Otto for children: instructions for use
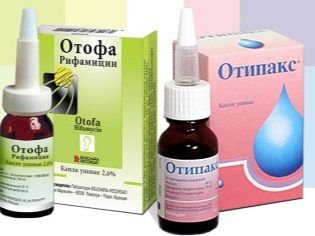
In the treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the ears often use topical agents. One of them is a French medicine called Otofa.
When is it prescribed and how does it affect the human body and the bacteria? Is it allowed to drip this medicine into the ears of children, in what dosage and how to properly bury the solution? Is it not better to replace Otofu with popular drops Otipaks or some other medicine?
Release form
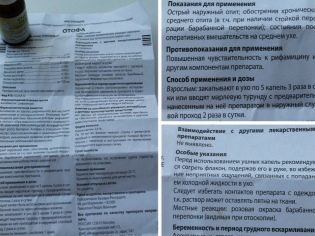
Otof is represented by only one dosage form - ear drops. The drug is available in glass vials, closed with cork and foil, to which is attached a separately packaged polymer dosing pipette.
One bottle contains 10 milliliters of a clear solution, which has a red-orange or red-yellow color.
Composition
Rifamycin in the form of rifamycin sodium acts as an active substance in drops of Otof. Its concentration in the solution is 2.6%, so the amount of this compound in 100 ml of the drug is 2.6 grams (in them the antibiotic is represented by the dosage of 2,000,000 IU).
In addition, the solution contains potassium disulfite, edetate disodium, and macrogol 400. Otopha contains ascorbic acid, purified water, and lithium hydroxide.
Operating principle
The active component of the droplet is an antibiotic of the rifamycin group. It is active against various harmful microorganisms that provoke infection of the ear (streptococci, Escherichia coli, Brucella, Pneumococci, Legionella, Proteus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Enterococci, Chlamydia, Pasteurella, Staphylococcus, etc.).
As a result of the effect of this antibacterial substance on the bacterial RNA polymerases, their growth stops and the pathogen is destroyed.
In this case, the drops act only locally, without penetrating into the bloodstream and not exerting any systemic effects.
In addition, the drug can destroy microbes that have developed resistance to the most common antibacterial agents (for example, penicillins).
Indications
Otofa is used in the treatment of:
- Otitis externa.
- Acute otitis media (including a disease that is complicated by perforation of the eardrum).
- Chronic otitis media.
The drug is also prescribed after various operations in the middle ear and manipulations in the ear canal, for example, after puncture of the eardrum. Some ENT doctors prescribe medication and infectious rhinitis (drip into the nose).
From what age is assigned to children?
The manufacturer does not mention any age restrictions in using otofa in children, however, such medication should be dropped into the ears of the children only after the specialist has examined the child.
The use of any ear drops without the advice of a doctor in childhood is not recommended.
Contraindications
The drug should not be dripped in case of hypersensitivity to rifamycin or another ingredient of the solution. There are no other contraindications for using otofa.
Side effects
In rare cases, when Otofoy is treating a child, an allergic skin reaction may occur. Getting on the eardrum, the medicine gives it a pink color, which can be clearly seen during otoscopy.
Instructions for use for children
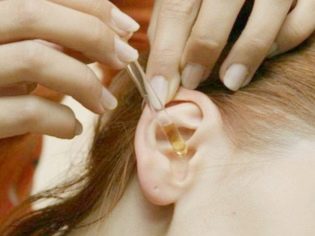
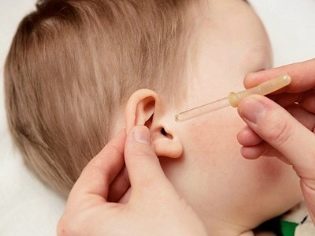
- To open the bottle, pull the tongue of the foil and remove the packaging, as well as the cork, then put a pipette free from the blister on the bottle.
- If the medication is stored in the refrigerator, then it should be slightly warmed in the hands before use so that the cold liquid does not fall into the ear (this causes severe discomfort).
- On average, the drug is prescribed for a course of 3-7 days. A single dose for children is often 3 drops, and the product is dripped three times a day.
