Conjugate jaundice of newborns
Every second newborn's skin turns yellow due to increased levels of bilirubin in the baby’s blood. Depending on the cause of this increase, different types of jaundice are distinguished, one of which is conjugation jaundice.
What it is?
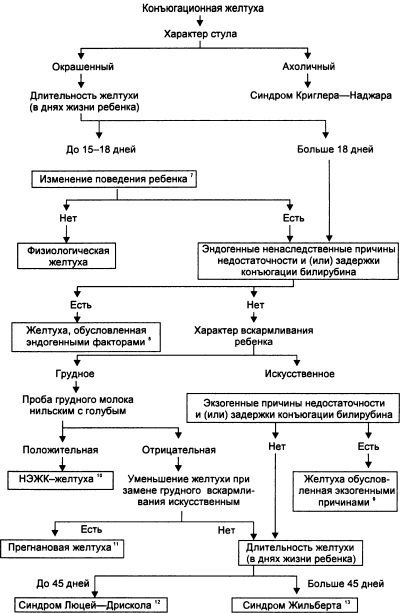
So called emerging in infants jaundice associated with a problem in the metabolism of bilirubin. In particular, with conjugation jaundice, indirect bilirubin is not converted into a direct fraction of this pigment.
The reasons
Most children conjugation jaundice is physiological. Its occurrence is associated with the breakdown of fetal hemoglobin (it is replaced by normal hemoglobin), an insufficient amount of albumin, and also the immaturity of the enzyme system of the liver.
With prematurity, jaundice appears more often due to even greater immaturity of the liver, so this condition not only lasts longer, but is also characterized by a high risk of infestation with indirect bilirubin of the baby’s brain. That is why such jaundice is often treated.
Separately distinguish jaundice of breastfeeding, the cause of which is the presence in the breast milk of substances that interfere with the conjugation of bilirubin. If you stop breastfeeding for one to three days, the level of bilirubin with such jaundice immediately falls.
Read more about jaundice in newborns in the next video.
The causes of the pathological form of conjugation jaundice are:
- Gilbert's syndrome is a genetic disease in which there is a lack of liver enzymes. With such a congenital pathology, the brain is not affected.
- Crigler-Nayar disease - jaundice caused by insufficiently active or absent liver enzymes responsible for bilirubin binding. Pathology can be complicated by encephalopathy.
- Lucy-Driscoll syndrome is a temporary deficiency of liver enzymes, in which jaundice is often difficult and can affect the brain. If the child suffers from this condition, such jaundice does not bother him more during his life.
- Hyperbilirubinemia associated with asphyxia during childbirth. The child is delayed the development of the enzyme system of the liver and there is a risk of nuclear jaundice.
- Some diseases of the endocrine system, for example, hypothyroidism. They are deficient in the enzyme responsible for the conjugation of bilirubin.
- Treatment of the newborn with certain drugs, for example, vitamin K in high dosage, chloramphenicol, salicylic drugs.
Symptoms
In conjugation jaundice, the skin and sclera of the child acquire a yellow color. The color of urine and feces may remain natural (in physiological form) or change. The fact that a baby may develop nuclear jaundice will tell the baby's drowsiness, the drooping of the head, the occurrence of episodes of vomiting of yellow milk or convulsions.
Diagnostics
It is important to distinguish conjugation jaundice from such types of pathological jaundice, such as hemolytic (it is caused by increased breakdown of red blood cells), parenchymal (its occurrence is associated with damage to liver cells) and obstructive (it causes mechanical obstruction of bile). To do this, the child conducts blood tests, liver and biliary tract.
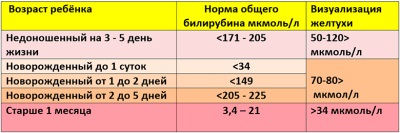
Norm bilirubin
Bilirubin in a newborn baby immediately after birth is determined at a concentration of 51-60 µmol / L.Normally, by the third day of life, its level rises, but not higher than 205 µmol / l. Yellowing of the skin is observed at rates above 85 µmol / l in premature babies and more than 120 µmol / l in children born at term. If the level of bilirubin increased above 172 μmol / l in premature babies and more than 256 μmol per l in babies who were born full-term, then they speak of pathological jaundice.
Treatment
Depending on the cause of conjugation jaundice, treatment will vary and be determined by doctors. Baby can assign:
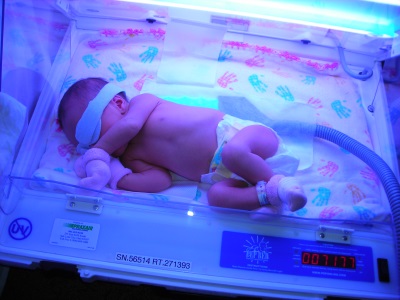
- Phototherapy The babies are kept under ultraviolet lamps, as a result of which the bilirubin becomes harmless and easily leaves the body of the crumbs.
- Infusion therapy. The child is injected with intravenous saline and glucose.
- Barbiturates. Such drugs affect the conjugation of bilirubin.
- Blood transfusion. It is prescribed for a serious condition of the baby.
When does it take place?
Conjugation jaundice caused by physiological causes usually lasts 10-14 days of life, leaving no consequences for the child. The duration of such jaundice in premature babies can increase up to 21 days or more.
Tips
Mom should not stop breastfeeding, and put the baby to the breast as often as possible, as breastfeeding at least 7 times a day contributes to more rapid elimination of bilirubin with feces.