Symptoms and treatment of hepatitis in children
Liver damage in a child can develop as a result of various causes. The danger of this condition is that it can lead to the development of numerous complications.
What it is?
The disruption of liver cells or hepatocytes as a result of various provoking factors is called hepatitis. In most cases, various subtypes of viruses lead to the development of this condition in babies. Such forms of the disease are called viral hepatitis. They are found in children's practice most often.
The number of babies who suffer from hepatitis is growing every year. In America, an increase in the incidence of up to 400 000 new cases annually. Among the most frequent options recorded in children in Russia are hepatitis B and A. They are found in the vast majority of cases. Hepatitis C is recorded much less frequently.
Scientists secrete several types of viruses that have a devastating effect on liver cells. They are called with the help of Latin letters - A, B, C, D, E, F, G, SEN, TTV. They differ not only in specific differences in the cellular structure, but also have different properties.
Once in the child's body, hepatitis viruses, along with blood, penetrate the liver cells, where they begin to actively proliferate and exert their destructive and toxic effect.
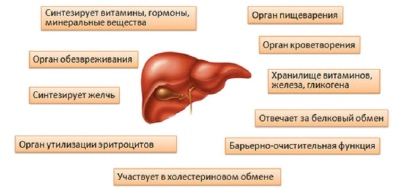
The liver performs over 40 different functions in the body. It is the main body in which detoxification (neutralization) of toxic metabolic products takes place. It also performs a barrier function, ensuring the protection of the internal environment of the body from the entry of foreign microorganisms. In the liver, important hormones and biologically active substances are also synthesized, which are involved in most of the chemical reactions that are very necessary for life.
Getting into the children's body, hepatitis viruses have a damaging effect on liver cells. In case of acute course - the child has very bright clinical symptoms. In the chronic form of the manifestation of the disease may be erased or expressed slightly. In this case, to establish the correct diagnosis requires additional diagnostic methods.
How is it transmitted?
Hepatitis viruses are very well preserved in the external environment. For a long time, they can be in conditions of cold temperatures, and die only with sufficiently long processing, which is carried out when heated above 60 degrees.
It is important to note that most of the subtypes of the hepatitis virus is quite sensitive to ultraviolet radiation.
A child can become infected in various ways:
- Direct contact with body fluids that contain viruses. These include: urine, saliva, blood. Viruses enter the blood through various microdamages. They are small in size and spread well throughout the bloodstream.
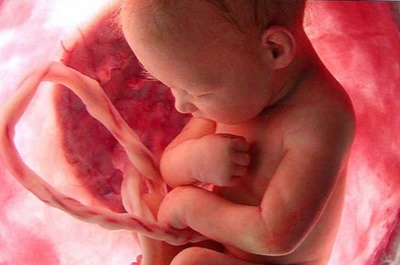
- Inborn. This method of infection is also called fetal. In this case, the hepatitis viruses are transmitted to the baby from the mother. Also, a child can become infected from the father if he was already sick before conception. Microorganisms pass through the placenta in different ways. For example, hepatitis C viruses are much more difficult to pass through the hemato-placental barrier than subtype B.
- Through breastfeeding. Global studies confirm the fact that some types of hepatitis viruses very easily reach the mammary glands. They are able to penetrate into breast milk. If a nursing mother suffers from hepatitis, especially in the active form, her baby can become infected.
- Through the drink. The source of infection in this case is poor-quality water. It usually contains a huge concentration of viruses. This method is most likely for hepatitis A. Also, this form is called Botkin's disease. Hepatitis A can also become infected by a baby swimming in a pond when it accidentally swallows water from it while swimming.
- Because of the violation of personal hygiene. The use of other personal hygiene products increases the chances of infection many times. A foreign toothbrush, towel, or shower sponge can lead to hepatitis infection in a child.
- During medical interventions. Of course, this is quite rare. However, nevertheless, cases of infection through the blood after surgical interventions or even when performing simple injection measures are recorded annually. Most often this variant of infection leads to the appearance of viral hepatitis B or C in a child.
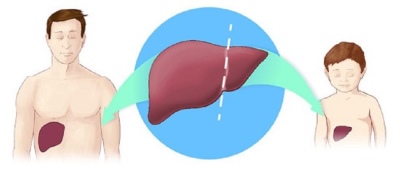
- After liver transplantation. In some situations, with various severe congenital or acquired diseases, the replacement of damaged tissue with a new one is required. For this, doctors use a liver transplant from a donor. Before carrying out this procedure, the entire necessary range of tests is carried out, which should prevent possible infection with hepatitis. However, there are cases when viruses are found in the blood after a liver transplant in a child.
