Anti-inflammatory drugs for children
Inflammatory processes often accompany many childhood diseases. The fact that there is inflammation in the baby’s body can be indicated by various signs. This is the appearance of edema, and an increase in lymph nodes, and an increase in body temperature, and redness of the mucous membranes and skin, and much more. To relieve pain and relieve inflammation of the baby, doctors recommend including anti-inflammatory drugs in the list of drugs for treating a baby.. We will talk about them in this article.
Classification
There are several large groups of drugs that suppress inflammatory processes:
Nonsteroidal (non-hormonal) anti-inflammatory drugs. The largest and most popular group of drugs. In addition to resisting inflammation, these drugs effectively anesthetize and reduce fever. This group includes "Analgin"," Ibuprofen "," Indomethacin ","Diclofenac"," Meloxicam "," Mesulide "and others. Non-steroidal drugs are divided into selective and non-selective. The first act selectively on a certain inflamed area, the second - systemically.
Steroid (hormonal) anti-inflammatory drugs. These are drugs based on synthesized hydrocortisone and cortisone, once isolated from the adrenal glands, as well as their derivatives. This group includes "Prednisolone"," Dexamethasone "and others.
Means of "slow" action. They are also called the means of "basic" therapy. These are drugs that act systemically and slowly. For example, "Hingamin", "Kuprenil" and others.
How to act?
All anti-inflammatory drugs act at the cellular level. Inflammation is a process in which the blood circulation increases at the local level (in the zone of concentration of inflammation). The body begins to produce specific substances that are designed to fight the pathogen.
These substances, which are also called mediators, are also localized mainly in one focus. Prostaglandins begin to enter the bloodstream. This is where inflammation occurs.
Anti-inflammatory drugs somewhat inhibit the incredible activity of mediators, prostaglandins, relieve puffiness, relieve pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can cope with virtually any type of inflammation, relieve swelling and do not cause the patient to develop drug dependence.
The inhibition of the action of prostaglandins explains both the anesthetic and antipyretic effects of all other types of anti-inflammatory drugs. Only they act selectively. "Basic" - are prescribed for long-term treatment, for patients with joints, for example. Steroids are used with great care as emergency medications when a very fast and very strong effect is required. At home, the use of hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs is prohibited.
By the time of the action of anti-inflammation, too, are different. There are drugs of a short period of action, such as "Ibuprofen", a little longer are "Sulindak" and the like. Record for the duration of action - "Phenylbutazone" and all the means of the group oxycam.
For children
Not all anti-inflammatory drugs that exist in medicine today are suitable for children. Many medicines of this destination can cause severe reactions in the children's body: gastric bleeding, impaired hearing and vision, allergies, including its edematous form, difficulty breathing. The most "harmless" side effects from taking anti-inflammatory drugs are digestive problems, constipation, nausea, and dizziness.
In this cycle, Dr. Komarovsky will tell us about antiviral drugs for pneumonia.
Anti-inflammatory drugs for children should be as soft, non-toxic. Non-steroid drugs and corticosteroids most often correspond to such requirements. For colds, viral infections, muscle pain and injuries, analgesics such as Paracetamol and preparations containing it are also prescribed.
The dosage of the drug for the child should be determined only by a doctor. It will take into account many factors, such as the age of the young patient, the degree of the inflammatory process and its distribution, the state of immunity of the baby, associated diseases and injuries, possible risks and side effects. After that, selects the drug that best meets all the safety requirements for a particular baby.
And this issue of Komarovsky is devoted to such an inflammatory disease as otitis.
Who and when to give?
Anti-inflammatory drugs can only be prescribed after a detailed diagnosis. Otherwise, they will only “disguise” the manifestations of the disease that caused the inflammation, and it will be very difficult even to install it for experienced doctors.
Most often, children need to take anti-inflammatory drugs for:
- Inflammation of the upper and lower respiratory tract (with tonsillitis, with bronchitis);
- Inflammation of the organs of hearing and vision (with otitis, conjunctivitis, blepharitis);
- Inflammation of the urogenital organs and kidneys (with pyelonephritis, with cystitis);
- Inflammation of the lungs (with pneumonia of various etiologies);
- With local inflammatory processes, as well as with inflammation of the joints.
Forms of release
Anti-inflammatory drugs for children are available in various dosage forms. The most common and easy to use are syrups. Moreover, the drug for inflammation can be added to any means, for example, introduced into the composition of cough syrup.
