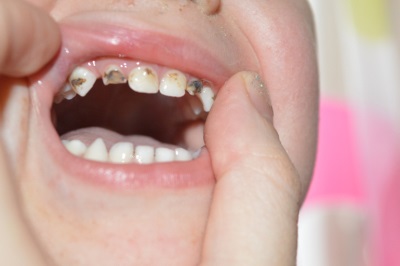
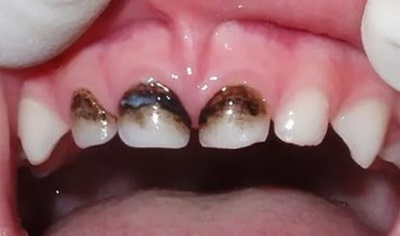
Silvering of milk teeth
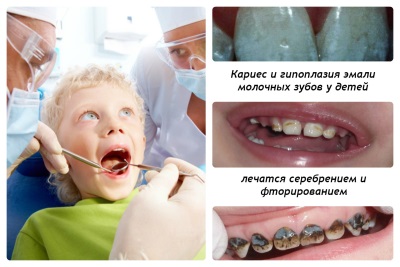
Milk teeth are less durable than indigenous ones, so they are often affected by caries. Having found a disease on the teeth of the baby, you should as soon as possible show the crumbs to the doctor. But do not be afraid that the child will immediately be treated with a drill, because now there are other methods of treatment, such as silvering.
What is it?
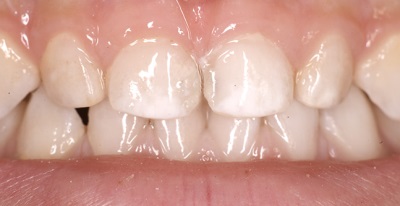
This is the name for the treatment of caries-affected milk teeth, in which silver preparations are used. It's about silver nitrate, which has an antiseptic effect. Due to its bactericidal effect and the formation of a film of insoluble silver salts, such drugs stop the further development of the infection, helping to keep baby teeth before their physiological change to the root ones.
pros
- The procedure is simple, it is performed quickly enough and does not cause children discomfort, so that the kids will not have bad associations with dentists.
- For the procedure using a natural and environmentally friendly material, in which there are no harmful impurities and toxins, as well as components with allergenic effects.
- Manipulation for the purpose of prevention rather effectively prevents damage to the enamel, the formation of white carious spots and cracks on it.
- At the beginning of caries, the procedure helps to delay the development of the disease until the moment when the baby’s teeth will no longer be needed by the child and begin to change with the original ones.
Minuses
- Over time, the silver layer on the teeth collapses, which also contributes to the consumption of acidic foods (juices, fruits, vegetables). This makes it necessary to repeat the procedure regularly.
- Silvering is not suitable for treating chewing teeth, as it will be ineffective and may make it difficult to diagnose new lesions with caries.
- The color of the treated teeth changes, and the teeth remain dark until it falls out.
- The technique does not help with neglected caries, because when it comes into contact with the pulp, silver preparations cause its dying off.
- If the composition, which is treated teeth, accidentally falls on the mucous membrane, it can lead to itching and redness, and sometimes to the formation of a chemical burn. In addition, the taste of the drug is very unpleasant.
Indications
The child will be recommended to perform silvering at:
- Detection of early caries, represented by demineralization sites (white spots).
- Loose and too thin enamel, on which chips and cracks are noticeable.
- Increased sensitivity of tooth enamel to sour and sweet products, as well as to temperature changes.
- Lack of fluoride in the diet (as a prevention of damage to the teeth).
- Desire to extend the life of seals.
- The desire to reduce the risk of recurrence of caries.
Contraindications
Silvering is not carried out if:
- Caries is neglected and rather deep or complicated by pulpitis.
- The water and food consumed by the child contains a lot of fluoride.
- Early caries hit permanent teeth.
- The child has an allergy to the components of the drug.
Stages of silvering
The procedure is performed only in the dental office for children who have formed a milk bite (older than 2.5-3 years).Before you treat your teeth, an inspection is required to determine indications for silvering and to identify possible contraindications. In addition, the teeth should be thoroughly cleaned from plaque.
Next, the doctor dips a cotton swab into a special solution and rubs the enamel on the smooth side of the teeth, after which it darkens. No abrasive materials and anesthetics are used for silvering. The procedure is repeated several times with an interval of 2-7 days, and then performed every six months or more, depending on the condition of the teeth after treatment.
The possibility of a psychological problem
For parents, the blackening of the teeth after treatment with silver solution is often a minor drawback, which has to be tolerated in order to save the child's teeth. But for a child such a flaw can cause bad mood and complexes. If a child reacts very sensitively to his appearance and the reactions of other people (ridicule of peers because of teeth), after silvering, he may be afraid to talk and laugh, which could result in depression.
So that the child does not suffer after silvering, parents should discuss all the nuances of this procedure in advance and emphasize its importance for dental health. Some kids, especially at the age of 4-5 years, when they see photos of children with blackened teeth, agree to tolerate a drill and filling, so that their smile remains bright.
If a child who is planning to perform silvering goes to kindergarten, parents should find out in advance whether there are children in the group who have teeth already treated with silver, and whether they will tease such babies. You can also ask the caregiver to tell the kids why the teeth turn black when silvering, so that the child is not teased.
Reviews
Parents speak about the silvering of teeth in different ways. Some say that it is a safe and affordable method to effectively deal with early caries. Its main advantages are the speed of processing and its painlessness. Others complain about a large number of shortcomings of the procedure, among which is usually referred to as a high frequency of treatments and an unpleasant, unaesthetic appearance due to blackening of the teeth.
Alternatives
In many countries, silvering is referred to as outdated methods of protecting teeth from caries, preferring such more modern alternatives to it:
- Fluoridation. This is the name of a prophylactic procedure prescribed for children over 4 years old, in which they use fluoride-containing drugs. Like silvering, it helps not to cure caries, but to delay its development; therefore, it is not indicated for moderate and deep teeth damage. Unlike silver plating, enamel remains white when treated with fluoride preparations. As with silvering, you need several sessions, but such manipulations are more expensive.
- Remineralization. In this procedure, the milk teeth of children over 6 years old are covered with special pastes or solutions with minerals that can eliminate cracks, reduce the sensitivity and vulnerability of enamel.
- Ozonation. The technique involves the treatment of teeth with ozone-containing agent to stop the process of enamel infection and the destruction of pathogenic bacteria.
- Sealing of fissures. This is the name of effective modern dental treatment with a special glassy material for reliable protection of teeth against negative external influences.
Opinion Komarovsky
The famous pediatrician emphasizes that silvering does not help to cure teeth, but rather acts as an attempt to “preserve” the infection. Komarovsky agrees that the technique has the right to exist, because it is fast and does not harm children if properly carried out. However, a popular doctor advises to pay attention to such nuances:
- If silvering was carried out 1-2 months ago, and caries is still active, you will have to resort to more traditional methods (filling).
- If the tooth is deeply affected by caries, Komarovsky believes that it is better to remove it than to leave the source of infection in the children's body.
- If the baby categorically refuses to handle canals with a drill and filling, it is better to resort to general anesthesia than to keep the child and cause him psychological trauma from dental treatment.
For the prevention of caries, Komarovsky advises to stop at sealing fissures, considering this method as the most effective. The pediatrician negatively responds to the use of fluoride varnish, asserting that such a cheap drug does not freeze on the child’s teeth and is often washed off on the day of treatment.
You can learn more about silvering teeth, about the pros and cons of this procedure, about parents' feedback in the following video.