- After poisoning with toxic substances. The liver, performing a neutralizing function, must eliminate all dangerous components from the body. Some toxic substances have a destructive and destructive effect on the liver cells. Typically, such acute conditions develop quite rapidly. This leads to almost complete blocking of the liver and significant violations in its work.
- As a result of unprotected sex. This form of infection is quite often recorded in adolescents. The lack of information and the neglect of the simplest contraceptive means leads to a huge number of cases of hepatitis B or C infection.
- Through dirty hands. After games on the street, kids often forget to wash their hands. Particles of dirt or earth can contain a huge number of various viruses, including hepatitis. When eating, the child puts the infection in your body. Viruses very quickly get into saliva, and then into the blood.
It is important to note that the infection carrier can be any person who has hepatitis viruses in their blood.
In some cases, the diagnosis can not detect them. However, this does not mean that there are no more viruses in the body. Often, for the detection of chronic forms of the disease requires an extended set of diagnostic measures.
The risk of transmitting hepatitis is quite high. Hepatitis A is more common in babies aged 3 to 12 years. Congenital variants of the disease are most often caused by viruses of subtype C. Hepatitis B is detected in children of school age and adolescents in the overwhelming number of cases. It occurs in about 80% of cases. The remaining subtypes of viruses cause hepatitis in babies rather rarely.
Kinds
Each hepatitis occurs with varying degrees of symptoms. It is more dependent on which virus subtype caused the disease. This circumstance also determines how hard the disease will be in a particular baby.
The most severe variant of the disease is fulminant. It is characterized by complete liver cell death (necrosis). This condition is irreversible and rather worsens the prognosis.It can occur at each stage of the disease. In the case of the fulminant course, a large number of antibodies can be detected, which is a consequence of an autoimmune lesion of the liver tissue.
Most often, such a dangerous form of hepatitis is registered in children of the first months of life.
This is due to the imperfection of the structure and work of the immune system in such babies. Immunity in infants is not able to cope with the toxic and destructive effect of viruses on liver cells. With the development of the fulminant course of hepatitis, doctors usually detect a large number of fairly massive foci of a destroyed liver.
Non-specific reactive hepatitis is characterized by diffuse dystrophic changes in the liver tissue. This form of the disease appears, as a rule, due to chronic diseases of internal organs. Usually such variants of the disease are manifested by the appearance of minor symptoms. The most frequent of them are: rapid fatigability, a violation of taste and appetite, some dry skin. In severe cases, jaundice may develop.
Different clinical forms of the disease require special treatment. For each form of the disease it is different. In some cases, the treatment of the disease is still imperfect. This can be said, mainly, about hepatitis C. Scientists from all over the world work every day to create new effective drugs that would lead to full recovery from this disease. Such difficulty in the selection of treatment makes hepatitis C close to herpes type 6, from which also specific therapy has not yet been found.
Incubation period
The time from the beginning of the entry of the pathogen into the bloodstream before the onset of the first clinical symptoms may be different. It is more dependent on the subtype of the virus and its infectious properties.
Different types of hepatitis are characterized by different duration of the incubation period:
- Option A - from 8 to 49 days. In most cases - two weeks.
- Option B - from 51 to 180 days. In the overwhelming number of children, the first signs of hepatitis B appear, on average, 3 months after the pathogen enters the blood.
- Option C - from 1.5 to 2 months. In some situations, the incubation period can be from two weeks to six months.
- Option D - usually in the first week after the penetration of the pathogen into the blood. In some cases, the appearance of the first symptoms may develop after 2-3 months from the moment of the initial infection.
- Option E - from 20 days to 1.5 months.
- Option F - Separately never occurs. Kids can only become infected with them when infected with viruses A, B and C. When combined with these viruses, their incubation periods may be shortened several times.
- Option G - mostly from two weeks to a month. In some babies, the first symptoms appear only after 35-45 days.
Symptomatology
These diseases are characterized by stepwise appearance of clinical signs.
The severity of symptoms in a baby will directly depend on its initial data. In more weakened children with comorbidities, the course of the disease can be quite severe, and the symptoms manifest themselves quite clearly.
There are several stages in the development of the disease:
- Predzheltushny period. It can manifest itself in several forms: catarrhal, gastritic, asthenovegetative or rheumatological. For hepatitis A, it usually takes about a week. The remaining forms, which are characterized by hematogenous infection, occur with the development of symptoms for 2-3 weeks.