Often, syrups and suspensions are prescribed for acute respiratory viral infections, which, in addition to antiviral agents, contain anti-inflammatory agents that have antipyretic and analgesic effects. Anti-inflammation created eye drops, drops in the ears, nose, rectal suppositories, ointments and gels. Very often, anti-inflammatory drugs are available in tablets and capsules.
Depending on the age of the child, the doctor may prescribe the most appropriate form. Syrup can be applied from the first years of life, the same can be said about rectal suppositories. Tablets are recommended for children after 5-6 years, and capsules are recommended for children after 12 years.
List of "children's" drugs against inflammation
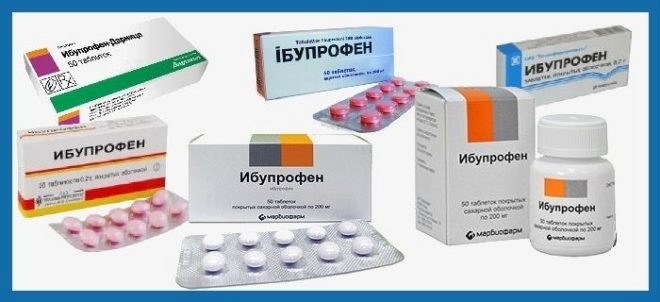
Ibuprofen
Anti-inflammatory agent, which is most often prescribed in pediatrics. Its effect has been carefully studied in the laboratory, the drug was tested. In pharmacies, it can be purchased in the form of tablets, both conventional and for resorption. And also in the form of capsules, suspensions, and ointments and gel for topical use.
Ibuprofen can be recommended for children with influenza and acute respiratory viral infections, fever, injuries, hematomas, and neuralgia. As an additional tool is used for pneumonia, toothache, with bronchitis, sinusitis, etc.
Children from the year prescribed the drug in the form of a suspension. For children of any age, except for newborns, "Ibuprofen" can be used topically in the form of ointments and gel. Tablets for resorption are recommended for ENT diseases, and the doctor expects the dosage for children under the age of twelve.Instructions for use prescribes with great care to use tablets for children from 1 year to 12 years.
Nise
Like most anti-inflammatory drugs, manufacturers recommend using this drug for children over 12 years old. However, in Pediatrics, the practice of “Nise” is practiced even at an earlier age, at the discretion of the physician. The medicine is produced in the form of tablets, suspensions and gel for external use.
Children whose weight is more than 40 kilograms are recommended two doses of the drug per day with a single dose of not more than 100 mg. For children who weigh less, the dose is calculated individually - 3-5 mg. for every kilogram of weight. The resulting amount of the drug is divided into three doses. Babies from 2 years to 12 years take the tool preferably in the form of a suspension.
Aspirin
Very effective anti-inflammatory drug with excellent antipyretic effect. However, children up to 14-15 years old cannot be given it, it can cause the occurrence of Ray syndrome, accompanied by encephalopathy and liver failure. Children after 14-15 years old are given Aspirin with great care, only after consulting a doctor.
Paracetamol
This well-known medication, as well as all syrups and suspensions, which it contains, does not have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, but well relieves pain and reduces the intense fever during fever. Candidas, panadol syrup, suspension are suitable for children from year to year (for children who are 2 years old). The dosage of drugs on the basis of paracetamol is made from the calculation of the amount of active ingredient per kilogram of patient weight.
Flurbiprofen
Nonsteroid drug, which is prescribed safely for children after 12 years. Previously - at the discretion of the doctor and only for children from 3 years. Teenagers are available forms of capsules and tablets. For younger children - in the form of rectal suppositories. Self-treatment with this drug is not allowed!
Sulindak
This anti-inflammatory drug can be taken in children when treating rheumatoid arthritis. Age limit - from 2 years. Other diagnoses to treat this rather strong drug is not recommended. In acute form of arthritis, babies are prescribed no more than 4.5 mg of the drug in two doses per day.
Meloxicam Amelotex, like Indomethacin, is not recommended for children under 15 years of age.
General recommendations
- Anti-inflammatory medications are not recommended to be combined with each other while taking. If a baby does not fit one name, the doctor will cancel it and prescribe another. They are interchangeable, but do not benefit from a duet, rather, they can cause an overdose.
- Tablets and capsules of anti-inflammation should be washed down with plenty of water.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs should not be given to children with diseases of the stomach and duodenum. For some diseases of the kidneys and liver, the intake of such medicines is possible, but with great care and in strict individual doses recommended by the doctor.
- Many anti-inflammatory drugs are sold in pharmacies by prescription, including eye and ear drops, as well as medicines based on medicinal herbs.