Uterus recovery after childbirth
The female reproductive organ is arranged by nature wisely: after the pregnancy ends in childbirth, special regenerative processes begin in the uterus, which are called “involution”. These processes are necessary for the woman to be able to get pregnant again and give life to the next child.
How is the recovery and how to contribute to it, we will tell in this article.
Terms and norms
While the baby was growing up in the womb, the uterus became the only organ in the female body, which changed beyond recognition: it increased in size, its ligamentous apparatus stretched and thinned. Therefore, it is not necessary to think that immediately after childbirth the reproductive organ acquires normal size. The uterus remains enlarged, but already empty. Involution starts immediately after the baby and the placenta leave its cavity.
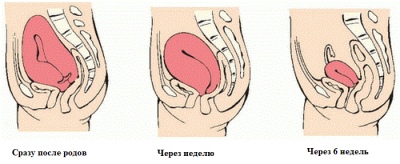
On the first day after birth, the uterus weighs about a kilogram, has a volume of about 5000 ml. The body is 23–24 cm long, and the lateral size is 13–14 cm. It is not in the small pelvis, but still in the abdominal cavity. For 6–8 weeks, which reproduce the female organ on average after the birth of the child is restored, the uterus will have to reach the initial parameters, which were characteristic of it before conceiving a child (5 ml in volume and 65 grams in weight), that is, to decrease completely.
Recovery begins with a reduction in the number of uterine muscle fibers. Myometrium in the first few days gets rid of excess fibers, the muscles gradually decrease due to the closure of blood vessels, and excess fibers die off. They go out in the blood bunches together with lochia - postpartum secretions from the genital tract.
Every day, the uterus gradually descends. Previously, the woman followed her growth, and after giving birth, the opposite development occurs. On average, a centimeter per day, the uterus moves lower, and within ten days after giving birth, it will completely return to its rightful place - in the small pelvis.
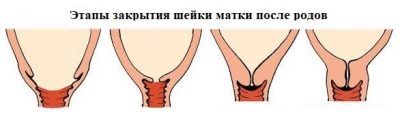
The restoration of the cervix takes longer, even if there are no birth injuries. On the first day, she diligently closes, for a day she manages to overcome about five centimeters, complete closure of the cervix occurs in 7-8 weeks.
Some more time for recovery may be required for women who have already given birth several times, because the muscles of their reproductive organs are stretched.
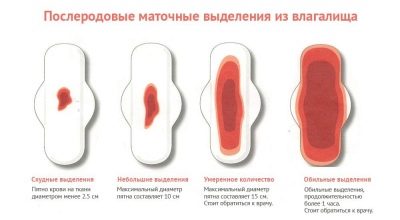
How much time will be allocated, the number of births does not depend. The placental wound on the wall of the uterus is bloody, it is she who remains at the place of separation of the placenta, with which the uterus has grown together with a reliable network of blood vessels. In the first 3-4 days, bleeding is stronger, with clots. The uterus contracts, stomach and lower back hurt. Then the placental wound begins to tighten, by the fifth day of the discharge become sukrovichno-mucous, and then - mucous, slightly stained.
Normally, the lochia should stop at the same time when the process of the reverse development of the uterus ends - at 6–8 weeks.
If a woman underwent a caesarean section, the recovery time of the uterus may be longer, because there is not only a placental wound on the wall of the reproductive organ, but also a surgical incision. On average, the recovery process takes from four months to six months.
Also, the recovery time can be extended for natural reasons, if at birth a rupture of the cervix occurs.
Deviations
In about 1-2% of all births, the early postpartum period is accompanied by anomalous uterus behavior — subinvolution. When her contraction occurs incomplete, the uterus is reduced too slowly, which is fraught with the development of severe inflammation. Quite often, the subinvolution itself is associated with an already initiated inflammatory process.
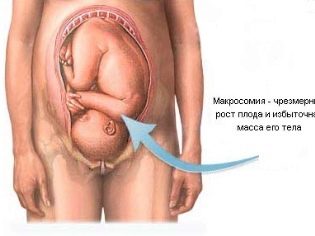
The reasons can be many: from impaired contractility of the uterine muscles due to certain individual characteristics or overstretching (large fetus, multiple pregnancy) to infection of the inner membranes of the uterus.
The likelihood that contraction and recovery will proceed with impairments and anomalies is increased if a woman has an incomplete discharge of the placenta (particles of the “children's place”), as well as fetal membranes that can remain in the uterus and cause an inflammatory process that interferes with normal contractile . Also, the weakness of the contractions may depend on the size of the baby, on multiple births, on the number of births (the more there are, the worse the reproductive organ can involution after the birth of the next baby).