- Period of jaundice. It is characterized by the appearance of the most specific marker of liver diseases - yellowing of the visible mucous membranes and skin. For Botkin's disease is characterized by a gradual increase in jaundice and its rapid disappearance. Other forms of hepatitis are accompanied by a rather long icteric period.
- Recovery or transition to the chronic form. The outcome of the disease depends on many data, including the characteristics of the virus that caused the disease. The overwhelming number of cases of Botkin's disease lead to full recovery. To achieve the absolute disappearance of hepatitis B and C viruses is quite difficult. This requires an intensive course of treatment, which can take several months or even years.
The preicter period may proceed in different ways. The catarrhal form is accompanied by the appearance of all the symptoms, which would also occur with any common cold. These include: a cough without sputum, a runny nose with liquid and watery discharge from the nose, an increase in body temperature to subfebrile or febrile numbers, an increase in general weakness and fast fatigue, as well as coming headache.
Quite often, in infants during this period, doctors make an incorrect diagnosis, considering these clinical signs as manifestations of acute respiratory illness or flu.
To identify the disease helps only laboratory tests that easily show the causative agent of infection. However, this period is quite a long time without the correct diagnosis.
For gastritis or dyspeptic forms characterized by the appearance of adverse symptoms of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The child may experience discomfort and pain in the epigastrium. The kid often hiccups, complains of nausea or vomiting. As a rule, during this period, the sick child's appetite decreases. Incorrect diagnostics leads doctors to the fact that they make a wrong diagnosis, implying that the baby has simple food poisoning.
Asthenovegetative variant is also not accompanied by the appearance of bright and specific symptoms. The child becomes a little lethargic, quickly gets tired even after performing his usual actions, eats without appetite, may complain of a headache. Usually, parents during this period think that the baby is not sick, but simply gets very tired or capricious. It is rather difficult to suspect the disease at this stage, even for an experienced doctor.
The rheumatological variant of the preicteric period is quite rare. Toddlers usually begin to complain of pain in the legs when walking. Visually, the joint area may not be altered. However, even the child’s gait begins to change. Usually, the baby tries not to step on the painful leg, as this markedly increases his pain. Some autoimmune forms of the disease are accompanied by the appearance of a child on the skin rashes, which in appearance may resemble allergic.
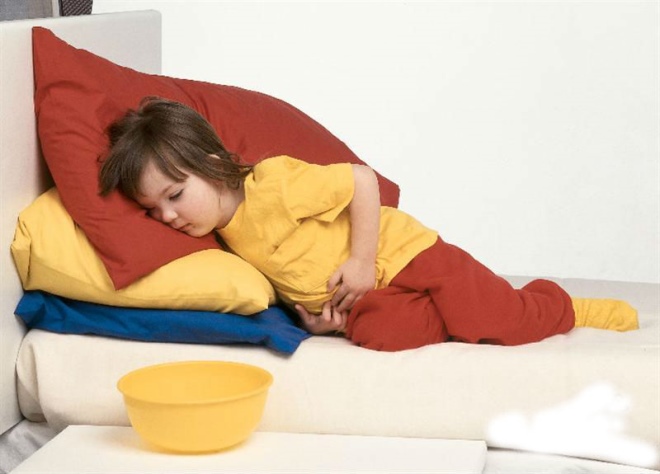
The preicteric period gradually subsides, and the baby has bright and specific signs of liver damage, which are well known to every mother. This is jaundice. It usually grows in a couple of days. Eye sclera, visible mucous membranes, and then the skin become yellow. It can be from bright lemon to olive. This is determined by the infectious features of the causative agent.
The severity of this characteristic also depends on age. In newborns and infants, yellowing of the skin can be expressed slightly. Some forms of jaundice are accompanied by intolerable pruritus. When viewed from these babies on the skin are visible numerous traces of scratching.
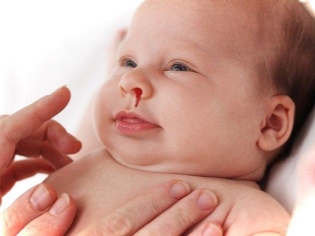
In severe illness, a child may experience various hemorrhages.
This is due to the fact that normally the liver synthesizes substances that have a positive effect on blood vessels and capillaries. When a violation occurs, their ruptures, and the outflow of blood out. The baby may develop nosebleeds or appear various bruises on the skin. At this time, as a rule, the child becomes more excitable.
