How long after cesarean section does the uterus contract?
The most painful, but necessary process after cesarean section is the involution of the uterus. The reverse development is necessary for the reproductive organ, since there is no physiological necessity either in large sizes or in stretched muscles, because the child has already been born.
Contraction of the uterus, if the birth was not without the participation of surgeons and the baby was taken through an incision on the anterior abdominal wall, has its own characteristics. In this article, we will describe how the reduction takes place, how long a woman will feel discomfort, how to speed up this process.
The state of the body after surgery
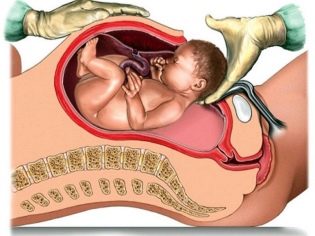
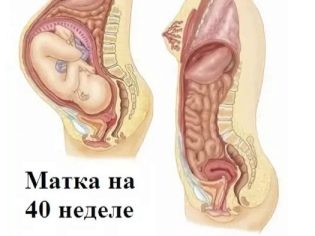
The uterus with the onset of pregnancy grows, and for childbirth its size is 500 times the original values. During pregnancy, she undergoes a lot of changes. Thus, the placenta is firmly attached to its inner wall, through which uteroplacental blood flow occurs, the walls of the uterus are better supplied with blood, and therefore become thicker, the uterine ligaments stretch.
During a cesarean section, the surgeon through the incision in the uterus (vertical, if the operation is emergency, or horizontal, if the operation is performed as planned) pulls the baby, and then manually separates the placenta from the uterine wall. Only after this, the female reproductive organ is sutured. The threads use self-absorbable. A separate suture is made on the abdominal cavity.
After surgery, the uterus is smaller than before surgery, but only because of the disappearance of the fetus, the sac of sac with amniotic waters and the placenta. The walls of the uterus themselves remain stretched, large. It resembles a deflated balloon.
Place of attachment of the placenta on the inner side of the muscular organ is bleeding, because the separation of the "children's site" was interrupted by the integrity of the blood vessels.
The incision in the uterus itself is a factor slowing down its contractile period. Gradually, under the action of the natural production of oxytocin, excess uterine cells (myocytes) die off and go out with lochia - blood secretions, which begin immediately after the operation and last up to 8 weeks on average.
Recovery
About the normal course of the process of reverse development of the uterus after the operation says the general well-being of the woman, the nature of her discharge.
In the first hours after the operation, the woman begins to receive reducing drugs. Oxytocin causes intense contractions of the smooth muscles of the uterus, which allows it to quickly get rid of blood clots and particles of the dead epithelium. The uterus is quite painful, therefore, an intramuscular anesthetic injection is recommended for a woman after a cesarean section for the first 2-3 days. Antibacterial drugs may be prescribed to prevent infection.
In the first 3-4 days the reduction is the most active pace. The excretions have a bright scarlet color, blood clots of various sizes are permissible. After the injection of oxytocin, the discharge is usually exacerbated, pulling pain in the lower back and abdomen, too.
Over the next two weeks, the excretions become more mucous, succinic, yellowish or brownish — they are no longer dominated by red blood cells, but white blood cells. The contraction of the uterus during this period is slower, but the female reproductive organ invariably decreases with each passing hour.The woman feels weaker, some no longer feel the pulling pain either in the lumbar region or in the lower abdomen.
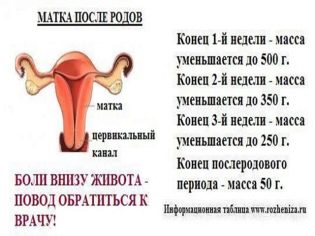
One and a half months after the operation, the secretions become transparent or translucent with a predominance of mucus, since the intensive process of restoring the endometrium is going on, including in the place of abutment of the former placenta. This process is not accompanied by any pain. The uterus is reduced to its former size after 6-7 weeks after cesarean section.
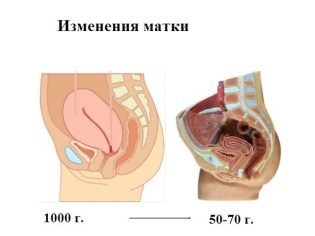
But the endometrial repair process is still ongoing. The musculature of the uterus after the first birth remains more elastic and stretched compared to the factional. Immediately after surgery, the length of the uterus is about 20 centimeters. A week later, the uterus "loses weight" three times, at the beginning of the 8th week after the operation, it finally assumes its former size, has a weight of about 50-70 grams, and the inner membranes are restored. The incision site grows together, the connective tissue in the area of the scar becomes more durable.
