Obsessive Movement Syndrome in a Child
The child began to bite his nails, make strange movements with his hands or head, often blinking or squinting for no reason. All these symptoms may be manifestations of obsessive movements syndrome. About what it is and what to do with it, we will tell in this material.
What it is
Neurosis of obsessive movements is quite common in children. Most often monotonous repetitive movements or series of such movements appear in children of preschool or primary school age. This is not a separate disease, but a whole complex of disorders both at the mental and emotional levels. The movements that a child makes are unmotivated, they are very difficult to control.
Medicine refers to the manifestations of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuroses of obsessive states are included in the classification of diseases. Despite this, the childhood syndrome is rather poorly studied, and one can only guess about its true causes and mechanisms.
In order not to frighten parents, it should immediately be noted that a mentally ill child with intrusive movements is not considered. He is not disabled, does not need isolation and does not pose any danger to others. The only person he can do harm to is himself. And even then, only in cases where intrusive movements are traumatic.
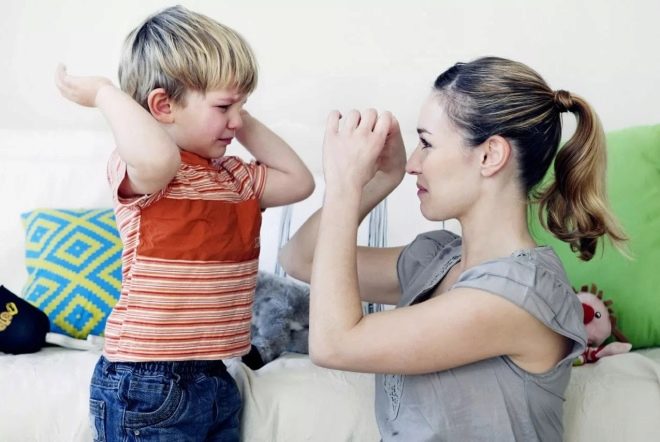
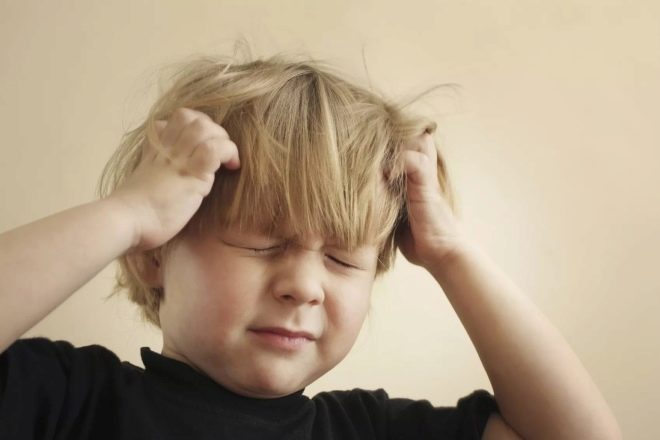
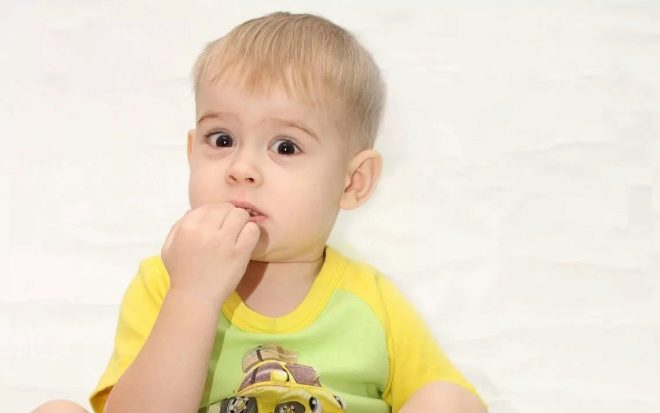
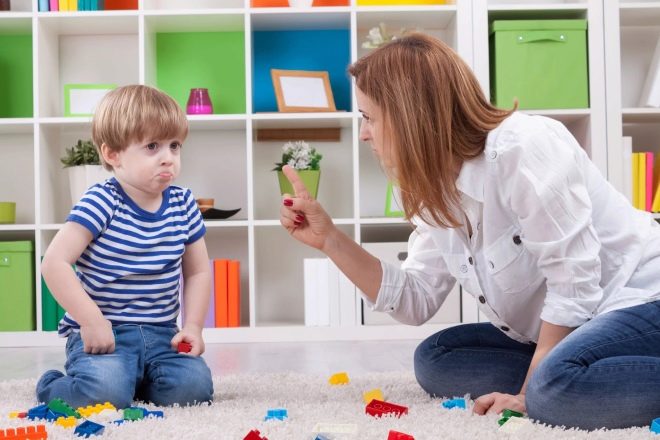
Most often, according to the pediatric practice available today, parents go to the doctor with complaints that the child began to bite his lips, bite his legs and skin on his hands, bite himself by the hands, pull out his hair or almost constantly twirl them on finger, swing your arms and shake your hands, swing your body from side to side. It is noteworthy that the baby begins to repeat such movements precisely when it finds itself in an uncomfortable or uncomfortable, from a psychological point of view, situation. If he is afraid, if he is confused, distressed, annoyed, offended, he begins to compensate for the discomfort with his usual and calming movement or a whole series of such.
