Multiple pregnancy with IVF: from likelihood to risk
The birth of twins or even triplets after IVF is not such a rarity. However, it is erroneous to assume that almost always after in vitro fertilization there is the likelihood of multiple pregnancy. Two or three babies in the womb are double or triple joy, but the risks associated with multiple fetuses increase proportionally. In this material, we will consider how much the birth of several babies after IVF can be, as well as the dangers of bearing fruit.
Statistics and Facts
In order to increase the chances of a positive outcome of the IVF protocol in a patient who is being treated for infertility, the ovaries are stimulated with hormonal drugs. Follicle stimulating preparations allow reproduction specialists to obtain several matured oocytes, while embryologists, respectively, will receive several embryos. Usually, several embryos are also transferred to the uterus, because the implantation process will not be feasible for each of them.
For women under 35 years old, the transfer of two embryos is recommended, for women older than this age - three. Bioethics implies a sensible approach that says that as many embryos are required to be transplanted into the uterus as a woman can tolerate if everyone takes root.
With natural conception, the chances of becoming parents of twins are no more than 1.5-2%, the probability of triplets is 0.2%. Due to the fact that 2-3 embryos are transferred into the uterine cavity at the end of the in vitro fertilization protocol, the probability that all of them will take root is much higher. If there was a preliminary stimulation of the ovaries with drugs such as Clomiphene, Clomtilbegit, then the chances for double or triple happiness are estimated at 6-8%.
And when using hormonal drugs based on gonadotropic hormones, the probability of having twins or three babies increases to 35%. With a stimulated protocol using different types of hormones (and such IVF protocols are carried out most often when providing reproductive care) the probability of multiple pregnancy increases to 40-45%.
A woman who wants to get pregnant through IVF is informed about this probability at the preparatory stage of the treatment cycle. She gives informed consent to him. If the birth of several babies at once is not included in the plans, then the woman may refuse to transfer 2-3 embryos, only one embryo will be transplanted to her, but the chances of becoming pregnant in this case will decrease several times. This patient also warn in advance.
Types of multiple pregnancy
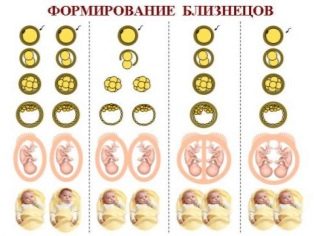
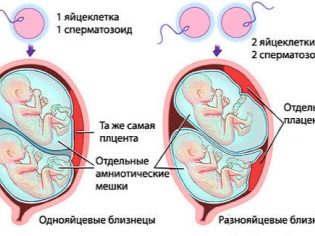
With the natural fertilization, twins can be monozygous (identical) or dizygotic (fraternal). In the first case, the woman will bear twins, and in the second - twins. At the same time, in the overwhelming majority of cases twins are born, the probability of dysygotic twins development is 70%. Twins come from a single ovum, have an identical set of genes - in 100% of cases they have the same sex and have a surprising external resemblance.
Twins all nine months "huddle" in one fetal bladder. The twins in the womb live somewhat easier - each has its own bladder, its own amniotic waters and its own placenta, which nourishes the baby and supplies it with oxygen.
After IVF, in the cycle of which two or three embryos of different genetic sets are planted, twins are born most often. Embryos initially have a different genetic nature, they differ from each other in a set of genetic information, gender (not always). If all embryos transferred to the uterus can be implanted under favorable conditions, then triplets, completely dissimilar to each other, or twins, are born.
With the replanting of two embryos, triplet birth is not excluded. If the fertilized egg at the age of 3 days is planted, it can be implanted and, according to its own genetic program, divides into two for 7-8 days of its embryonic life, then twins can form. In this case, the second embryo of the two transferred ones may well also be implanted. However, such a scenario is rare.
If the separation of the ovum occurs on days 9-13 from the day of fertilization, then both fetuses will be in the same bubble and will be monozygotic twins. The separation of the ovum two weeks after fertilization leads to the formation of the so-called Siamese twins - babies, who grow together with each other in separate parts of the body.
Risks
If a woman is contraindicated in multiple fertility for a number of medical reasons, fertility specialists initially try to transfer only one embryo. But situations can be different, and sometimes they transfer several embryos, or an existing embryo can divide. A woman may face a big ethical problem - what to do with "extra" kids. In this case, doctors may suggest a reduction procedure — removing one or two embryos from the uterus so that only one child remains.
From the spiritual, religious, moral and ethical points of view, reduction is essentially an abortion, the infanticide of living babies. The decision here is for the woman and her doctor. But it will not be easy. From a medical point of view, the reduction reduces the possible risks during pregnancy and childbirth. It is often resorted to in situations where three or four embryos have taken root. Two are left, because the risk of intrauterine death after IVF is quite high.
Reduction can be carried out only up to 10 weeks of pregnancy. The most commonly used is vaginal reduction, in which a woman is injected with a needle through the vagina under anesthesia and pierces the embryo to be resected. This is a very difficult procedure, the risk of losing all children with her is from 35 to 45%.