By the end of the icteric period, all the main functions of the liver are gradually normalized. This leads to the fact that the negative symptoms of the disease disappear. The baby starts to feel much better. On average, this period lasts only a couple of weeks. However, in more severe cases of the disease, it can be up to several months. These situations speak about the development of a protracted period of the disease.
Also in children's practice, there are alternative forms of the disease:
- Anicteric. With this option, the child's skin remains pale pink. Bilirubin levels may be normal or slightly elevated. The boundaries of the liver usually do not exceed the norm. During the examination, it is possible to identify the causative agent of the disease, as well as a slightly increased level of special liver enzymes - transaminases.
- Erased. Practically does not cause discomfort in a baby. When examining a doctor, some enlargement of the liver is detected. Diagnosis of the disease in this form of the disease is most difficult.
- Subclinical. With this variant of the disease in the baby does not appear any clinical manifestations of the disease. The baby is doing well. Identify the disease in this course - very difficult. To establish the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct special laboratory tests that determine the pathogen in the blood, as well as antibodies developed by the body to it.
The first signs in newborns and infants
Doctors call congenital forms of the disease fetal. In this case, the infection occurs intrauterinely: from mother to child. If a pregnant woman is infected with hepatitis viruses, and also if she has an acute form of the disease, she can easily infect her unborn baby.
Congenital hepatitis increasingly began to occur in the neonatal practice of treating pediatricians and infectious disease doctors. This is largely due to the lack of all the necessary vaccinations for future mothers. Specialists may also call serum hepatitis in newborns. This means that the virus got to the baby through the liquid component of the blood - serum.
The development of the disease in newborns and infants can be quite rapid. In some cases, this leads to the development of numerous complications. Many of them are even capable of contributing to life-threatening conditions: shock or coma. In these cases, intensive care is already required in the intensive care unit.
But not always in a newborn baby viral hepatitis occurs in severe form. If a child is born with a good weight, and also without various accompanying pathologies of internal organs, then the disease can develop quite easily. Such children necessarily require increased attention from parents and medical staff.
Among the distinguishing features of babies of the first year with hepatitis are the following:
- In some cases, the disease may occur with erased symptoms.. This option is also called anicteric, since the baby does not have jaundice.
- Sharp increase in liver enzymes. Liver transaminases can increase several times. This indicates damage to the liver cells. With the development of the cholestatic variant of the disease, which is accompanied by a violation of the outflow of bile, an increase in the level of bilirubin is also observed.
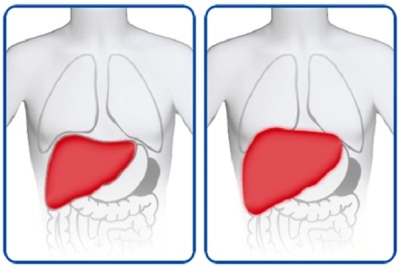
- Enlarged liver. Its boundaries can significantly exceed the maximum permissible for this age. In autoimmune variants of hepatitis, an enlarged spleen also occurs. The doctor will be able to identify these deviations during the examination, as well as when performing an ultrasound examination.
- Frequent transition of the disease to the chronic form. This is usually characteristic of those forms of the disease that have developed with the subacute course. The prolonged and destructive effect of viruses on hepatocytes leads to their damage and disruption of the basic functions of the liver.
- Mixed forms of the disease. In some weakened babies, viral hepatitis is combined with bacterial. Most often - with streptococcal. Such forms of the disease are quite difficult and require the appointment of not only antiviral drugs, but also antibiotics.
- Course without symptoms. Also, doctors call this form latent. To suspect its presence in a child is possible only under close observation of the baby. Observant parents will be able to notice dark spots on the diaper of urine, which are the result of elevated levels of liver enzymes. Toddlers suffering from the latent form of the disease, can excessively regurgitate food, as well as refuse to breastfeed.
- Possible development of fulminate forms of the disease. Such hepatitis is most dangerous in babies of the first six months of life. If this disease is detected in a newborn child at this age, then it is usually hospitalized in the infectious disease ward for intensive treatment.
- Violation of the main periods of hepatitis, as well as changing the timing of the incubation period. In this case, the period without jaundice in the baby may not be at all. The child rises sharply. It usually increases to febrile numbers.
- Lengthening the time of the icteric period. It can even last up to one and a half months. When examining the child revealed a very high level of bilirubin. In several cases, it may even exceed the norm several times. When examining such babies, doctors usually detect large spleen sizes. In this case, the boundaries of the liver for a long time can remain within the age norm.