Not always manifestations of the syndrome have pathological neurological or psychiatric causes. Due to the lack of knowledge, it is sometimes very difficult to establish what has become a “trigger”. But this diagnosis, if it was given to a child, is not a sentence and in most cases does not even require classical treatment.
Causes
It is believed that the main reason for the occurrence of bad habits to make obsessive movements, is a strong stress, a deep emotional shock that the child has experienced. Due to the fact that the baby cannot express in words the feelings that beset him, emotions find a way out on a physical level. Such a disorder is usually temporary, and as soon as the baby recovers from the experience, he will be able to get rid of unnecessary movements and actions.
Psychological reasons also include:
- mistakes in bringing up the baby (severity, physical punishment, connivance and permissiveness)
- severe psychological climate in the family (divorce of parents, scandals and quarrels of adults with a child, physical abuse);
- abrupt change of habitual habitat (sudden relocation, transfer to another school, another kindergarten, the transfer to the education of my grandmother, etc.);
- child conflicts with peers.
Physical reasons that can lead to or contribute to the development of the disorder under adverse environmental conditions include:
- traumatic brain injury in history;
- unfavorable heredity (there are close relatives with mental disorders, diseases of the central nervous system, as well as abusing alcohol or drugs);
- concomitant neurological diagnoses (hyperactivity syndrome);
- congenital mental illness (autism, schizophrenia);
- congenital pathologies of the brain and central nervous system.
Sometimes children have a whole complex of causes that unites both physical and psychological factors contributing to the development of obsessive movements. Establishing the true cause is an incredibly difficult task, even for an experienced doctor, but it is necessary to do this in order to know what kind of help a child needs. Some of the reasons are easily solved by a confidential conversation with a baby or visiting the office of a child psychologist, and some will have to be treated with medication.
Symptoms
The syndrome of obsessive movements has a great many manifestations. It all depends on the child’s personality, character, temperament, physical development, age. Most often in children up to six years, there are tics. They are always of a physiological nature, are involuntary and often pass as suddenly as they appeared.
Obsessive movements of a more complex level are better amenable to volitional effort. Theoretically, a person may forbid himself to bite his nails, but the child is not very well with will and motivation, and therefore he simply cannot cope with such movements. Most often the syndrome of obsessive movements is manifested by the fact that the child bites his nails, the skin around them, with an enviable regularity smacking or pulling his lip, biting his lips, often blinking deliberately, constantly coughing or sniffing. Sometimes the syndrome manifests itself more pronounced - by rocking the body back and forth or side to side, shaking the head, unjustified waving of the hands.
All such movements do not represent any danger if they are single or rare.
Syndrome of obsessive states is characterized by cyclicality, regularity, monotony and constancy of repetitions of well-defined movements.
Often parents try to just stop such manifestations. In case of their pathological origin, the child does not perceive criticism and demands to stop adequately, the movements are intensified, and with the persistence of adults, the baby may become hysterical.
Diagnostics
No doctor in the world, when parents turn to him with complaints about obsessive movements of a child, will not be able to say exactly what this baby’s behavior is about. Because mom and dad need to carefully look at the child, analyze the events of the last time and only after that go to the doctor.
It is better to start the diagnosis with a visit to a neurologist. Parents will have to tell this specialist in detail, in what situations and how often a series of movements are repeated, what character they are, and also - whether the child has recently had stress or upheavals.
In addition, you should write down on paper and bring the doctor a list of all the drugs that the child consumed over the past couple of months. Some medications can have this effect on the nervous system.
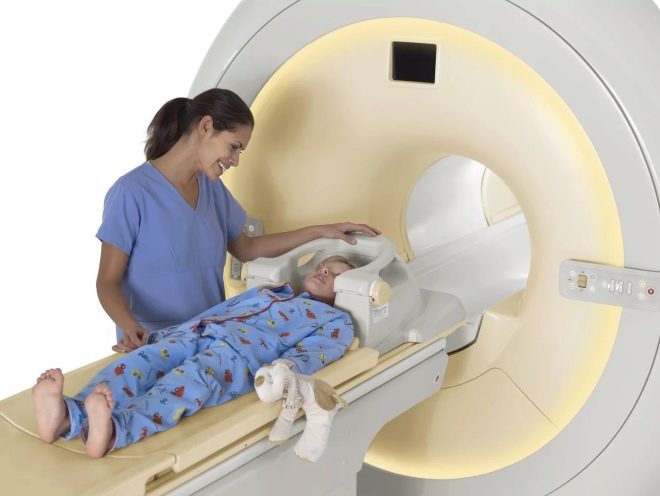
If there is no clear reason after this, the doctor will advise you to get an MRI scan of the brain. (to exclude brain pathologies), and also make a visit to a child psychiatrist, who will examine the child for mental disorders. It will be useful to pass blood and urine tests, which will help determine whether there are any inflammatory processes in the body of the body, and also whether it has a deficiency of vitamins and some minerals (in particular, calcium).Their lack can also lead to disorders of the nervous system.
