How to check the hearing of a child?
Good hearing is the key to a harmonious speech and psycho-emotional development of the child. But the auditory function of a person is one of the most difficult, and therefore at any age it can be reduced. That is why hearing testing in children is an indispensable part of any physical examination. Check how well the child hears, and you can independently.
When is verification needed?
Medical examinations of the auditory function are carried out from 2-3 days after the birth of the baby and from time to time repeated throughout the person’s life. The child is tested at 3 months, half a year, a year, when applying for kindergarten and school, at school medical examinations and as part of a medical examination, when entering a university or at a military registration and enlistment office.
The fact is that minor hearing loss from birth is very difficult to diagnose at an early age, and a born healthy baby may well lose a good ear after severely suffered from SARS, flu, after an acoustic trauma or a blow to the head. Hearing is more unstable than sight, and it needs to be checked more often.
Parents should think about unscheduled verification in the event that doubts arise that the crumb hears well and perceives the surrounding world by ear.
There are many signs of hearing loss. At each age, they are their own. Check hearing in a medical institution is, if:
- a child aged 1-2 months does not pay attention to loud sudden sounds (the alarm clock rang, the doorbell rang, the door slammed loudly, a heavy object fell). The child does not flinch, does not look for the source of the sound, does not frighten, does not throw up the handles, legs;
- at the age of 3 months and older, the baby does not respond to the voice of the mother, does not recognize him, does not try to look for his mother with his eyes if she speaks away from his bed;
- at 4 months does not respond to the voices of other people, to the sounds of toys;
- up to 6 months there are no signs of walking;
- a year a child only moans, does not utter sounds and syllables;
- in two years there is no minimum vocabulary, the child does not fulfill the requests of an adult;
- if the child communicates little, is not interested in this, often shows aggression;
- the child often asks;
- during dialogue, the child closely watches articulation, lips and facial expression;
- watching a movie or cartoon, trying to make it louder;
- it is difficult to perceive the telephone words, all the time carries the tube from one ear to another.
In addition to the general hearing loss, the symptoms of which we have described, there is loss of perception of certain ranges. So, some children normally perceive conversational speech, but do not perceive the singing of birds in the street, they do not hear the leaves rustling under their feet. And some do not hear tap water dripping, but they can watch TV at normal volume.
The degree and form of hearing loss are different, and they manifest themselves in different ways.
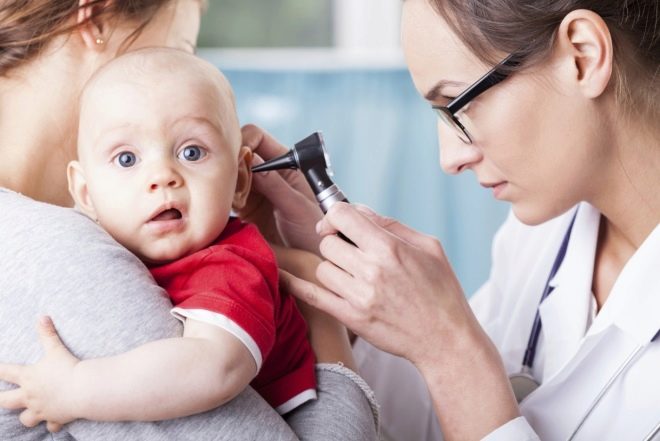
If it seems to you that the baby does not hear or hear something, does not understand, the distinctness of perception of sounds suffers, you should definitely show it to the ENT specialist and pediatric audiologist at the audiology center.
Hardware methods
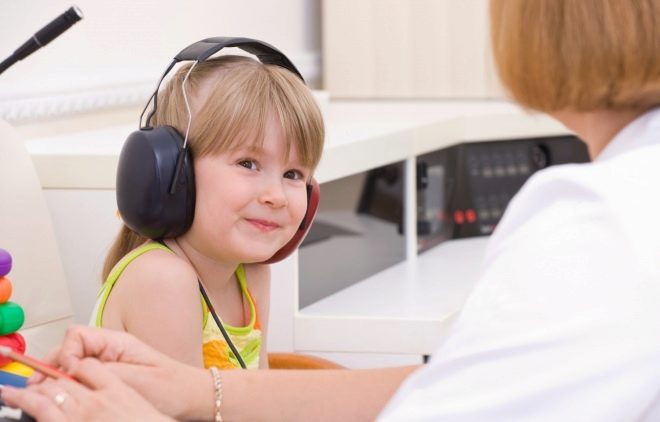
There are many medical ways to check how your child hears. For small ones, it is often used gaming audiometry. This method is optimal for children aged two to four years.The baby is given headphones and announces the rules of the game: you need to throw the ball in a bucket or basket when the beep sounds. Headphones sound different frequencies. According to the reaction of the baby, the audiologist determines which frequencies are available for his perception and which are not.
Another option for gaming audiometric testing is for the child to press a key while sitting in front of a computer monitor. The headphones give the child the sounds of nature, animals, people's speech, his task is to press the button when he hears sounds and can identify them.
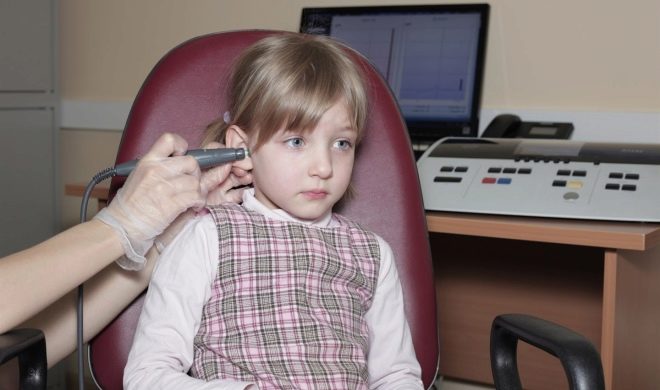
Universal hearing test, widely used at audiology centers, in polyclinics - tonal audiometry method. Testing is carried out in a special soundproof cabinet. The child is offered to wear headphones and reproduce sounds of different bands and frequencies. If he hears a sound, he presses a button or raises his hand, if not, the doctor reproduces the next sound, and so on until the threshold when the child will hear. Thus, the hearing threshold of a particular child in different ranges is determined.
