Colitis in children: from symptoms to treatment
Intestinal infections in childhood are more common than in any other. And if some children have intestinal flu relatively easily, without complications, others develop inflammation in the intestines, and colitis begins. But not only the infection can cause it.
About the disease
Colitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process localized in the colon. It is accompanied by pain, the inflamed intestinal membranes cannot fully cope with all their functional responsibilities. This is how intestinal dysfunction develops..
It is noteworthy that among young and adults with a diagnosis of chronic colitis, approximately one in ten of the pathological changes in the state of the large intestine began in childhood. And this is the main task of doctors - in time to detect the pathology and prescribe the correct treatment.
In early childhood, the digestive organs have their own anatomical and functional features. And because in its pure form colitis occurs less frequently. Usually the colon is inflamed at the same time as the small intestine, and then the disease is called enterocolitis. But already at school age, these two inflammatory processes are increasingly found in isolation from each other - there is only enteritis (inflammation of the lining of the small intestine) and exclusively colitis (inflammatory changes in the mucous membranes of the large intestine).
Common causes
Considering that children have more widespread intestinal infections, the most common cause of the disease is infection — this is how infectious acute colitis develops, and sometimes post-infectious (developed as a complication of a postponed intestinal infection). The inflammatory process in the large intestine can occur during the illness of salmonellosis, dysentery, escherichiosis, rotavirus and enterovirus infection.
Most often, colitis is associated with acute gastritis with an infectious disease, enteritis, or gastroenteritis. All departments of the digestive tract are communicated, they are interrelated, and therefore the inflammatory process that has arisen in one department quickly spreads and reaches the large intestine.
To provoke an attack of acute colitis in an allergic child or a child with gastrointestinal diseases can be a violation of the recommended therapeutic diet, intolerance to certain products.
The danger of acute colitis is that the disease can become chronic, which most often occurs with colitis associated with dysentery. The chronic process with inflammation and degenerative changes in the large intestine often develops against the background of long-term helminthic invasion, parasites, against the background of severe chemical poisoning.
Parents can also provoke colitis by giving the child unreasonably medication that the doctor did not prescribe. The most dangerous to the health of the intestines are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, laxatives, antibiotics.
Specialists have long noticed that psychogenic triggers contribute to the development of colitisFor example, increased impressionability, prolonged chronic stress in a baby. Also, children born prematurely born with congenital abnormalities of the gastrointestinal tract and children with pathologies from the central nervous system, for example, diagnosed with cerebral palsy, also suffer from colitis more often than others.
By secondary school and adolescence, colitis begins in children who lead a sedentary lifestyle, spend a lot of time at the computer, in front of the TV, amid teenage bad habits. With some hormonal disorders, the secondary form of the disease may develop - children with functional thyroid insufficiency suffer more often than others with such colitis.
Types of disease
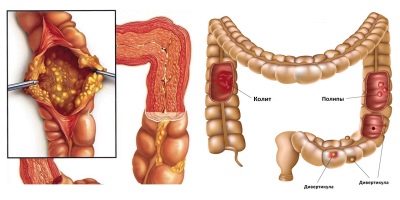
The inflammatory process in the colon is small and large-scale. If only a few segments are affected, then the colitis is considered to be isolated; if the lesion covers the entire colon, then they are talking about widespread colitis.
Depending on which segments of the intestine are affected, an isolated type of children's colitis is:
- typhlitis - inflammation in the cecum;
- tiflocolit - inflammatory and degenerative process of both the cecum and ascending intestine;
- transverse - inflammatory process in the transverse colon;
- angulite - the process of inflammation in the isthmus between the transverse colon and descending colon;
- sigmoiditis - inflammatory changes in the sigmoid colon;
- proctosigmoiditis - synchronous inflammatory process in the sigmoid and rectum;
- proctitis - inflammatory process in the rectum;
- pancolith - generalized form.
After identifying the pathogen that caused the inflammatory changes, additional characteristics of the disease are given - it can be infectious (bacterial), nutritional, allergic, toxic, parasitic, pharmacological, neurotic (psychosomatic, psychogenic).
Depending on how strong the inflammation is and whether there are signs of membrane degeneration, the following are distinguished:
- catarrhal form;
- atrophic;
- erosive and ulcerative.
At a tender age, acute catarrhal, chronic colitis, ulcerative colitis, and spastic colitis are very common. Also pseudomembranous colitis (developing with long-term antibiotic treatment), hemorrhagic colitis (mainly bacterial with bleeding) are also found. The most severe is necrotizing colitis, in which the mucous membrane of the large intestine dies. Fortunately, in childhood this form of illness is not as common.