- You can also fill Otofu in the ear in large quantities and leave for a few minutes. Such use is prescribed 2 times a day.
- Drip medication should be carefully, because the solution may leave stains on clothes.
- During the procedure, the child must lie with his head turned on his side, and immediately after dropping into the ear canal, he cannot turn his head. You need to wait about 5 minutes and only then get up or roll over on your back.
- If by the end of the course of treatment prescribed by the doctor, the child has otitis signs, a re-examination and another therapy is required. To show a small patient ENT should be and in the absence of improvement after 2-3 days of application of the medicine.
Overdose
Since the ingredients of the drops are practically not absorbed, cases of overdose have not previously been recorded, and the manufacturer calls them unlikely.
Drug interaction
There is no information about Otof’s incompatibility with any other drugs, including local remedies, but ENT doctors do not recommend dropping any other medicine at the same time as Otof.
When prescribing other drugs between their use usually take a break for at least 30 minutes.
Terms of sale
In pharmacies, Otofa is sold with a prescription, so to buy such drops, you should first go with your child to the doctor. The average price of one bottle is 180-200 rubles.
Storage conditions
You can keep a bottle of droplets at home at room temperature, but many mothers prefer to keep Otof in the fridge, which is also allowed. The shelf life of a sealed medicine is 3 years and does not change in any way for an opened bottle.
Reviews
About treatment of otitis in children with drops of Otof speak mostly positively. Since pathogenic bacteria are very often the cause of ear inflammation, the use of such medication for purulent otitis gives a fairly quick and noticeable effect, improving the child’s condition and, on average, for 4-5 days, completely eliminating the inflammatory process.
According to parents, young patients tolerate drops mostly well. There are no negative effects of antibiotics such as suppression of local immunity and the development of dysbacteriosis. Only rarely does a child react to the use of a medication with an allergic rash, due to which the medication has to be canceled.
In most children, the use of such drops does not provoke any side effects.
The main disadvantage of Otofa is the bright color of the solution, because of which its use changes the color of ear tissues and can stain clothes.
The cost of medication most mothers consider available, so other complaints about the drug are very rare.
Analogs
The most frequent replacement drops Otto choose Otipaks, but these ear drops have both advantages and some disadvantages:
- Otipaks has a more pronounced anesthetic effect, because its composition includes two components with an anesthetic effect.
- Otipaks, like Otofu, can be dripped at any age, even babies, because both drugs act only locally.
- Unlike Otofa, Otipaks does not include any antibacterial components, therefore it acts only as a symptomatic treatment, but does not affect the infectious agents in any way.
- Since lidocaine is present in Otipax, the risk of an allergic reaction to such drops is higher than when using Otofa.
- Otipaks can not drip with a damaged eardrum.In addition, such a drug is not prescribed for chronic otitis media.
Other ear drops can replace Otofu, for example:
- Anauran. Such drops include lidocaine and two antibiotics, so they are in demand for otitis with severe pain. The drug is prescribed to patients older than a year.
- Polydex. This medicine also contains 2 antibacterial substances, but they are supplemented with a glucocorticoid. It is used in children from birth.
- Candiotics. Such a multicomponent agent contains an anesthetic, an antibacterial substance, a glucocorticoid hormone and an antifungal component, therefore it has a very wide range of effects in otitis. In the treatment of children, these drops are allowed from 6 years.
- Sofradex. The composition of this medication includes a hormonal component and compounds with antibacterial action. Children are prescribed for him at the age of 1 month and older.
- Otyrelax. This medicine is an analogue of Otipaksa and is used for earaches. He is prescribed to children from birth.
The composition of these and other local agents prescribed by ENT doctors is different, so you should not use any of these drops without consulting a doctor.
All physicians, including the popular pediatrician Komarovsky, emphasize that the use in the treatment of children, even approved at any age of drugs that have only local action, without the prescription of a specialist is unacceptable.
If a child has pains in the ear, a feeling of congestion or other signs of otitis, first of all you need to consult a doctor and get examined, and only then drip the medicine that he is prescribed.
How to treat otitis media in children, see the following video.