On this available list of diagnostic measures ends. In medicine today there is no single standard for assessing such a state as obsessive neurosis, and therefore doctors will make a diagnosis relying mainly on the stories of the parents.
Treatment
If a psychiatrist and a neurologist thought that the child is healthy, and the tests did not show any significant deviations from the norm, then the parents may not be worried and not be in a hurry to stuff the child with pills and injections. It requires a different approach. Therapy will be to eliminate all phenomena and events that are traumatic for the child’s psyche.
You need to communicate with the child, talk, walk, engage in drawing, watching movies, reading. And be sure to discuss everything.
Sooner or later, the crumb will surely report that he was so excited, and the parents will be able to understand what caused the obsessive movements.
In no case can not strongly stop the attempts of the child to make movements, you should not once again focus on them and pay attention to the child. If the child’s movements are dangerous for him (he bites himself, scratches his face), it is necessary to attend classes with a child psychologist with him, and if necessary, with a psychotherapist. For the baby you need to more closely monitor.
Drug and concomitant treatment for obsessive neurosis is prescribed mainly when medical specialists find sound medical reasons for the onset of the disorder.
In particularly difficult cases, antidepressants are prescribed. In all others, trying to do with softer treatment options.
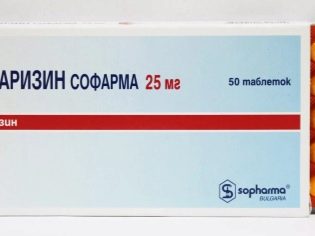
Assign mild sedatives, preferably of natural or vegetable origin, which include «Glycine» and «Persen», to improve cerebral blood supply is prescribed «Cinnarizine» together with the magnesium drug Asparkam. To strengthen the nervous system prescribed B vitamins, in particular, the drug «Milgamma». As a sedative, sedative-style herbal teas can be recommended - based on mint, valerian, oreganomotherwort. At home, it will be possible to make a child soothing therapeutic baths with medicinal herbs, however, provided that the doctor approves it, because such procedures often cause an inadequate reaction in children with a predisposition to allergies.
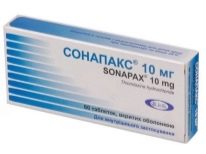
Truly "heavy artillery" - drugs of psychotropic action in obsessive-compulsive disorder are prescribed only in short courses, and only if the psychiatrist is able to formulate an accurate psychiatric diagnosis. Children with these goals are usually prescribed "Phenibut», «Sonapaks», "Tazepam". Simultaneously with taking the medicine, the child is given massage, psychotherapy, and psychologist classes. In some cases, hypnotherapy is indicated, but it is not performed for very young children. Electrosleep and electrostimulation of the brain are good physical procedures, but one should not count on a lasting therapeutic effect from them with such a neurosis.
By themselves, medications are not able to cure neurosis. They only temporarily relieve the condition, remove some of the symptoms. And only a comprehensive treatment, favorable changes in the life of the child will be able to help him get rid of obsessive movements completely.
Children are shown a quiet developmental and educational program, frequent walks in the fresh air. If the age of the offspring allows, he can be given a spin on a spinner that is fashionable and popular among children and adolescents - it fully satisfies the need for simple movements during emotional instability. Actually, for this, this toy was created.
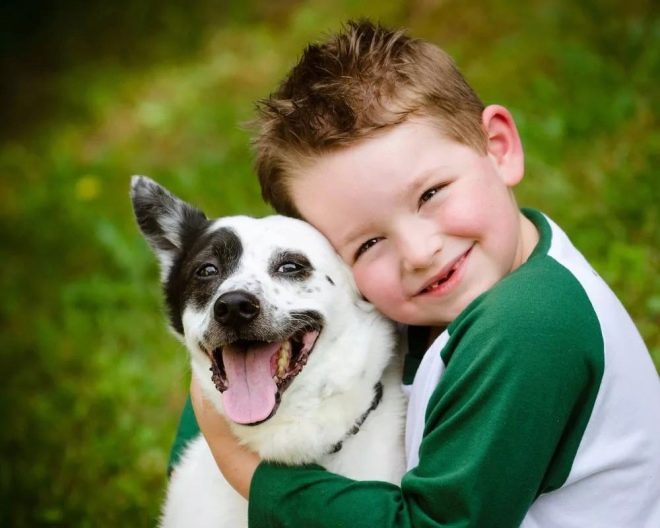
A good result, according to parents who were engaged in the treatment of obsessive-movements syndrome in their children, gives communication with pets.
A puppy or a kitten can be given to a child as an adjunctive therapy, of course, if the baby does not have allergies to wool, and age allows him to consciously communicate and take care of the pet.
About this syndrome rasasyvaet psychologist Elena Belokurova. Watch the interview with him in our next video.