effects of the disease.
- Reduction of adverse symptoms of the disease using the tools from the home kit. Some moms offer to cure dropsy of the testicles with sea salt. This method of treatment has very controversial reviews. Usually, such self-medication only reduces the adverse symptoms, however, the disease does not completely cure.
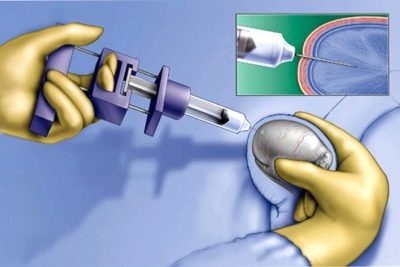
- Puncture of the affected testicle. The puncture in this case allows you to eliminate all excess fluid from the scrotum. The method is traumatic and has a number of contraindications. It is held under strict indications. The decision on the need for puncture is made by the attending pediatric urologist.
- Performing sclerotherapy. Also refers to the surgical treatment of dropsy of the testicles.During the procedure, the doctor using a special tool pumps out the liquid from the scrotum and injects a drug into it, which helps reduce the formation of secretions in the future. At present, this method is not used in children's practice. It can cause serious reproductive problems in the child and in the future and even lead to the development of infertility.
- Winkelman surgical method. The doctor conducts layer-by-layer disclosure of testicular membranes. Usually the size of the surgical field is 4-6 cm. All the fluid from the cavity of the scrotum is pumped out. After that, the doctor unwraps all the shells and holds them stitched on the back surface, which allows you to continue to form an excessive amount of fluid inside the cavity of the scrotum.
After surgery, the postoperative period usually ranges from two weeks to a couple of months. This time is required to restore all structures of the intimate area.
For good and fast healing of tissues, it is necessary to limit strong physical exertion, as well as good nutrition, enriched with protein products.
Doctors also recommend that babies do not wear too narrow and tight underwear, as this leads to squeezing of the external genital organs. During the postoperative period, the urologist is required to regularly examine the baby. Six months after the operation, it is enough to visit the doctor only once a year.
Forecast
The course of the disease usually takes place in mild or moderate form. With timely diagnosis, the prognosis of the disease is usually favorable.
Almost 75% of babies who have had dropsy of the testicle in childhood recover completely. In the future, they do not have any long-term adverse effects.
When the disease progresses, there can be various dangerous consequences. Such conditions most often develop if parents do not treat their child with due attention. A late visit to a doctor only aggravates the development of the disease. Treatment of the disease should not be done at home, but under the supervision of a specialist. This will reduce the likelihood of the development of dangerous consequences of the disease that occur in more adulthood.
Prevention
In order to prevent various clinical forms of the disease, one should:
- Regular hygiene procedures. With the appearance of redness of the scrotum and external genital organs, you can use a variety of medicinal herbs with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. These include: chamomile, calendula, string and other herbs. You can use herbal teas in the form of lotions or add to the baths.
- Monitor the state of the intimate organs in the baby. Having seen reddening or increase in a scrotum, it is necessary to show the child to the doctor. Disturbance or increased urination may also be one of the adverse symptoms of hydrocele. Frequent urging, especially at night, should alert parents and motivate them to contact a specialist.
- Avoid marked physical exertion. Proper selection of the optimal training regime will contribute to the normal functioning of the reproductive system of the boy. During sports activities, whenever possible, any damage to the external genital area should be prevented.
- Planning a healthy pregnancy. Any infections that have arisen in this special period for each future mom contribute to the development of various anatomical defects and abnormalities in the baby.
Monitoring the course of pregnancy helps to prevent the appearance of many pathologies in the baby.
- Timely diagnosis and treatment of associated diseases. All chronic pathologies of the urinary tract must be treated without fail.Children suffering from these pathologies should regularly visit the pediatric urologist. Such dispensary observation will help prevent the progression of the disease in the future.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle. A full-fledged diet, enriched with vitamins and containing a sufficient amount of protein foods, helps to maintain the optimum body weight of the baby. Obesity in most cases contributes to the development of various pathologies in boys. in the area of the external genitalia. Proper nutrition ensures optimal functioning of all organs in the children's body.
- Matched lingerie. Wearing overly tight or tight pants in boys often contributes to the development of diseases of the intimate organs. Underwear for babies should be made only from natural materials. When wearing it, the child should not have any uncomfortable symptoms.
See the next video on what is edema of the testicle and how to treat it.