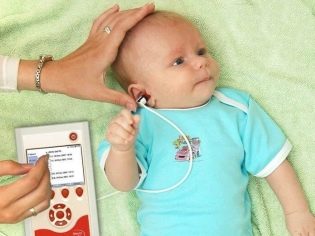
Otoacoustic emission method is used for the smallest - this is the method used for hearing screenings in the maternity hospital for 2-3 days after the birth of the child, in the clinic at the monthly, three-month, six-month age. It is better if the child sleeps at the time of the examination or is at rest, for example, sucks the breast.
A flexible probe connected to the portable device is inserted into the eye of the baby. The device sends sounds of different frequencies into the ear and after some time registers the return response of the vibrations of the hair cells of the inner ear. If there is an answer, the child hears, if there is no answer, there is no sound perception.
Tympanometry is another informative method for assessing auditory function. It is designed to evaluate the work of the middle ear and eardrum. A probe is inserted into the ear, which will record vibrations of the membrane during conduction of sounds.
If these methods reveal abnormalities, they use the method of tuning forks to establish the causes of hearing loss. Evaluation of the perception of high and low sounds makes it possible to judge which department of auditory analyzers has suffered.
Testing by yourself
Testing the hearing acuity at home in terms of accuracy, naturally, cannot be compared with testing on the device, but this is not required of it. A home check is needed by parents in order to confirm their fears and go to the doctor later, or to calm down and stop worrying.
Home independent testing of a child’s hearing depends on his age.
Up to a year
In infancy, you can independently only assess the big picture - is there a hearing or not. Deviations of the auditory function, if the child does not have complete deafness, is rather difficult to assess. Usually, the baby’s behavioral reactions are checked — in response to the sound, from two months the child becomes animated, takes off the knobs, and from three months begins to look for the source of his eyes.
You can apply the so-called cereal test. Three identical jars filled with cereal half: one - semolina, the other - buckwheat, the third - peas.
One adult distracts the child with a toy without sound, and the second shakes a jar two feet from the child’s ear. First apply semolina, then buckwheat, because the peas.
So assess whether the child is able to hear high, medium and low sounds. Between jars you need to pause for a couple of minutes. Ideally, the child will indicate his interest in sound, distracted from the contemplation of the toy, starting to look for the source of the sound.
From 1 to 3 years
At this age, you can actively use toys with a variety of sounds - from quiet rattles to loud pipes and drums. The main thing is to make a sound from the back of the child and evaluate his reaction.. Increases the distance at which the sound is produced. Now it is no longer 0.5-1 meters, but about 2 meters.
Above 3 years old
Older children who already know how to speak are tested for hearing in a whisper and colloquial language. If the child is still not speaking well, it is better to use the methods described above. From the age of 4-5 years, the method of assessing hearing by speech has been applied to everyone.
It is important to understand that a child with a healthy ear perceives colloquial speech from a distance of up to 20 meters and further, and a whisper from 6 meters. Ensure silence in the room, turn off all that distracts (fan, TV).
Ask the child to stand against the wall and move away from him to six meters. Baby turned right side to the parent, the left ear should be closed with a cotton swab. If the child is large, he can close the second ear with his fingers.
Without voice effort, on an exhalation in a whisper, an adult utters numbers from 1 to 100 or a couple of words, which the audiologists and otolaryngologists usually use to assess the auditory function. The task of the child is to repeat the spoken word or number.
If the child does not hear three consecutive words spoken from six meters, you need to approach a meter and repeat them. If again there is no audibility, they are still a meter closer and everything repeats again.
When the child hears and repeats the words, you need to record how far he could do it with his right and left ear. This will help you understand how big the hearing loss is:
- 6 meters or more at each ear - normal hearing;
- 5-2 meters - slight hearing loss;
- 1 meter - the average degree of hearing loss;
- 0.5 meter - does not perceive at all - a strong degree of decrease in auditory function.
For a whisper check, use phonetically balanced words for high and low sounds. Here are a few pairs you can use for your child:
- mother is a boy;
- the house is a lamp;
- table - hour (hours);
- grandfather - boots;
- school desk - a fly;
- doctor - tea.
Do not try to pronounce words the meaning of which the child does not know due to age.
After checking in a whisper, you can check the conversational speech from 20 meters from the back.
Useful programs and applications for self-diagnosis
On the Internet, there are many audio programs and applications for self-testing hearing. But they are not suitable for kids because require individual calibration.
From 8-10 years of age the child may well use them.
It is enough to download and install the application on your device and buy good headphones. There are checks online. They are based on the fact that a person perceives an audible range from 15 to 20 thousand Hz by the ear. The program will play sounds and the person will press the button if he hears them.
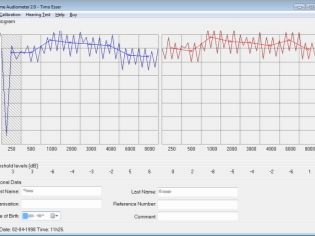
As a result, you get data similar to audiometry data, but, alas, less accurate, although for home checking more accurate than whisper or colloquial speech.
Some of the programs can be found on sites that distribute music content as test setup files for multichannel audio systems. Some are made specifically for home audiometry, for example, Home Audiometer or Mimi hearing test.