- Frequent complications. The risk of possible negative consequences of the disease in newborns increases several times. The younger the child, the higher the risk of developing complications. Usually the most severe course of the disease in babies of the first 3-6 months of life.
Basic diagnostics
In the overwhelming number of cases, the diagnosis of viral hepatitis is quite easy to establish. 75% of babies with jaundice, doctors find signs of this disease. The doctor may be suspicious of the disease during a routine examination and determination of the size of the internal organs. After such a clinical examination, the doctor writes out several tests and studies that allow you to accurately establish the diagnosis.
The following tests are used to detect hepatitis in a child:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- Urine test for the detection of bile pigments in it.
- ELISA blood test to find the causative agent of the disease. A positive analysis indicates the presence of viruses in the child’s body. However, the test has not enough high specificity. This leads to a false positive result. In such situations, repeated monitoring is required after a few months.
- Serological test to detect antibodies. Some time is required for their formation, therefore it is impossible to detect them at the initial stage of the disease.
- PCR. Quite an accurate study that helps detect various viruses within the body.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. It helps to establish the actual size of the liver and spleen, and also gives a qualitative description of the existing anomalies in these organs.
Is it possible to give birth to a healthy baby mother with hepatitis?
The risk of intrauterine infection during pregnancy is quite high. Most often this question is asked by women with hepatitis B or C. A type B virus is small and very easy to cross the placenta. Mothers with viral hepatitis B, according to statistics, already infected babies are born in the vast majority of cases.
You can affect it. To reduce the risk of intrauterine infection, it is very important to plan a pregnancy.Before the onset of conception, the future mother can be given all the necessary treatment. It will help reduce the concentration of viruses in the body. In the future, during pregnancy, this will help to significantly reduce the risk of possible infection of the baby.
All expectant mothers who are planning a child should be vaccinated.
The schedule of hepatitis B vaccinations is approved in Russia by an official document. Information about the timing of vaccination can be found in the National Calendar of preventive vaccinations. For reliable protection against hepatitis B, only three doses of the vaccine will be required. Such a simple measure of prevention will help protect the future baby from possible infection with a dangerous disease.
Hepatitis C is also a fairly frequent threat during pregnancy. Scientists have shown that viral pathogens of this disease can hardly penetrate the placenta. However, the risk of infection still exists. Most infections are recorded during childbirth. Passing through the birth canal, the child may become infected.
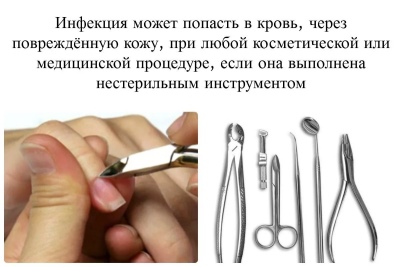
Hepatitis C vaccine does not currently exist. Therefore, every mommy during pregnancy should follow the basic rules of prevention. It is necessary to limit and minimize all possible contacts that could lead to infection of her and the future baby. In some situations, it is possible even to get infected with hepatitis C in a beauty salon when cutting. manicure.
Complications
Many forms of hepatitis end in complete recovery. 90% of babies who have had Botkin's disease in childhood never remember it again. Parenteral forms that occur during infection through the blood usually do not have such a good course and prognosis. Quite often, from an acute course, they become chronic.
In hepatitis B, adverse complications may develop during the preicter period. According to statistics, they are observed in children in 5-15% of cases. The most common complications include hemorrhagic bleeding, the appearance of skin rashes, pain in the joints, the appearance of blood in the urine.
After hepatitis C, a child may experience an autoimmune disease.
Some babies develop some rheumatological diseases. Doctors have noted the appearance of symptoms of late cutaneous porphyria, lichen planus and other pathologies in such children. Until now, scientists have not given an answer to why these conditions develop in children with viral hepatitis C.
Lightning forms of hepatitis, accompanied by mass death of liver cells, occur in 1-5% of cases. Such a rapid development of the disease is accompanied by abundant necrosis in the liver. The condition of the baby is deteriorating. In some cases, even shock or coma may develop. The treatment requires urgent hospitalization in the hospital and a massive infusion therapy.
Chronization process occurs in about 40-50% of babies. Chronic hepatitis significantly impairs the child’s quality of life. The baby may suffer from excessive fatigue, learn poorly and get tired very quickly. In such children, as a rule, appetite is reduced or disturbed. Some babies have difficulty falling asleep or often wake up in the middle of the night.
How to treat?