After many years of treatment for infertility, complex IVF, rarely does a woman agree to resection, and not only for moral and ethical reasons - if the pregnancy is interrupted, you will need to start all over again, and this is very troublesome and very expensive.
Pregnancy after IVF is often associated with various risks, primarily with the risk of miscarriage, the occurrence of missed abortion, the threat of pathology of the placenta and premature birth. In case of a double pregnancy, the load on the organs and systems of a woman is double, and the triple load is triple. In emergency mode, work the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, liver. Considering that women over 35 often come to IVF, increased loads may be dangerous for the life of the future mother herself.
The number of complications during multiple pregnancies after IVF is estimated by the Association of gynecologists and reproduction specialists to be about 7 times higher. The more fruit harvested, the harder and more dangerous it can be.
Against the background of almost cosmic loads on the female body, chronic diseases are exacerbated in almost 100% of cases, and the rare woman to 35 has not acquired them. In the third trimester of pregnancy increases the likelihood of severe preeclampsia, which, in turn, can lead to placental abruption, the occurrence of severe complications that can lead to fetal death and even mother's death.
Edema and increased pressure in case of multiple fetuses, especially at longer periods, are not uncommon, but rather the norm. So the woman's body reacts to the increased needs of children in nutrients, oxygen and minerals. Malnutrition, in general, often excusable for a healthy and uncomplicated singleton pregnancy, is unforgivable for an expectant mother who bears two or three eco-kids. Against the background of a metabolic disorder, she may develop severe pathologies, and children may experience problems with growth and development.
Carrying babies hard. Enough to understand that by the end of pregnancy, a woman with twins gains about 22 kilograms in weight! Moreover, in 95% of cases of multiple birth IVF pregnancy, anemia develops in late periods.
The situation in which one fruit is smaller than the other is quite normal. Two babies cannot develop completely identical, and even with monozygous twins, one of the babies is always larger and larger than the other. The expectant mother has to worry about the health of not one, but several babies at once after a very “fruitful” IVF. One of the twins can develop normally, and the second does not exclude problems with fetoplacental blood flow.
Often is the situation in which one of the embryos ceased to develop. In this case, everything will depend on the timing. In the early stages, a resection can be performed, in the middle of the pregnancy, the deceased baby is preferred to be left in the uterus and hemodialysis is performed on a regular basis by the woman, and late delivery will be indicated an urgent delivery. In the postpartum period, the woman does not exclude the development of massive bleeding.
Tactics of reference and childbirth
Multiple pregnancies after IVF require special monitoring due to the increased risk of complications. A woman will have to visit her obstetrician-gynecologist more often than others, to be tested more often, to do ultrasound, CTG and USDG. Given that complications can develop at any gestational age, this rule will be effective right from the moment of registration and up to the birth. On maternity leave, however, it will be possible to leave earlier than others. The hospital is laid from the 28th week of pregnancy, and not from the 30th week, as women bearing one child.
To deliver such pregnant women in 95% of cases try by cesarean section. This avoids the many risks that lie in wait for women and babies in labor. A planned operation is usually carried out at 37-39 weeks (more often at 38 weeks gestation), hospitalized in the maternity hospital should be about three weeks before the expected date of birth or a week before the scheduled operation.
The pre-pregnancy cash benefit is provided in one, not double, but the child benefits that a woman can count on after delivery will be double or triple - on each of the children. In addition, a woman will be able to rely on receiving maternity capital and a number of federal and regional benefits placed on the second, third and subsequent children.
Reviews
According to numerous reviews, women who have traveled this difficult path are very happy that they have been able to become mothers of several babies at once. At the same time, they warn that the moral preparation for difficulties should be literally from the first days after the ultrasound diagnoses a multiple pregnancy.
First, you will have to encounter frequent and detailed medical examinations, the amount of which significantly exceeds the norm for other pregnant women, and from about the fifth month of pregnancy, while the others are still “flitting”, the expectant mother of twins or triplets becomes difficult not only to lead a normal life, but also just to move - pelvic bones begin to hurt, legs, swelling and pressure increase.
The course of multiple pregnancies after IVF, as well as the risk of complications, largely depends on how accurately a woman complies with the recommendations and prescriptions of the doctor.Many women note that during the gestation period they had to lie down for 5-6 times in the hospital on conservation and with other pathologies. Obstetricians and gynecologists are afraid of such pregnancies as much as the expectant mothers themselves, because for the tragic incident they will be asked the full program. That is why, if any suspicion of a threat or other complication arises, they give the woman a referral for hospitalization.
Despite this somewhat biased medical attitude, mothers of IVF twins and IVF triplets recommend not giving up the opportunity to lie in a hospital. This is peace, and the opportunity to sleep, and round-the-clock observation by medical specialists, which will definitely not be superfluous.
In the next video you will find more information about multiple pregnancies with IVF.