How to recognize?
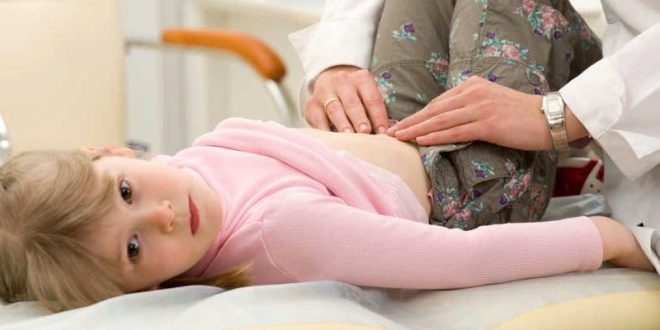
A child with acute colitis caused by infections is usually accompanied by signs of intoxication - the child has a fever, he is weak, he feels sick. When inflammation of the intestinal mucous membranes begin spasms, with the result that the baby complains of abdominal pain, the urge to defecate, which may well be false.
Diarrhea can be repeated from 5 to 15 episodes per day.. Fecal masses with inflammation in the colon have a watery structure, they are frothy, have an unpleasant odor, often greenish, dirty brown, they are clearly visible impurities of mucus, and in hemorrhagic form - bloody blood.
The urge to defecate can be so frequent and strong that it is possible the development of complications in the form of prolapse of the rectum.
But the main danger of colitis in its acute form lies not even in this, but in the possibility of dehydration. It is from him with intestinal infections most often occurs fatal. The younger the child, the faster dehydration occurs.. The baby’s features will sharpen, the baby is thirsty, he is very weak, his skin loses elasticity, his lips, tongue and mucous membranes are dry. With severe loss of fluid, there is delirium, loss of consciousness, convulsions. Acute severe colitis is especially dangerous for infants and babies.
You can suspect chronic colitis in a child by the characteristic alternation of periods of exacerbation and calm. Inflammation of the large intestine will be mainly pain in the abdomen and upset stool.
It hurts mainly in the area near the navel, aching pain, unexpressed, most often appear a short time after eating.Constipation can alternate with diarrhea. Fecal masses at the same time have a characteristic look, a smell, color and a consistence, described above. Children who are prone to constipation may have cracks in the anus.
Children with chronic forms of colitis are slowly gaining weight and often do not reach the age norm. They often complain of headaches, weakness, get tired quickly, sleep badly at night.
What to do?
Colitis is a serious condition, and self-medication is unacceptable here. Parents when detecting the described signs must show the child to the doctor. If symptoms are observed in a child under 1 year old, it is necessary to call an ambulance.. The diagnosis is made after laboratory microscopic examination of vomiting, fecal masses, blood analysis and endoscopic examination.
Almost always, the level of hemoglobin is reduced in the blood of a baby with colitis, and a biochemical blood test shows an imbalance of electrolytes.
Before the arrival of the ambulance, the kids are not given any medication. The exception is high temperature (above 38.0 degrees). In this case, you can give a single age dose of antipyretics.
How to treat?
Treatment of the disease requires the elimination of the cause of the inflammatory process and the restoration of normal functioning of the large intestine. No matter what causes the disease, the baby is recommended a special diet that does not create an increased load on the digestive organs - This is a weak "secondary" broth, porridge, "mash", omelets, jelly.
If colitis is infectious or parasitic, prescribe the appropriate drugs. With the bacterial form of the disease take antibiotics. When worm invasions are detected, they are treated with anti-parasite drugs.
To restore the lost water-salt balance, it is recommended to water the child “Regidronom”, “Smektoy” abundantly. If the child’s condition is severe or because of his age, he cannot be drunk, the baby is hospitalized and electrolyte solutions are injected intravenously.
Children with a chronic form of the disease recommended a strict diet not only at the time of exacerbation, but the rest of the time too. Enzyme preparations, probiotics, enterosorbents are recommended to restore bowel function and prevent recurrent attacks. Clinical recommendations include the appointment of physiotherapy after an attack is stopped.
If the treatment is carried out on time and correctly, the prognosis for acute colitis is always favorable. Chronic form in compliance with diet and medical appointments has all chances to proceed with long periods of remission.
After an acute illness for some time, it is advisable for the child to be seen by a pediatric gastroenterologist. Usually, if the seizures are not repeated for 2 years or more, the child is removed from the register.