Each clinical form of viral hepatitis is treated differently. Botkin's disease self goes away in a few weeks. This form of the disease requires only the appointment of symptomatic treatment. The use of any special antiviral agents to eliminate the virus is not required. Usually the children's body copes with the elimination of microorganisms and the normalization of their work.
Therapy of parenteral viral hepatitis is a rather difficult task. The choice of drug treatment regimen is carried out by an infectious diseases doctor.The child, who was found in the blood of infectious pathogens, put on dispensary registration. The baby must undergo mandatory consultations of doctors and pass all the necessary tests. Hospitalization is usually not required during the acute period of the disease.
The only exceptions are cases in which the child suffers from severe and especially fulminant hepatitis. In this situation, the baby is hospitalized in the infectious disease ward of the children's hospital for all the necessary treatment.
The complex treatment of the acute period of the disease includes:
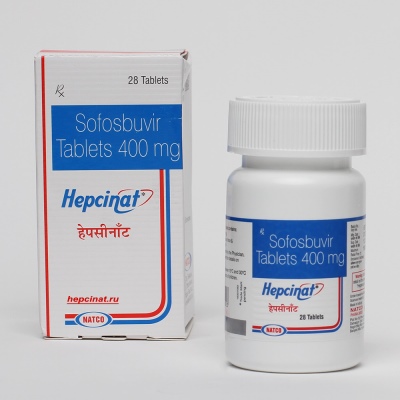
- Antiviral treatment. It is prescribed for parenteral forms of hepatitis. Various schemes of drug therapy are used. Sofosbuvir therapy is used to treat hepatitis C. This tool has a sufficiently high efficiency and good tolerance spectrum.
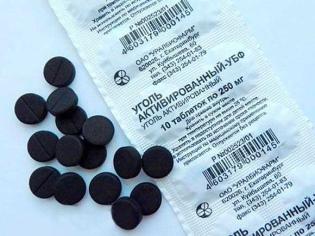
- Elimination of intoxication. This is facilitated by abundant drinking, as well as the use of sorbent and antipyretic drugs. As sorbents can be used: activated carbon, Smektu and other drugs.
To eliminate the high temperature, it is better to choose paracetamol-based drugs, since they do not have a toxic effect on the liver.
- Immunomodulatory. They help restore the normal functioning of the immune system. Immunoglobulin therapy has positive effects in the treatment of hepatitis C. Interferon-series drugs can also be used.
- Choleretic. Appointed with severe cholestasis syndrome. In this case, the stagnation of bile and the violation of its outflow through the biliary tract. As a similar treatment fit: Hofitol, Cholenim and other means. Prescription drugs is carried out only after an ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder. In the presence of stones in these organs to use cholagogue can not.
- Hepatoprotectors. They are prescribed to eliminate and prevent the death or severe damage of liver cells. The choice of drug depends on the age of the child, as well as taking into account the variant of the pathogen.
- Medical nutrition. Babies with chronic hepatitis should follow a diet throughout their lives. Fried and fatty foods for them under strict prohibition. Also, all fast food products and cooked with a lot of butter are excluded from the menu. Proper nutrition with adequate intake of low-fat varieties of meat and poultry, as well as cereals and dairy products is a successful guarantee of the normal functioning of the liver for many years.
- Bed rest during jaundice. This simple measure helps to reduce the risk of further complications. To achieve a faster recovery, the baby should be given a sufficient amount of fluid. This will help to quickly deal with negative symptoms of the disease.
Forecast
Even the transition to the chronic form of the disease does not have a significant effect on the life expectancy of the child. Kids keep active lifestyle for many years. Only in 2% of children can sufficiently dangerous complications occur. Usually they develop in newborns and babies. Quality of life depends on the form of the disease.
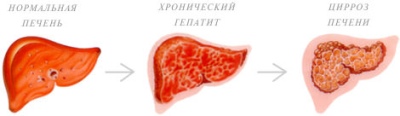
Viral hepatitis C usually occurs without any marked symptoms over a long period of time. If not treated, they can lead to the development of long-term effects in the child. Already in adulthood, he forms a total damage and death of liver cells - cirrhosis. In this case, the person already has to receive therapy for life, sometimes it is even an indication for establishing a disability group.
To prevent viral liver disease can only be through prevention. Today, there are excellent and effective vaccines against hepatitis B and A. They will help protect the children's body from dangerous parenteral infections. Vaccination against hepatitis B is already underway at the maternity hospital.The schedule of vaccinations is strictly regulated and included in the National Calendar.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you about viral hepatitis in the next video.