As the height of the bottom of the uterus increased during pregnancy, it was monitored for its reverse development after surgery. It is considered normal to reduce the height of the bottom of the uterus by 10 mm every day.
Possible complications
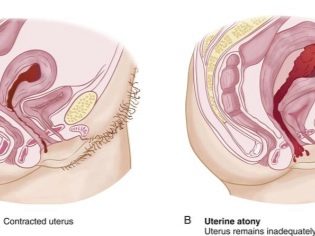
Disorders of the contractile functions of the main female reproductive organ after the operation can be of two types - hypotension or atony. In the first case, the uterus contracts too slowly, the pace of its involution lags behind the norms adopted in obstetrics. In the second case, the cuts do not occur at all.
Hypotension often develops in women who have given birth to their first child. At risk - too young moms (who are not 19 years old) and age moms (if at the time of the operation the woman in labor was already 36 years old). Previously performed abortions, curettage of a diagnostic sense increase the likelihood of an increase in uterine contractions over time and a decrease in their intensity.
The presence of a scar in itself is a risk of hypotension, and it is for this reason that the reducing drugs are shown.
But sometimes oxytocin, which is administered to a woman according to a certain scheme, does not have the desired effect. The reason may lie in the endocrine diseases of the newly-made mother, as well as in the low location of the fetus during pregnancy, in which the uterine tone was initially uneven (one part of the muscle walls experienced more tension than the others).
Atonia is extremely rare and almost always represents a serious danger to the life of a woman, as it is accompanied by prolonged and abundant bleeding. The causes of atony are poorly understood, but there is reason to assume that women at risk include tumors in the uterus, congenital anatomical impairment, and underdevelopment of the muscular organ. Also, the absence of contractions can be a consequence of severe bleeding disorders.
In both cases, in addition to the weak contractile function of the uterus or its absence, additional symptoms are observed - the discharge is abnormally strong, less often - on the contrary, weak, unproductive. A woman has pain in the peritoneum, body temperature rises, signs of infection appear - purulent, gray, frothy discharge from the genital organs.
Treatment is prescribed. Sometimes there is a need for curettage - the uterus must be freed from blood clots and dead epithelium cells. Antibiotic therapy and oxytocin-reducing drugs are prescribed.
The condition of the uterus is controlled by ultrasound. In most cases, the problem can be managed. Only in isolated cases it is necessary to resort to curettage, and very rarely comes to the amputation of the uterus due to its complete and unexplained atony within a few days or weeks.
How to speed up the process?
Contraction of the uterus - a process that is laid by nature. But a woman and doctors may well influence his speed.In order for the uterus to quickly return to its former form, a woman must strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
In the very early period of rehabilitation, early verticalization is recommended. After 10-12 hours, ideally, you need to get up to facilitate the discharge of lochia from the uterus. Physical activity helps to reduce, but activity should be moderate, adequate and reasonable. It should be combined with a good rest. The longer a woman lies in bed after surgery, the higher the likelihood of developing inflammation and impaired contractile function of the reproductive organ.
After the puerperal rises from the bed, begins to walk, sit, she should follow the following recommendations.
- Do not allow the overflow of the bladder and intestines, increased gas formation in the intestine. The pressure on the uterus will be stronger, the cuts will be less effective. Therefore, a woman is recommended to empty her bladder more often.
- On the first day, you cannot eat, on the second, kissel and bouillon are acceptable, in the evening - white croutons. On the third day it is allowed to eat porridge, vegetable puree. On the fourth day, you can eat everything, except for products that cause fermentation in the intestine and the formation of gases - peas, muffins, white cabbage, etc.
- It is important to avoid constipation, in time, if necessary, use microclysters or rectal suppositories with a laxative effect.
- You can not have sex and masturbate. During the entire period of uterine contraction, the use of lochia is strongly forbidden by physicians to give birth to sexual relations. The uterus should be relatively calm, without flushes of blood to it, which occur during sexual arousal and orgasm. Violation of this prohibition increases the likelihood of infection, mechanical injury of the connective tissue in the area of the internal scar on the uterus. Sex is allowed after discharge stops, not earlier than 8 weeks after surgery.
- It is impossible to lift weights, and also it is desirable to wear a postoperative bandage.
- Frequent breastfeeding increases the contraction of the uterus.
- Lying on the abdomen is helpful in the recovery process.
- Folk remedies to reduce - a decoction of nettle and juice of burdock, minced.
More information about the postpartum period can be found in the following video.