Both heredity and the nature of the generic process (with fast and fast births, the probability of subsequent subinvolution is higher) affects the reduction. In small women, the uterus may shrink worse than in tall women, and recovery may also be difficult in women who are less than 19 years old and more than 35 years old.
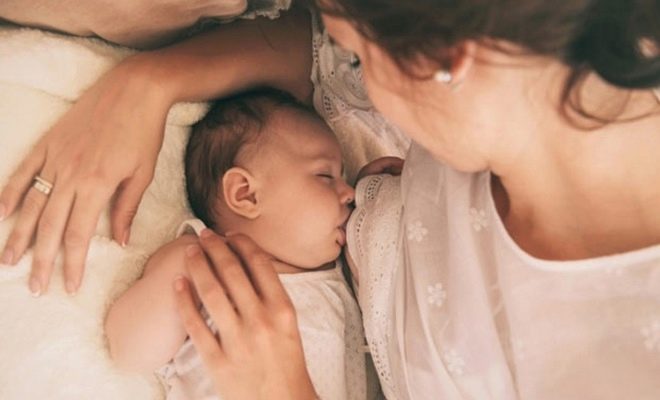
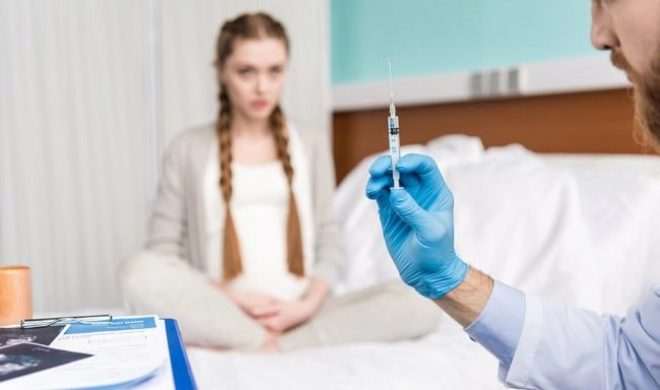
If a woman does not breastfeed her baby for some reason in the first days after his birth, then her body suffers from a lack of oxytocin, a hormone necessary for contractions of the reproductive organ (its involution). In this case, the puerperal must necessarily receive this hormone injections.
How to recover faster?
To accelerate the involution of the uterus after childbirth is possible only in one case - if there were violations of its course. In this case, the woman is treated, antibacterial drugs are used to treat the inflammatory process, and oxytocin is given by injection to stimulate uterine contractions.
If the process of reducing and restoring the uterus proceeds without features, then there is no need and opportunity to speed it up. All women who are at risk for possible subinvolution in the maternity hospital are given oxytocin injections after childbirth to prevent unpleasant consequences.
The woman who gave birth to the baby must remember that normal restoration of the reproductive organ is a guarantee of her female health in the future, her fertility and the possibility of becoming pregnant again and carrying out the child when the time comes. Therefore, the question of how to quickly restore the uterus, which women like to ask the fair sex doctors, is inappropriate. The uterus will recover within normal periods (6–8 weeks) if the woman abides by the recommendations.
First of all, it is important to remember that when breastfeeding a baby, enough oxytocin is produced in the body to ensure the contractility of the myometrium. That is why it is important as soon as possible to attach the crumbs to the mother's breast.
Subsequently, the lactation must be adjusted so that the baby can receive the necessary mother's milk every 3-4 hours. Such a regime will also benefit the mother: her reproductive organ, under the influence of natural oxytocin, will be reduced at regular intervals.
It is important not to lift weights, not to start an intimate life before the uterus completely cleans, that is, the process of isolating lochia is completed and the cervix is closed. That is why doctors recommend abstinence after childbirth for 7–8 weeks.
It is necessary to wash away after childbirth so that raw water does not get into the vagina. It is also better to give up douching, because viruses and pathogenic bacteria that can cause an inflammatory process can get into the genital tract with water.
A woman should be especially attentive in the first month after birth. If the discharge is too heavy after the first week, if it lasts too long, changes color to yellow-green, becomes unpleasantly smelling, itchy, pains in the lower abdomen, the body temperature rises, bleeding opens - it is important to immediately seek medical help. It is possible that endometriosis has started, and this is a very dangerous postpartum complication.